Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zolotarev, Andrey A.
Krivovichev, Sergey V.
Avdontceva, Margarita S.
Shilovskikh, Vladimir V.
Rassomakhin, Mikhail A.
Yapaskurt, Vasiliy O.
and
Pekov, Igor V.
2020.
Crystal Chemistry of Alkali–Aluminum–Iron Sulfates from the Burnt Mine Dumps of the Chelyabinsk Coal Basin, South Urals, Russia.
Crystals,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 11,
p.
1062.
Nekrasova, Diana O.
Siidra, Oleg I.
Zaitsev, Anatoly N.
Ugolkov, Valery L.
Colmont, Marie
Charkin, Dmitry O.
Mentré, Olivier
Chen, Ruiqi
Kovrugin, Vadim M.
and
Borisov, Artem S.
2021.
A fumarole in a one-pot: synthesis, crystal structure and properties of Zn- and Mg-analogs of itelmenite and a synthetic analog of glikinite.
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 1,
Borisov, Artem S.
Siidra, Oleg I.
Kovrugin, Vadim M.
Golov, Andrey A.
Depmeier, Wulf
Nazarchuk, Evgeny V.
and
Holzheid, Astrid
2021.
Expanding the family of mineral-like anhydrous alkali copper sulfate framework structures: new phases, topological analysis and evaluation of ion migration potentialities.
Journal of Applied Crystallography,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 1,
p.
237.
Siidra, Oleg I.
Borisov, Artem S.
Charkin, Dmitri O.
Depmeier, Wulf
and
Platonova, Natalia V.
2021.
Evolution of fumarolic anhydrous copper sulfate minerals during successive hydration/dehydration.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 85,
Issue. 2,
p.
262.
Borisov, Artem S.
Siidra, Oleg I.
Charkin, Dmitri O.
Zagidullin, Karim A.
Burshtynovich, Ruslan K.
and
Vlasenko, Natalia S.
2022.
Exploring new belousovite-related zinc and cadmium alkali sulfate halides: synthesis and structural variability.
Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials,
Vol. 78,
Issue. 3,
p.
499.
Pekov, Igor V.
and
Pushcharovsky, Dmitry Yu.
2023.
Celebrating the International Year of Mineralogy.
p.
69.
Pekov, Igor V.
Zubkova, Natalia V.
Yapaskurt, Vasiliy O.
Belakovskiy, Dmitry I.
Britvin, Sergey N.
Agakhanov, Atali A.
Turchkova, Anna G.
Sidorov, Evgeny G.
Kutyrev, Anton V.
Blatov, Vladislav A.
and
Pushcharovsky, Dmitry Y.
2023.
Nishanbaevite, KAl2O(AsO4)(SO4), a new As/S-ordered arsenate-sulfate mineral of fumarolic origin.
Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 117,
Issue. 2,
p.
247.
Nazarchuk, Evgeni V.
Siidra, Oleg I.
Charkin, Dmitri O.
Nikolaevich, Gleb V.
Borisov, Artem S.
and
Ugolkov, Valery L.
2024.
Vergasovaite to cupromolybdite topotactic transformation with crystal shape preservation.
American Mineralogist,
Vol. 109,
Issue. 3,
p.
471.
Borisov, A. S.
Siidra, O. I.
Charkin, D. O.
Nikolaevich, G. V.
Baikina, A. S.
Nazarchuk, E. V.
and
Holzheid, A.
2024.
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Cu6O2(MoO4)3(SO4), New Copper Molybdate Oxosulfate, Structurally Related to Vergasovaite and Glikinite.
Journal of Structural Chemistry,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 12,
p.
2371.
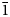 $\bar{1}$), 3.942(52)(101), 3.483(100)(00
$\bar{1}$), 3.942(52)(101), 3.483(100)(00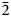 $\bar{2}$), 3.294(49)(020), 2.936(43)(120), 2.534(63)(201), 2.501(63)(20
$\bar{2}$), 3.294(49)(020), 2.936(43)(120), 2.534(63)(201), 2.501(63)(20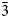 $\bar{3}$) and 2.395(86)(02
$\bar{3}$) and 2.395(86)(02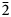 $\bar{2}$). The chemical composition determined by electron-microprobe analysis is (wt.%): ZnO 42.47, CuO 19.50, SO3 39.96, total 101.93. The empirical formula calculated on the basis of O = 9 apfu is Zn2.07Cu0.97S1.98O9 and the simplified formula is Zn3O(SO4)2. Glikinite is a Zn,Cu analogue of synthetic Zn3O(SO4)2. The crystal structure of glikinite is based on OZn4 tetrahedra sharing common corners, thus forming [Zn3O]4+ chains. Sulfate groups interconnect [Zn3O]4+ chains into a 3D framework.
$\bar{2}$). The chemical composition determined by electron-microprobe analysis is (wt.%): ZnO 42.47, CuO 19.50, SO3 39.96, total 101.93. The empirical formula calculated on the basis of O = 9 apfu is Zn2.07Cu0.97S1.98O9 and the simplified formula is Zn3O(SO4)2. Glikinite is a Zn,Cu analogue of synthetic Zn3O(SO4)2. The crystal structure of glikinite is based on OZn4 tetrahedra sharing common corners, thus forming [Zn3O]4+ chains. Sulfate groups interconnect [Zn3O]4+ chains into a 3D framework.