Article contents
Observation and characterization of memristive silver filaments in amorphous zinc-tin-oxide
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 August 2018
Abstract
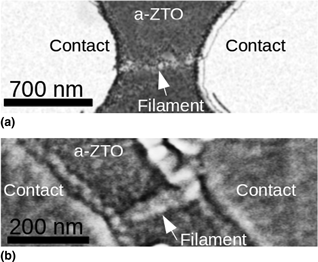
Lateral memristors consisting of planar Ag electrodes (with sub-micrometer separation) supported on thin films of amorphous zinc-tin-oxide have been characterized. After an initial filament-forming process, each device exhibited volatile, resistive switching. In the low resistance state, the transport mechanism and conductance depended on prior activity and on the imposed current limit, mimicking biologic synaptic plasticity. Microscopic observations performed on each device revealed nanoscale filaments between the electrodes. These filaments were subject to Rayleigh instability and exhibited relaxation times determined by their effective radii. The relaxation times and on:off resistance ratios suggest suitability for threshold switching selector devices.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
- 2
- Cited by


