Article contents
Nanometre scale textures in agate and Beltane opal
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
We have carried out TEM observations of agates of geode origin and Beltane opals. Optically observable individual fibres in agates are composed of many fine fibres which consist of quartz crystallites of 8 to 100 nm in length stacked together parallel to <11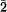 0> or <1
0> or <1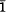 00> with c-axes perpendicular to the fibre elongation. The optically observable systematic striations in agate are found to consist of cyclic alternation of layers due to variation in grain size and porosity. Large quartz crystals, protruding into the spaces of geodes, represent the last stage of formation of these bands, and are merely a continuation of the banding sequence. Nanometre scale textures of cristobalite fibres were revealed in Beltane opals. The cristobalite crystallites have the size of 3 to 20 nm in length and are also stacked together. Our TEM results suggest that embryonic particles were formed in their corresponding growth environments and agglutinated to form fibres.
00> with c-axes perpendicular to the fibre elongation. The optically observable systematic striations in agate are found to consist of cyclic alternation of layers due to variation in grain size and porosity. Large quartz crystals, protruding into the spaces of geodes, represent the last stage of formation of these bands, and are merely a continuation of the banding sequence. Nanometre scale textures of cristobalite fibres were revealed in Beltane opals. The cristobalite crystallites have the size of 3 to 20 nm in length and are also stacked together. Our TEM results suggest that embryonic particles were formed in their corresponding growth environments and agglutinated to form fibres.
Keywords
- Type
- Mineralogy
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 1995
References
- 2
- Cited by


