Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2018
The complete mineral description of potassic-magnesio-arfvedsonite, a recently approved (IMA2016-083) new species of the amphibole supergroup is provided using electron microprobe analysis (EMPA), laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, single-crystal structure refinement, Mössbauer and Raman spectroscopy, as well as measurement of optical and physical properties. The holotype material was found in syenitic and granitic dyke rocks in association with quartz, potassium feldspar and aegirine–augite from the Buhovo–Seslavtsi pluton, Bulgaria. Potassic-magnesio-arfvedsonite is monoclinic C2/m, with unit-cell parameters: a = 9.9804(11), b = 18.0127(19), c = 5.2971(6) Å, β = 104.341(2)° and V = 922.61 Å3. In transmitted plane-polarised light (λ = 590 cm–1), potassic-magnesio-arfvedsonite is pleochroic: X = yellow pale-green, Y = green and Z = dark-violet brown. It is biaxial (–), α = 1.645(2), β = 1.655(2), γ = 1.660(2) and 2Vmeas. = 60° and 2Vcalc. = 70°. The empirical unit formula obtained from EMPA and structure refinement is A(K0.86Na0.0.08)0.94B(Na1.74Ca0.25 Mn2+0.01)2.00C(Mg2.67Fe2+1.42Fe3+0.76Ti0.12Mn2+0.03)5.00TSi8O22W(OH1.58F0.22O0.20)2.00. The Fe3+/Fetot ratio (0.35) is consistent with both the Mössbauer spectra and the single-crystal structure refinement. The 10 strongest X-ray powder reflections [d values (in A°), I, (hkl)] are: 8.519, 80.5, (110); 3.402, 67.3, (131); 3.295, 41.0, (240); 3.173, 65.0, (310); 2.752, 35.6, (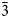 $\bar{3}$31); 2.715, 100.0 (151); 2.591, 44.1, (061); 2.542, 73.2, (
$\bar{3}$31); 2.715, 100.0 (151); 2.591, 44.1, (061); 2.542, 73.2, (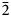 $\bar{2}$02); 2.348, 38.5, (
$\bar{2}$02); 2.348, 38.5, (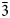 $\bar{3}$51); 2.174, 42.0, (261). Potassic-magnesio-arfvedsonite is the product of strongly peralkaline and potassic (perpotassic) magma compositions. Trace-element analysis shows that this amphibole did not exert significant control on trace-element distribution in the crystallising peralkaline magma.
$\bar{3}$51); 2.174, 42.0, (261). Potassic-magnesio-arfvedsonite is the product of strongly peralkaline and potassic (perpotassic) magma compositions. Trace-element analysis shows that this amphibole did not exert significant control on trace-element distribution in the crystallising peralkaline magma.
Associate Editor: Oleg I Siidra