Article contents
Canutite, NaMn3[AsO4][AsO3(OH)]2, a new protonated alluaudite-group mineral from the Torrecillas mine, Iquique Province, Chile
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
The new mineral canutite (IMA2013-070), NaMn3[AsO4][AsO3(OH)]2, was found at two different locations at the Torrecillas mine, Salar Grande, Iquique Province, Chile, where it occurs as a secondary alteration phase in association with anhydrite, halite, lavendulan, magnesiokoritnigite, pyrite, quartz and scorodite. Canutite is reddish brown in colour. It forms as prisms elongated on [20 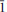 ] and exhibiting the forms {010}, {100}, {10
] and exhibiting the forms {010}, {100}, {10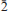 }, {201} and {102}, or as tablets flattened on {102} and exhibiting the forms {102} and {110}. Crystals are transparent with a vitreous lustre. The mineral has a pale tan streak, Mohs hardness of 2½, brittle tenacity, splintery fracture and two perfect cleavages, on {010} and {101}. The calculated density is 4.112 g cm−3. Optically, canutite is biaxial (+) with α = 1.712(3), β = 1.725(3) and γ = 1.756(3) (measured in white light). The measured 2V is 65.6(4)°, the dispersion is r < v (slight), the optical orientation is Z = b; X ^ a = 18° in obtuse β and pleochroism is imperceptible. The mineral is slowly soluble in cold, dilute HCl. The empirical formula (for tabular crystals from near the mineshaft), determined from electron - microprobe analyses, is (Na1.05Mn2.64Mg0.34Cu0.14Co0.03)∑4.20As3O12H1.62. Canutite is monoclinic, C2/c, a = 12.3282(4), b = 12.6039(5), c = 6.8814(5) Å, β = 113.480(8)°, V = 980.72(10) Å3 and Z = 4. The eight strongest X-ray powder diffraction lines are [d obs Å(I)(hkl)]: 6.33(34)(020), 4.12(26)(
}, {201} and {102}, or as tablets flattened on {102} and exhibiting the forms {102} and {110}. Crystals are transparent with a vitreous lustre. The mineral has a pale tan streak, Mohs hardness of 2½, brittle tenacity, splintery fracture and two perfect cleavages, on {010} and {101}. The calculated density is 4.112 g cm−3. Optically, canutite is biaxial (+) with α = 1.712(3), β = 1.725(3) and γ = 1.756(3) (measured in white light). The measured 2V is 65.6(4)°, the dispersion is r < v (slight), the optical orientation is Z = b; X ^ a = 18° in obtuse β and pleochroism is imperceptible. The mineral is slowly soluble in cold, dilute HCl. The empirical formula (for tabular crystals from near the mineshaft), determined from electron - microprobe analyses, is (Na1.05Mn2.64Mg0.34Cu0.14Co0.03)∑4.20As3O12H1.62. Canutite is monoclinic, C2/c, a = 12.3282(4), b = 12.6039(5), c = 6.8814(5) Å, β = 113.480(8)°, V = 980.72(10) Å3 and Z = 4. The eight strongest X-ray powder diffraction lines are [d obs Å(I)(hkl)]: 6.33(34)(020), 4.12(26)(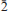 21), 3.608(29)(310,
21), 3.608(29)(310,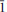 31), 3.296(57)(
31), 3.296(57)(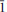 12), 3.150(28)(002,131), 2.819(42)(400,041,330), 2.740(100)(240,
12), 3.150(28)(002,131), 2.819(42)(400,041,330), 2.740(100)(240,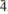 02,112) and 1.5364(31)(multiple). The structure, refined to R 1 = 2.33% for 1089 F o > 4σF reflections, shows canutite to be isostructural with protonated members of the alluaudite group.
02,112) and 1.5364(31)(multiple). The structure, refined to R 1 = 2.33% for 1089 F o > 4σF reflections, shows canutite to be isostructural with protonated members of the alluaudite group.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 2014
References
- 9
- Cited by


