Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Švenekite (IMA 99-007), Ca[AsO2(OH)2]2, is a rare supergene arsenate mineral occurring in the Geschieber vein, Jáchymov ore district, Western Bohemia, Czech Republic. It grows directly on the granite rocks and occurs isolated from other arsenate minerals otherwise common in Jáchymov. Švenekite usually forms clear transparent coatings composed of indistinct radiating to rosette-shaped aggregates up to 3 mm across. They are composed of thin lens- or bladed-shaped crystals, usually 100 – 150 μm long. Švenekite is transparent to translucent and has a white streak and a vitreous lustre; it does not fluoresce under ultraviolet light. Cleavage is very good on {010}. The Mohs hardness is ∼2. Švenekite is biaxial, non-pleochroic. The refractive indices are α' = 1.602(2), γ' = 1.658(2). The empirical formula of švenekite (based on As + P + S = 2 a.p.f.u., an average of 10 spot analyses) is (Ca1.00Mg0.01)Σ1.01[AsO2(OH)2]1.96[PO2(OH)2]0.03(SO4)0.01. The simplified formula is Ca[AsO2(OH)2]2 and requires CaO 17.42, As2O571.39, H2O 11.19, total 100.00 wt.%. Raman and infrared spectroscopy exhibit dominance of O – H vibrations and vibration modes of distorted tetrahedral AsO2(OH)2 units. Švenekite is triclinic, space group P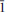 , with a = 8.5606(5), b = 7.6926(6), c = 5.7206(4) Å, α = 92.605(6), β = 109.9002(6), γ = 109.9017(6)º, and V = 327.48(4) Å3, Z = 2, Dcalc = 3.26 g·cm–3. The a:b:c ratio is 0.7436:1:1.1082 (for single-crystal data). The six strongest diffraction peaks in the X-ray powder diffraction pattern are [d (Å)/I(%)/(hkl)]: 3.968(33)(2
, with a = 8.5606(5), b = 7.6926(6), c = 5.7206(4) Å, α = 92.605(6), β = 109.9002(6), γ = 109.9017(6)º, and V = 327.48(4) Å3, Z = 2, Dcalc = 3.26 g·cm–3. The a:b:c ratio is 0.7436:1:1.1082 (for single-crystal data). The six strongest diffraction peaks in the X-ray powder diffraction pattern are [d (Å)/I(%)/(hkl)]: 3.968(33)(2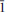 0); 3.766(35)(2
0); 3.766(35)(2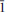
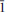 ); 3.697(49)(101); 3.554(100)(020); 3.259(33)(2
); 3.697(49)(101); 3.554(100)(020); 3.259(33)(2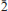 0); 3.097(49)(1
0); 3.097(49)(1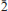 1). The crystal structure of švenekite was refined from single-crystal X-ray diffraction data to R1 = 0.0250 based on 1309 unique observed, and to wR2 = 0.0588, for all 1588 unique reflections (with GOFall = 1.20). The structure of švenekite consists of sheets of corner-sharing CaO8 polyhedra and AsO2 OH2 groups, stacked parallel to (001). Adjacent sheets are linked by hydrogen bonds. The švenekite structure possesses very short symmetrical hydrogen bonds (with the D–H lengths ∼1.22 Å). The mineral is named to honour Jaroslav Švenek, the former curator of the mineralogical collection of the National Museum in Prague, Czech Republic.
1). The crystal structure of švenekite was refined from single-crystal X-ray diffraction data to R1 = 0.0250 based on 1309 unique observed, and to wR2 = 0.0588, for all 1588 unique reflections (with GOFall = 1.20). The structure of švenekite consists of sheets of corner-sharing CaO8 polyhedra and AsO2 OH2 groups, stacked parallel to (001). Adjacent sheets are linked by hydrogen bonds. The švenekite structure possesses very short symmetrical hydrogen bonds (with the D–H lengths ∼1.22 Å). The mineral is named to honour Jaroslav Švenek, the former curator of the mineralogical collection of the National Museum in Prague, Czech Republic.
Deceased June 22, 2006