Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Eggleston, H. G.
1953.
A correction to a paper on the dimension of Cartesian product sets.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 3,
p.
437.
Marstrand, J. M.
1954.
The dimension of Cartesian product sets.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 2,
p.
198.
Eggleston, H. G.
1954.
A measureless one-dimensional set.
Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 3,
p.
391.
Ohtsuka, Makoto
1957.
Capacité des Ensembles Produits.
Nagoya Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 12,
Issue. ,
p.
95.


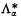 as follows (
as follows (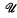 (δ,
(δ, 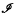 (δ,
(δ, 