Article contents
Tolstykhite, Au3S4Te6, a new mineral from Maletoyvayam deposit, Kamchatka peninsula, Russia
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 September 2022
Abstract
Tolstykhite, ideally Au3S4Te6, is a new mineral from the Gaching ore occurrence of the Maletoyvayam deposit, Kamchatka peninsula, Russia. It occurs as individual anhedral grains up to 0.05 mm or as intergrowths with native Se, native Te and tripuhyite. Other associated minerals include calaverite, fischesserite, Cu–Te-rich ‘fahlores' [stibiogoldfieldite, ‘arsenogoldfieldite', tennantite-(Cu), tetrahedrite-(Zn)], galena, gold, maletoyvayamite, minerals of famatinite–luzonite series, pyrite, baryte, ilmenite, magnetite, quartz and V-bearing rutile. Tolstykhite is bluish-grey, opaque with metallic lustre and grey streak. It is brittle and has an uneven fracture. Cleavage is good on {010} and {001}. Dcalc = 7.347 g/cm3. In reflected light, tolstykhite is grey with a bluish shade. No bireflectance, pleochroism and internal reflections are observed. In crossed polars, it is weakly anisotropic with bluish to brownish rotation tints. The reflectance values for wavelengths recommended by the Commission on Ore Mineralogy of the International Mineralogical Association are (Rmin/Rmax, %): 32.6/34.3 (470 nm), 32.4/34.1 (546 nm), 32.6/34.5 (589 nm) and 33.0/35.0 (650 nm). The Raman spectrum of tolstykhite contains the main bands at 297, 203, 181, 151 and 127 cm–1. The empirical formula calculated on the basis of 13 atoms per formula unit is (Au2.98Ag0.01)Σ2.99(S3.59Se0.41)Σ4.00Te6.01. Tolstykhite is triclinic, space group P$\bar{1}$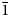 , a = 8.977(5), b = 9.023(2), c = 9.342(6) Å, α = 94.03(3), β = 110.03(3), γ = 104.27(4)°, V = 679.0(3) Å3 and Z = 2. The strongest lines of the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern [d, Å (I, %) (hkl)] are: 8.59 (18) (010); 2.90 (100) (0$\bar{1}$
, a = 8.977(5), b = 9.023(2), c = 9.342(6) Å, α = 94.03(3), β = 110.03(3), γ = 104.27(4)°, V = 679.0(3) Å3 and Z = 2. The strongest lines of the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern [d, Å (I, %) (hkl)] are: 8.59 (18) (010); 2.90 (100) (0$\bar{1}$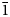 3); 2.23 (13) (13$\bar{3}$
3); 2.23 (13) (13$\bar{3}$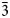 ); 1.89 (21) (13$\bar{4}$
); 1.89 (21) (13$\bar{4}$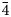 ). Tolstykhite is the S-analogue of maletoyvayamite, Au3Se4Te6. The structural identity between them is confirmed by powder XRD and Raman spectroscopy. The mineral honours Russian mineralogist Dr. Nadezhda Dmitrievna Tolstykh for her contributions to the mineralogy of gold and platinum-group elements and the study of ore deposits.
). Tolstykhite is the S-analogue of maletoyvayamite, Au3Se4Te6. The structural identity between them is confirmed by powder XRD and Raman spectroscopy. The mineral honours Russian mineralogist Dr. Nadezhda Dmitrievna Tolstykh for her contributions to the mineralogy of gold and platinum-group elements and the study of ore deposits.
Keywords
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland
Footnotes
Associate Editor: Owen Missen
References
- 7
- Cited by


