Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 September 2016
Let  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ be an arithmetic function and let
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ be an arithmetic function and let 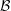 ${\mathcal{B}}$ be the set of positive integers
${\mathcal{B}}$ be the set of positive integers 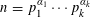 $n=p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{k}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{k}}$ which satisfy
$n=p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{k}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{k}}$ which satisfy 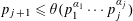 $p_{j+1}\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{j}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{j}})$ for
$p_{j+1}\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(p_{1}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{1}}\cdots p_{j}^{\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}_{j}})$ for 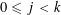 $0\leqslant j<k$. We show that
$0\leqslant j<k$. We show that 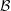 ${\mathcal{B}}$ has a natural density, provide a criterion to determine whether this density is positive, and give various estimates for the counting function of
${\mathcal{B}}$ has a natural density, provide a criterion to determine whether this density is positive, and give various estimates for the counting function of 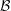 ${\mathcal{B}}$. When
${\mathcal{B}}$. When 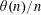 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(n)/n$ is non-decreasing, the set
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(n)/n$ is non-decreasing, the set 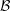 ${\mathcal{B}}$ coincides with the set of integers
${\mathcal{B}}$ coincides with the set of integers  $n$ whose divisors
$n$ whose divisors 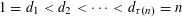 $1=d_{1}<d_{2}<\cdots <d_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}(n)}=n$ satisfy
$1=d_{1}<d_{2}<\cdots <d_{\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}(n)}=n$ satisfy 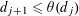 $d_{j+1}\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d_{j})$ for
$d_{j+1}\leqslant \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}(d_{j})$ for 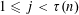 $1\leqslant j<\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}(n)$.
$1\leqslant j<\unicode[STIX]{x1D70F}(n)$.