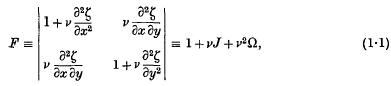Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Berry, M.V.
and
Upstill, C.
1980.
Vol. 18,
Issue. ,
p.
257.
Hesselink, Lambertus
and
White, Benjamin S.
1983.
Digital image processing of flow visualization photographs.
Applied Optics,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 10,
p.
1454.
Kofman, Lev
Kaiser, Nick
Lee, Man Hoi
and
Babul, Arif
1997.
Statistics of Gravitational Microlensing Magnification. I. Two‐dimensional Lens Distribution.
The Astrophysical Journal,
Vol. 489,
Issue. 2,
p.
508.


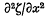 ,
, 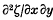 ,
, 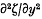 have a normal joint distribution. The problem considered is the statistical distribution of the quantity
have a normal joint distribution. The problem considered is the statistical distribution of the quantity