No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 September 2019
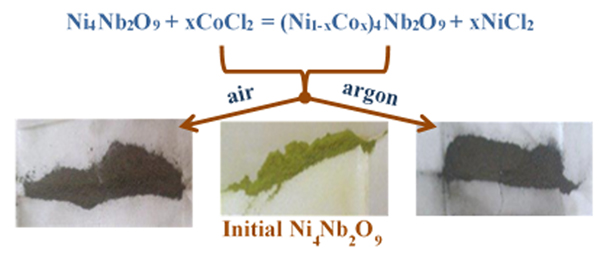
Thermal stable chloride melts were used as the reaction medium for modifying the chemical composition of complex oxides ensuring a marked improvement of their working properties. This paper discusses the original results of the direct effect of molten KCl–CoCl2 mixtures on the fine Ni4Nb2O9 powders under argon- and oxygen-containing gaseous atmospheres at 500 °C. The initial Ni4Nb2O9 powder and the reaction products were studied in detail using the differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetry, x-ray diffractometry, Raman and IR spectroscopies, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and conductometry which demonstrated clearly the formation of the thermal stable single-phase Ni–Co niobates.