Article contents
The Quartz-Crystal-Microbalance Study of Protein Binding on Lipid Monolayers at the Air-Water Interface
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 November 2013
Extract
Interactions of proteins with cell membranes are of great interest in studies such as molecular recognition at cell surfaces. A monolayer lipid film at the airwater interface is useful in cell-surface modeling. Studies in binding behavior of proteins from a solution with a lipid monolayer have been reported by using various in situ techniques: surface-tension measurements, fluorescent-labeling techniques, radio-labeling techniques, fluorescence reflection methods, surface plasmon resonance, and surface-force measurements. These methods have potential applications in the observation of protein bindings. However, they require large, expensive equipment for in situ measurements and present difficulties for quantitatively obtaining the amount of protein adsorbed and the time frame for both binding and dissociation processes.
In this article, we discuss a new, easy in situ technique to detect interactions of adsorbed proteins with a phospholipids monolayer through the use of a Langmuir film balance on which a quartz-crystal microbalance (QCM) is horizontally attached to the lipid monolayer from the air phase (see Figure 1). QCMs are known to be very sensitive mass-measuring devices because their resonance frequency decreases with an increase of a given mass on a QCM at the nanogram level. Adsorption and penetration behavior of proteins can be observed quantitatively from the frequency changes (ΔF) of the QCM on the monolayer and the surface-pressure changes (Δπ) of the monolayer responding to the addition of proteins. The amount of adsorbed proteins (Δm) was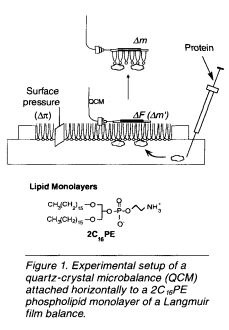 also obtained from the frequency changes after lifting and drying the sample in air.
also obtained from the frequency changes after lifting and drying the sample in air.
Recently, QCMs have become popular tools for detection of bioactive compounds such as odorous and bitter substances, and for measurement of protein adsorption, immuno-assays, DNA hybridization, enzyme reactions, and cell growth.
- Type
- Organic Thin Films
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1995
References
- 6
- Cited by


