No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 December 2004
Afin d'étudier la structure fine de la turbulence pariétale en présence de variations importantes de densité, une analyse statistique des données expérimentales, dans une soufflerie à recirculation, est effectuée. Les résultats montrent que la relaxation du facteur de dissymétrie de $u'(S_{u'}$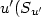 ) s'effectue plus rapidement dans la couche externe que près de la paroi, aussi bien pour l'injection de l'air que pour l'injection d'hélium. $S_{u'}$
) s'effectue plus rapidement dans la couche externe que près de la paroi, aussi bien pour l'injection de l'air que pour l'injection d'hélium. $S_{u'}$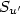 croît près de la fente d'injection de façon appréciable et cette augmentation est nettement plus accentuée pour l'injection de l'air que l'injection d'hélium. Cette croissance du facteur de dissymétrie près de la fente d'injection peut s'expliquer par l'augmentation du flux convectif longitudinal de l'énergie turbulente dans cette zone. Les résultats montrent, pour la distribution du facteur d'aplatissement $F_{u'}$
croît près de la fente d'injection de façon appréciable et cette augmentation est nettement plus accentuée pour l'injection de l'air que l'injection d'hélium. Cette croissance du facteur de dissymétrie près de la fente d'injection peut s'expliquer par l'augmentation du flux convectif longitudinal de l'énergie turbulente dans cette zone. Les résultats montrent, pour la distribution du facteur d'aplatissement $F_{u'}$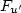 , qu'il n'y a pas d'effet important du gradient de densité sur la structure intermittente de la vitesse longitudinale instantanée dans la zone développée, $x/\delta \ge 5$
, qu'il n'y a pas d'effet important du gradient de densité sur la structure intermittente de la vitesse longitudinale instantanée dans la zone développée, $x/\delta \ge 5$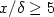 . L'analyse statistique menée dans cette étude montre que l'injection d'hélium, dans la couche limite, engendre des éjections plus violentes que dans le cas d'une injection d'air. Ce résultat est confirmé par la contribution importante des éjections au flux massique turbulent.
. L'analyse statistique menée dans cette étude montre que l'injection d'hélium, dans la couche limite, engendre des éjections plus violentes que dans le cas d'une injection d'air. Ce résultat est confirmé par la contribution importante des éjections au flux massique turbulent.