No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 October 2019
We show that if A is a finite K-approximate subgroup of an s-step nilpotent group then there is a finite normal subgroup 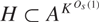 $H \subset {A^{{K^{{O_s}(1)}}}}$ modulo which
$H \subset {A^{{K^{{O_s}(1)}}}}$ modulo which 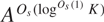 ${A^{{O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K)}}$ contains a nilprogression of rank at most
${A^{{O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K)}}$ contains a nilprogression of rank at most 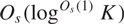 ${O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K)$ and size at least
${O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K)$ and size at least 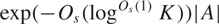 $\exp ( - {O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K))|A|$. This partially generalises the close-to-optimal bounds obtained in the abelian case by Sanders, and improves the bounds and simplifies the exposition of an earlier result of the author. Combined with results of Breuillard–Green, Breuillard–Green–Tao, Gill–Helfgott–Pyber–Szabó, and the author, this leads to improved rank bounds in Freiman-type theorems in residually nilpotent groups and certain linear groups of bounded degree.
$\exp ( - {O_s}(\mathop {\log }\nolimits^{{O_s}(1)} K))|A|$. This partially generalises the close-to-optimal bounds obtained in the abelian case by Sanders, and improves the bounds and simplifies the exposition of an earlier result of the author. Combined with results of Breuillard–Green, Breuillard–Green–Tao, Gill–Helfgott–Pyber–Szabó, and the author, this leads to improved rank bounds in Freiman-type theorems in residually nilpotent groups and certain linear groups of bounded degree.
The author is the Stokes Research Fellow at Pembroke College, Cambridge.