Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 August 2017
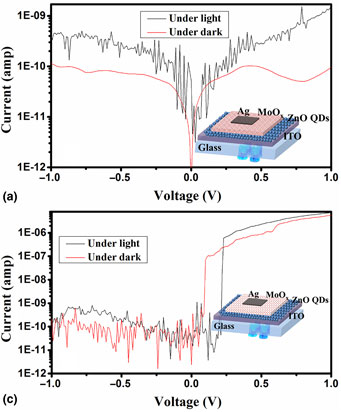
In this work, effects of heat treatment on the heterojunction between MoOx and ZnO quantum dots (QDs) are analyzed possibly for the first time. Solution-processed and thermal deposition technique is used for the growth of MoOx over the ZnO QDs and compared for the electrical analysis. The absorption and photoluminescence properties of ZnO QDs and MoOx have been analyzed for the optical behavior. Further, the heat-treated heterojunctions are analyzed for built-in potential (0.25 V), carrier density (~2.9 × 1018 cm−3), and responsivity (3.93 mAW−1). The heterojunction of solution-processed MoOx and ZnO QDs shows better stability after heat treatment compared with other devices.
To send this article to your Kindle, first ensure no-reply@cambridge.org is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about sending to your Kindle. Find out more about saving to your Kindle.
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox.
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive.