Article contents
Banach spaces whose algebras of operators have a large group of unitary elements
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2008
Abstract
We prove that a complex Banach space X is a Hilbert space if (and only if) the Banach algebra 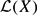 (of all bounded linear operator on X) is unitary and there exists a conjugate-linear algebra involution • on
(of all bounded linear operator on X) is unitary and there exists a conjugate-linear algebra involution • on 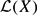 satisfying T• = T−1 for every surjective linear isometry T on X. Appropriate variants for real spaces of the result just quoted are also proven. Moreover, we show that a real Banach space X is a Hilbert space if and only if it is a real JB*-triple and
satisfying T• = T−1 for every surjective linear isometry T on X. Appropriate variants for real spaces of the result just quoted are also proven. Moreover, we show that a real Banach space X is a Hilbert space if and only if it is a real JB*-triple and 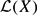 is
is  -unitary, where
-unitary, where  stands for the dual weak-operator topology.
stands for the dual weak-operator topology.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society , Volume 144 , Issue 1 , January 2008 , pp. 97 - 108
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge Philosophical Society 2008
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


