No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Ag-Cu exchange equilibria between α-miargyrite, chalcostibite, pyrargyrite, and high-skinnerite: constraints on Ag-Cu mixing in α-miargyrite and chalcostibite
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
Ag-Cu exchange equilibria between α-miargyrite AgSbS2 and pyrargyrite Ag3SbS3 and between chalcostibite CuSbS2 and both pyrargyrite and high-skinnerite Cu3SbS3 are reported for the temperature range 150–350°C. All of these features are constrained by Ag-Cu exchange experiments (evacuated silica tubes; variable mass ratio) over the temperature range 120–400°C. Chalcostibite is found to take very little Ag into its structure. Utilizing Ag-Cu data from this study as well as the Ag-Cu solution models for pyrargyrite and high-skinnerite, a two-site Ag-Cu non-convergent ordered solution model for α-miargyrite (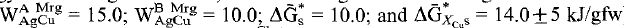 ) and a one-site Ag-Cu mixing model for chalcostibite (
) and a one-site Ag-Cu mixing model for chalcostibite (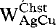 = 25.0 kJ/gfw) are formulated. These results are constrained by a miscibility gap between α-miargyrite and chalcostibite from 225 to 325°C. The mixing model for α-miargyrite is expanded to include As for which α-miargyrite has a limited solubility along the Sb-As join with smithite AgAsS2.
= 25.0 kJ/gfw) are formulated. These results are constrained by a miscibility gap between α-miargyrite and chalcostibite from 225 to 325°C. The mixing model for α-miargyrite is expanded to include As for which α-miargyrite has a limited solubility along the Sb-As join with smithite AgAsS2.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 1999


