Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 May 2018
Dargaite, ideally BaCa12(SiO4)4(SO4)2O3, is an additional member of the arctite group belonging to minerals with a modular intercalated antiperovskite structure derived from hatrurite. The holotype specimen was found at a small outcrop of larnite pseudoconglomerates in the Judean Mts, West Bank, Palestinian Autonomy. Larnite, fluorellestadite–fluorapatite, brownmillerite, fluormayenite–fluorkyuygenite and ye'elimite are the main minerals of the holotype specimen; ternesite, shulamitite and periclase are noted rarely. Dargaite, nabimusaite and gazeevite occur in linear zones with higher porosity within larnite rocks. Pores are filled with ettringite and Ca-hydrosilicates, less commonly with gibbsite, brucite, baryte, katoite and calciolangbeinite. Dargaite is colourless, transparent with a white streak and has a vitreous lustre. It exhibits pronounced parting and imperfect cleavage along (001). Mohs’ hardness is ~4.5–5.5. The empirical formula is (Ba0.72K0.24Na0.04)Σ1(Ca11.95Mg0.04Na0.01)Σ12([SiO4]0.91 [PO4]0.05[AlO4]0.03[Ti4+O4]0.01)Σ4([SO4]0.84[PO4]0.14[CO3]0.02)Σ2(O2.54F0.46)Σ3. Dargaite is trigonal R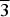 $\overline 3 $m, the unit-cell parameters are: a = 7.1874(4) Å, c = 41.292(3) Å, V = 1847.32(19) Å3 and Z = 3. The crystal structure of dargaite was refined from X-ray single-crystal data to R1 = 3.79%. The calculated density is 3.235 g cm–3. The following main Raman bands are distinguished on the holotype dargaite (cm–1): 122, 263, 323, 464, 523, 563, 641 and 644, 829 and 869, 947, 991 and 1116. The formation conditions of dargaite are linked to the local occurrence of pyrometamorphic by-products (gases, fluids and melts) transforming earlier mineral associations at ~900°C.
$\overline 3 $m, the unit-cell parameters are: a = 7.1874(4) Å, c = 41.292(3) Å, V = 1847.32(19) Å3 and Z = 3. The crystal structure of dargaite was refined from X-ray single-crystal data to R1 = 3.79%. The calculated density is 3.235 g cm–3. The following main Raman bands are distinguished on the holotype dargaite (cm–1): 122, 263, 323, 464, 523, 563, 641 and 644, 829 and 869, 947, 991 and 1116. The formation conditions of dargaite are linked to the local occurrence of pyrometamorphic by-products (gases, fluids and melts) transforming earlier mineral associations at ~900°C.
Associate Editor: Stuart Mills