Introduction
Lasallia hispanica (Frey) Sancho & A. Crespo represents one of three species of the genus Lasallia which occur in central Western Europe (Sancho & Crespo Reference Sancho and Crespo1989). The three Lasallia species differ in distribution, habitat preference, morphology and mode of reproduction. Lasallia pustulata has the widest distribution, occurring in Mediterranean to boreal-montane habitats from southern Europe to northern Scandinavia (Hestmark Reference Hestmark1992; Rolshausen et al. Reference Rolshausen, Dal Grande, Sadowska-Deś, Otte and Schmitt2018). The other two congeners are endemic to the Mediterranean region: L. hispanica prefers supra- and oro-Mediterranean habitats in the Iberian Peninsula, southern Italy and northern Morocco, and L. brigantium is confined to coastal areas in west Corsica and north-west Sardinia below 300 m a.s.l. (Sancho & Crespo Reference Sancho and Crespo1989). Lasallia hispanica is sympatric with L. pustulata in the supra- and oro-Mediterranean bioclimatic belts (Sancho & Crespo Reference Sancho and Crespo1989) where the two species often share the same photobiont (Dal Grande et al. Reference Dal Grande, Sharma, Meiser, Rolshausen, Büdel, Mishra, Thines, Otte, Pfenninger and Schmitt2017). Lasallia hispanica and L. pustulata differ in their water acquisition strategies: L. pustulata relies on surface run-offs, whereas L. hispanica takes up moisture directly from fog and low-lying clouds, therefore becoming desiccated more rapidly and more frequently (Vivas et al. Reference Vivas, Pérez-Ortega, Pintado and Sancho2017). A recent study comparing the photosynthetic performance of the two species in nature and under laboratory conditions suggests that L. hispanica might be more resistant to environmental stress than L. pustulata. This is probably due to the more efficient and rapid activation of stress-related repair mechanisms in L. hispanica (Vivas et al. Reference Vivas, Pérez-Ortega, Pintado and Sancho2017). The three Lasallia species have a mixed asexual and sexual reproductive strategy. However, reproduction in L. pustulata is predominantly vegetative, by means of isidia, while L. hispanica and L. brigantium predominantly reproduce sexually (Sancho & Crespo Reference Sancho and Crespo1989). While L. pustulata has been used as a model to explore climate adaptation in lichens (Dal Grande et al. Reference Dal Grande, Rolshausen, Divakar, Crespo, Otte, Schleuning and Schmitt2018) and symbiont-driven ecological expansion (Rolshausen et al. Reference Rolshausen, Dal Grande, Sadowska-Deś, Otte and Schmitt2018), molecular studies on L. hispanica are lacking. The genetic differentiation among the three species has yet to be explored.
The genomics revolution is transforming the way we study evolution and ecology (Wolfe & Li Reference Wolfe and Li2003; Grube et al. Reference Grube, Berg, Andrésson, Vilhelmsson, Dyer and Miao2014). Evolutionary genomics and phylogenomics further our understanding of speciation, phylogenetic relationships and the evolutionary origin of functional traits in lichenized fungi. Phylogenomic datasets have been used to resolve evolutionary relationships in the Rhizoplaca melanophthalma species complex (Chan & Ragan Reference Chan and Ragan2013; Leavitt et al. Reference Leavitt, Grewe, Widhelm, Muggia, Wray and Lumbsch2016). Comparative genomics has been used to reveal gene family size changes and gene deletions associated with lichenization in Endocarpon pusillum (Wang et al. Reference Wang, Liu, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang, Li, Yu, Zhang, Hao and Wang2014), to derive phylogenetic markers useful for resolving relationships among close relatives (Magain et al. Reference Magain, Miadlikowska, Mueller, Gajdeczka, Truong, Salamov, Dubchak, Grigoriev, Goffinet and Sérusiaux2017), and to study the properties and evolution of mitochondrial genomes (Xavier et al. Reference Xavier, Miao, Jónsson and Andrésson2012).
Ecological genomics is an emerging field in lichenology. It allows questions to be addressed related to, for example, niche differentiation, ecological specialization and local adaptation. Transcriptomics has been employed to infer the response of Peltigera membranacea and its cyanobiont to thermal stress (Steinhäuser et al. Reference Steinhäuser, Andrésson, Pálsson and Werth2016), and of Trebouxia to desiccation (Candotto Carniel et al. Reference Candotto Carniel, Gerdol, Montagner, Banchi, De Moro, Manfrin, Muggia, Pallavicini and Tretiach2016). Recently, we used a population genomics approach based on whole-genome resequencing of pools of DNA from lichen populations to study the genomic signatures of adaptation in L. pustulata along an altitudinal gradient (Dal Grande et al. Reference Dal Grande, Sharma, Meiser, Rolshausen, Büdel, Mishra, Thines, Otte, Pfenninger and Schmitt2017). In this study we revealed the existence of two locally adapted ecotypes using correlations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and environmental parameters.
Lichen metagenomics (i.e. the direct sequencing of mixed genomic material from lichen thalli) represents a cultivation-independent approach to explore the diversity and functional aspects of the lichen symbiosis. For instance, it is possible to reconstruct the genomes of the individual symbiotic partners using a single, short-read sequencing library layout (i.e. metagenome skimming; Greshake Tsovaras et al. Reference Greshake Tsovaras, Zehr, Dal Grande, Meiser, Schmitt and Ebersberger2016; Meiser et al. Reference Meiser, Otte, Schmitt and Dal Grande2017). Metagenomic lichen samples have also been used to apply restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (RADseq) for phylogenetic reconstructions of lichenized fungi based on genomic sequence information (Grewe et al. Reference Grewe, Huang, Leavitt and Lumbsch2017). Genome mining is increasingly employed to survey lichens for genes associated with the biosynthesis of active metabolites, revealing in some cases unexpected biosynthetic potential (e.g. Kampa et al. Reference Kampa, Gagunashvili, Gulder, Morinaka, Daolio, Godejohann, Miao, Piel and Andresson2013). For example, Cladonia uncialis contained a gene cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of a halogenated isocoumarin (Abdel-Hameed et al. Reference Abdel-Hameed, Bertrand, Piercey-Normore and Sorensen2016). The advent of long-read sequencing technologies from Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies will drastically improve the assembly process as well as the in-silico separation of organisms from mixed DNA samples.
Here we present the de novo assembly and annotation of the genome of L. hispanica. Using Illumina next-generation sequencing technology we obtained and annotated a high-quality draft genome. We identified gene clusters associated with secondary metabolite biosynthesis, mating-type loci and transposable elements, and compared them to the closely related L. pustulata (Davydov et al. Reference Davydov, Peršoh and Rambold2010). Finally, we established synteny and orthology between L. hispanica and L. pustulata. In addition to providing structured data for various phylogenetic studies, the work presented here will provide a genomic resource for further studies aiming to 1) understand the basis of polygenic adaptation in L. hispanica based on population genomic resequencing of natural populations, 2) study the impact of different reproductive strategies on the evolution of genomes and populations in L. hispanica and L. pustulata, and 3) infer the genomic footprints of niche differentiation of the two species.
Materials and Methods
In vitro cultivation of the lichen-forming fungus Lasallia hispanica
The lichen-forming fungus L. hispanica was isolated in vitro from a specimen collected from Puerto de Pico (Ávila, Spain; 40·322527°, −5·013808°, 1350 m a.s.l.; hb. Senckenbergianum voucher no. FR-0265086) in June 2014. The mycobiont culture (Schmitt laboratory, SBiK-F, C0002) was obtained from a multispore discharge from a single apothecium of L. hispanica following the method of Yamamoto et al. (Reference Yamamoto, Mizuguchi and Yamada1985). Briefly, apothecia were picked from the thallus, washed under distilled running water for several minutes and transferred individually onto inverted 4% water agar plates with sterile nylon membrane filters for 48 h. After ejection, the filters with the spores were transferred to germination medium in Petri dishes (Denison Reference Denison2003). Upon germination, the spores were transferred to malt yeast extract medium. The mycobiont colonies were maintained at room temperature in darkness and were sub-cultured monthly onto fresh medium until sufficient biomass for genomic analysis was obtained (c. 6 months; Fig. 1).
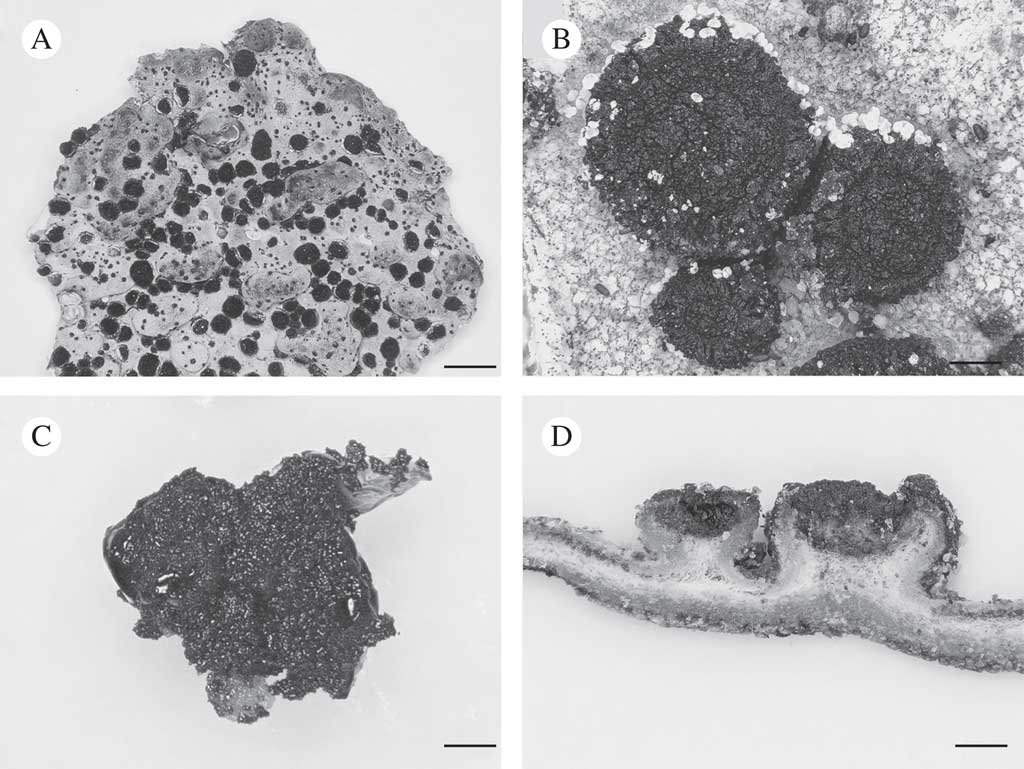
Fig. 1 Lasallia hispanica. A, thallus with apothecia; B, apothecia; C, mycobiont culture used for genome sequencing; D, section of thallus with apothecia. Scales: A=10 mm; B–D=1 mm.
DNA isolation and sequencing
About 0·5 g of mycobiont mycelia was collected and ground in liquid nitrogen with a mortar and pestle. Genomic DNA was isolated using the CTAB Maxi-prep method (Cubero & Crespo Reference Cubero and Crespo2002), resulting in a total yield of c. 5 µg DNA. Three Illumina genomic libraries were sequenced: 1) short-insert DNA library, paired-end (300 bp), on Illumina MiSeq, 2) Nextera mate-pair library with 3 kb inserts, 3) Nextera mate-pair library with 8 kb inserts. Sequencing was performed at StarSeq (Mainz, Germany).
Genome assembly and annotation
Adapters and low quality short-insert reads were trimmed (i.e. Q score<20 in a sliding window of 5 bp, minimum length<100 bp) using Trimmomatic 0.36 (Bolger et al. Reference Bolger, Lohse and Usadel2014). The reads were further quality-filtered using the software Sickle v.1.33 (-l 127 -q 20; available at https://github.com/najoshi/sickle). Adapters were removed from the mate-pair reads using NxTrim v.0.3.2 (O’Connell et al. Reference O’Connell, Schulz-Trieglaff, Carlson, Hims, Gormley and Cox2015). Prior to genome assembly, we assembled overlapping pairs of short-insert reads using PEAR v.0.9.6 (Zhang et al. Reference Zhang, Kobert, Flouri and Stamatakis2014). Reads were subsequently assembled de novo using SPAdes v.3.9.0 (-k 21,33,55,77,99,127; Bankevich et al. Reference Bankevich, Nurk, Antipov, Gurevich, Dvorkin, Kulikov, Lesin, Nikolenko, Pham and Prjibelski2012).
We filled gaps between contigs using SSPACE (Boetzer et al. Reference Boetzer, Henkel, Jansen, Butler and Pirovano2011) and GapFiller (Boetzer & Pirovano Reference Boetzer and Pirovano2012). To filter the assembly from potential contaminants and to extract contigs of fungal origin, we taxonomically assigned the scaffolds using MetaWatt v.3.5.3 (Strous et al. Reference Strous, Kraft, Bisdorf and Tegetmeyer2012) against a non-redundant database consisting of genomes from 122 Archaea, 1747 Bacteria, 514 Eukaryota and 535 Viruses. We estimated genome completeness of the newly assembled L. hispanica genome using BUSCO v.2.0 (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs; Simão et al. Reference Simão, Waterhouse, Ioannidis, Kriventseva and Zdobnov2015) and a lineage-specific set of Ascomycota single-copy orthologs.
The newly assembled genome of L. hispanica was annotated using funannotate v.0.5.4 (https://github.com/nextgenusfs/funannotate). As training data for funannotate, RNAseq data from L. pustulata (Dal Grande et al. Reference Dal Grande, Sharma, Meiser, Rolshausen, Büdel, Mishra, Thines, Otte, Pfenninger and Schmitt2017) was assembled using Trinity and PASA and used along the unassembled reads. Furthermore, we used the predicted protein sequences from Xanthoria parietina (https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Xanpa2/Xanpa2.home.html) and Cladonia grayi (https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Clagr3/Clagr3.home.html) as training data for the gene prediction. Blast2GO v.4.1.9 (Conesa et al. Reference Conesa, Götz, García-Gómez, Terol, Talón and Robles2005) was used to annotate the predicted protein sequences with gene ontology (GO) terms and protein names using the NCBI nr database at an E-value cut-off of 1×10−3 and default weighting parameters. The functional annotations were simplified to a set of broad terms by mapping the GO annotations to the Generic GO-Slim terms using Blast2GO.
Repeat elements
We surveyed the draft genome of L. hispanica for transposable elements (TEs) and repeated sequences. For this purpose, we first constructed a reference TE consensus library using the TEdenovo (Flutre et al. Reference Flutre, Duprat, Feuillet and Quesneville2011; Hoede et al. Reference Hoede, Arnoux, Moisset, Chaumier, Inizan, Jamilloux and Quesneville2014) and the TEannot (Quesneville et al. Reference Quesneville, Bergman, Andrieu, Autard, Nouaud, Ashburner and Anxolabehere2005) from the REPET TE annotation pipelines for the high quality PacBio assembly of the L. pustulata genome. These sequences were used as probes to annotate the L. hispanica genome with TEannot from the REPET pipeline. TE consensus nucleotide sequences were classified according to the Repbase database (Jurka et al. Reference Jurka, Kapitonov, Pavlicek, Klonowski, Kohany and Walichiewicz2005) and named according to the classification proposed by Wicker et al. (Reference Wicker, Sabot, Hua-Van, Bennetzen, Capy, Chalhoub, Flavell, Leroy, Morgante and Panaud2007).
Secreted proteins
To identify proteins with an extracellular secretion signal, we used SignalP v.4.0 (Petersen et al. Reference Petersen, Brunak, von Heijne and Nielsen2011), TargetP v.1 (Emanuelsson et al. Reference Emanuelsson, Brunak, von Heijne and Nielsen2007) and Tmhmm2.0c (Krogh et al. Reference Krogh, Larsson, von Heijne and Sonnhammer2001). Only annotated protein-coding genes having a signal peptide and not having a membrane localization domain were considered as putatively secreted.
Mating-type annotation
MAT alleles are typically flanked by the putative DNA lyase (APN2) and the cytoskeleton assembly control (SLA2) genes (Debuchy & Turgeon Reference Debuchy and Turgeon2006). We identified the MAT locus in L. hispanica and L. pustulata using BlastP searches against a database composed of ADN2, SLA2, MAT1-1, and MAT1-2 protein sequences of various ascomycetes, including lichen-forming fungi.
Annotation of genes and gene clusters associated with secondary metabolite biosynthesis
Genes and gene clusters involved in secondary metabolism in L. hispanica and L. pustulata were predicted using antiSMASH fungal v.4.0.0 (fungiSMASH; Blin et al. Reference Blin, Wolf, Chevrette, Lu, Schwalen, Kautsar, Suarez Duran, de Los Santos, Kim and Nave2017).
Synteny and orthology analysis
We compared the genome of the closely related species L. pustulata (Greshake Tsovaras Reference Greshake Tsovaras2018) to find orthologous gene pairs between the two species. For this purpose, we identified reciprocal best BLAST hits (RBH) between the two gene sets. This approach constitutes a relatively simple and fast method for finding orthologs between different assemblies of the same or closely related species (Ward & Moreno-Hagelsieb Reference Ward and Moreno-Hagelsieb2014). We ran BLAST v.2.2.30+ using Smith-Waterman alignment and soft filtering (use_sw_tback, soft_masking true, seq yes, evalue 1e-6) for better detecting orthologs as RBH (Moreno-Hagelsieb & Latimer Reference Moreno-Hagelsieb and Latimer2008; Ward & Moreno-Hagelsieb Reference Ward and Moreno-Hagelsieb2014). To identify RBH we filtered the BLAST output for a minimum identity of 70% over the alignment length and a minimum query coverage of 50% (Camacho et al. Reference Camacho, Coulouris, Avagyan, Ma, Papadopoulos, Bealer and Madden2009), sorted for the highest bitscore and lowest E-value, and manually removed multiple identical top hits, if present.
Lasallia hispanica and L. pustulata assemblies and gene sets were compared to identify genomic portions in which gene order is conserved (i.e. syntenic regions). For this purpose, we used SyMap v.4.2 (Synteny Mapping and Analysis Program; Soderlund et al. Reference Soderlund, Bomhoff and Nelson2011) to compute and display syntenic relationships between L. hispanica and L. pustulata. For this, we aligned scaffolds longer than 50 kb of each species using MUMmer (Kurtz et al. Reference Kurtz, Phillippy, Delcher, Smoot, Shumway, Antonescu and Salzberg2004) and used synteny to order the draft genome (L. hispanica) against the reference (L. pustulata). To calculate the percentage of genes located in syntenic blocks, gene coordinates of the two species were imported into SyMap as .gff.
Results and Discussion
Genome assembly and annotation
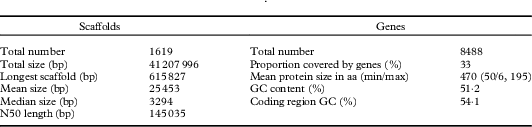
After adapter removal, and length and quality filtering, we obtained 11 313 695 short-insert paired-end reads, plus 3 163 139 and 3 351 197 mate pair reads for the 3 kb and 8 kb libraries, respectively. These reads were assembled using SPAdes into 1619 scaffolds longer than 500bp (N50=145035; Table 1). The draft assembly has a total length of 41·2 Mb and a coverage of approximately 160×. The evaluation of the genome completeness of our draft genome assembly based on 1315 single-copy fungal orthologs showed that most of the gene space was covered (96·3%). The L. hispanica genome assembly contained 1256 complete and single-copy, 10 duplicated, 27 fragmented and 22 missing BUSCO genes. The overall GC content of the L. hispanica genome is 51·2%. The GC content of gene coding sequences increases to 54·1% and is similar to that of L. pustulata (overall GC=51·7%; CDS GC=53·2%).
Table 1 Information on the L. hispanica genome assembly
We predicted a total of 8488 ab initio gene models, of which 3929 (46·3%) were assigned a total of 15 820 GO terms. The most abundant biological process GO-Slim terms were organic substance metabolic process (15·6%), cellular metabolic process (15·2%), primary metabolic process (14·7%) and nitrogen compound metabolic process (10·6%). Abundant molecular function GO-Slim terms included organic cyclic compound binding (17·8%), ion binding (15·6%), hydrolase activity (11·7%) and transferase activity (11·2%). Finally, most of the cellular components GO-Slim terms were categorized as intracellular (19·9%), intracellular part (19·4%), intracellular organelle (15·3%) and membrane-bounded organelle (13·2%) (Fig. 2).
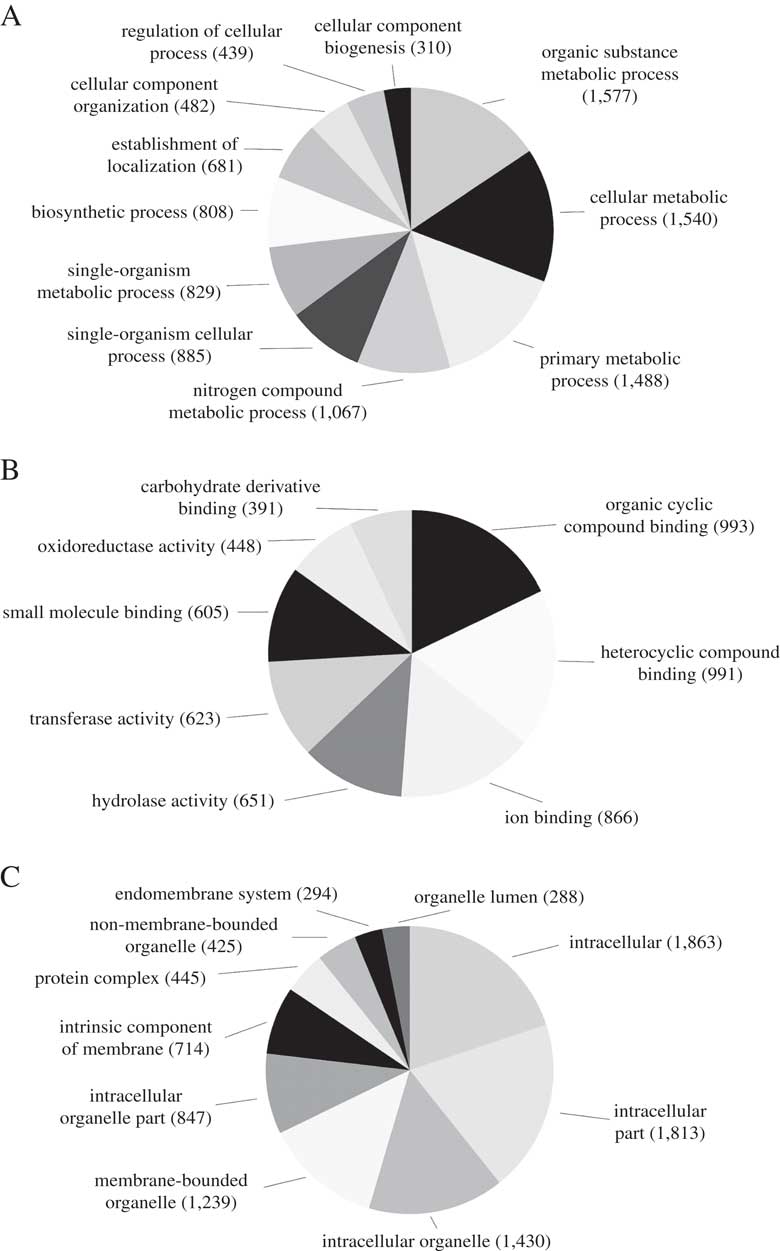
Fig. 2 Distribution of Blast2GO annotations for L. hispanica. Charts show level 3 annotations for Biological Process (A), Molecular Function (B) and Cellular Components (C).
Transposable elements
Transposable Elements (TEs) are DNA fragments with the ability to move within the genome by generating new copies of themselves. TEs are an important source of mutations in genomes and may promote genome restructuring and chromosome instability due to their repeated nature (Bonchev & Parisod Reference Bonchev and Parisod2013). TEs are typically divided into two classes depending on their mechanism of mobility: retrotransposons (class I) and DNA transposons (class II) (Wicker et al. Reference Wicker, Sabot, Hua-Van, Bennetzen, Capy, Chalhoub, Flavell, Leroy, Morgante and Panaud2007). The cut-and-paste transposition mechanism of retrotransposons involves an RNA intermediate which is reverse transcribed by a reverse transcriptase often encoded by the TE itself. DNA transposons instead transpose directly from DNA to DNA.
In fungi, 0–30% of the genome consists of transposable elements, with LTR (Long Terminal Repeats)-retrotransposons usually representing the largest fraction (Castanera et al. Reference Castanera, López-Varas, Borgognone, LaButti, Lapidus, Schmutz, Grimwood, Pérez, Pisabarro and Grigoriev2016). The repetitive nature of TE sequences, in combination with short-read sequencing technologies, exacerbates the correct assembly of TEs, especially for TE families exhibiting high sequence identity, high copy number or complex genomic arrangements (Nilsson Reference Nilsson2016).
Transposable elements were found to cover 21·23% of the L. pustulata genome for a total of c. 7 Mbp, including 70 class I and 35 class II elements with full length copies (444–11 000 bp, mean size: 4021 bp) (see Supplementary Material Table S1, available online). Conversely, the draft genome of L. hispanica displayed an almost complete absence of full length elements. These results confirm the limitation of the short-read sequencing technology in reconstructing TEs. Therefore, the current resolution of this draft genome, like most Illumina-based genome assemblies, is insufficient to give a detailed picture of the TE content.
Secreted proteins
The secretion of proteins and other enzymes into the extracellular environment is a vital process in fungi (Krijger et al. Reference Krijger, Thon, Deising and Wirsel2014). In particular, secreted proteins play an essential role in nutrient acquisition and self-protection. Furthermore, the fungal secretome directly or indirectly modulates interactions of the fungus with living and non-living substrata, including recognition processes (Wessels Reference Wessels1993). We found 104 genes encoding putatively secreted proteins in L. hispanica, including 16 glycoside hydrolases, six carboxipeptidases and two glucoamylases. Putatively secreted proteins ranged in length from 61 to 1672 aa (see Supplementary Material Table S2, available online).
Mating types
The mating system of filamentous ascomycetes is usually represented by one locus (i.e. the MAT locus) which encodes proteins of the high-mobility-group (HMG) superfamily (Coppin et al. Reference Coppin, Debuchy, Arnaise and Picard1997). The MAT locus is typically present in two complementary forms (i.e. idiomorphs) referred to as MAT1-1 and MAT1-2 (or MAT-1 and MAT-2). Homothallic species typically contain both MAT genes (i.e. MAT-1 encoding a protein with a MATα_HMG domain and MAT-2 encoding a protein with a MATA_HMG domain) within the same genome. Heterothallic species instead contain a single MAT locus; isolates can thus carry either MAT-1 or MAT-2 genes (Kronstad & Staben Reference Kronstad and Staben1997). In this study we identified the MAT loci in the L. hispanica and L. pustulata genomes.
Only one complete mating-type locus was found in the genome assembly for L. hispanica: MAT1-2 containing the MATA_HMG domain. The orthologous MAT1-2 idiomorph was also found in a newly assembled genome of L. pustulata (Greshake Tsovaras Reference Greshake Tsovaras2018). As in L. hispanica, the MAT1-2 idiomorph of L. pustulata includes an unknown gene containing a homeodomain. The complementary mating idiomorph (i.e. MAT1-1) was also found in our first draft assembly of L. pustulata available at the European Nucleotide Archive GCA_000938525.1 obtained from a different thallus. This region lacks MAT1-2 and the homeodomain-containing gene, while it includes a full MAT1-1 gene with the MATα_HMG (Fig. 3). Our results provide evidence for a heterothallic lifestyle of both Lasallia species. However, inferences based on genome sequence analysis require additional experimental validation, including analysis of single-spore isolates and estimation of MAT frequencies in natural populations using MAT-idiomorph specific probes (Honegger et al. Reference Honegger, Zippler, Gansner and Scherrer2004; Singh et al. Reference Singh, Dal Grande, Cornejo, Schmitt and Scheidegger2012, Reference Singh, Dal Grande, Werth and Scheidegger2015; Alors et al. Reference Alors, Dal Grande, Cubas, Crespo, Schmitt, Molina and Divakar2017; Ludwig et al. Reference Ludwig, Summerfield, Lord and Singh2017).
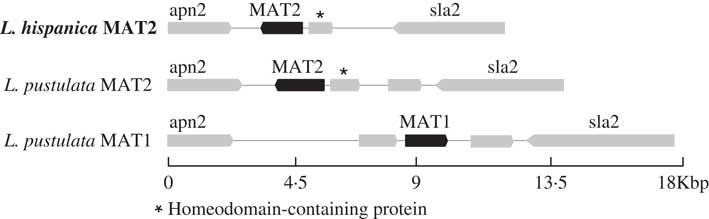
Fig. 3 Configuration of the MAT loci in L. hispanica and in two L. pustulata assemblies (MAT1: European Nucleotide Archive GCA_000938525.1; MAT2: Greshake (Reference Greshake Tsovaras2018)).
Secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters
The advent of genome sequencing technologies is revolutionizing the field of natural product discovery (Doroghazi et al. Reference Doroghazi, Albright, Goering, Ju, Haines, Tchalukov, Labeda, Kelleher and Metcalf2014). Whole-genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters has revealed a large number of uncharacterized secondary metabolite gene clusters in various organisms, including lichen-forming fungi (e.g. Kampa et al. Reference Kampa, Gagunashvili, Gulder, Morinaka, Daolio, Godejohann, Miao, Piel and Andresson2013; Abdel-Hameed et al. Reference Abdel-Hameed, Bertrand, Piercey-Normore and Sorensen2016).
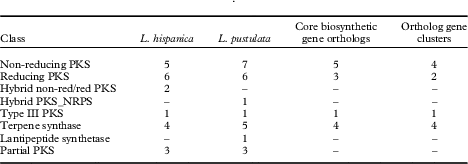
HPLC analyses revealed similarities in the chemical profiles of L. hispanica and L. pustulata, with gyrophoric acid as the major compound and traces of lecanoric, umbilicaric, hiascic acids and skyrin (Posner et al. Reference Posner, Feige and Leuckert1991). In the L. hispanica genome we identified 18 secondary metabolite clusters with complete core biosynthetic genes (core biosynthetic genes=polyketide synthases (PKS), non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS), etc.) (Table 2, Supplementary Material Table S3). Among the non-reducing type I PKS, three genes showed duplicated ACP domains (Supplementary Material Table S4, available online). Interestingly, we found only partial homology between the biosynthetic gene clusters of L. hispanica and L. pustulata, with 13 putative orthologs among 40 complete, core biosynthetic genes of the two species (Table 2, Supplementary Material Table S3). Eleven biosynthetic clusters, including four non-reducing and two reducing PKS, four terpene synthases and one type III PKS, showed high similarity of core genes and genes coding for tailoring enzymes. These clusters therefore represent ideal candidates for the biosynthesis of natural compounds that are shared between the two lichen species (Fig. 4). Our results suggest that both Lasallia species have a far greater potential to produce specialized secondary metabolites than previously thought. Genomics-driven discovery of fungal natural products and comparison of gene clusters between closely related species with similar chemical profiles is just the first step towards linking these gene clusters to their metabolites (Chooi & Solomon Reference Chooi and Solomon2014).
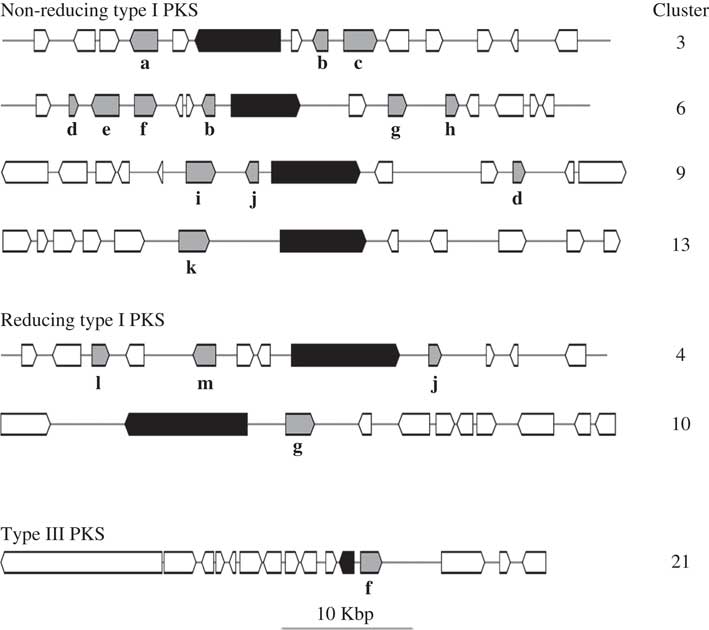
Fig. 4 Configuration of L. hispanica biosynthetic gene clusters with orthologs in L. pustulata. Black boxes represent core biosynthetic genes (PKSs in the upper six clusters and a chalcone and stilbene synthase in the bottom cluster). Shaded boxes indicate genes coding for tailoring enzymes: a, acyltransferase; b, metallo-beta-lactamase family protein; c, halogenase; d, aldo/keto reductase; e, drug resistance transporter EmrB/QacA; f, cytochrome P450; g, O-methyltransferase; h, haloalkane dehalogenase; i, dioxygenase TauD/TfdA; j, FAD-linked oxidase domain protein; k, serine/threonine protein kinase; l, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; m, AMP-dependent synthetase and ligase.
Table 2 Biosynthetic genes and gene clusters in L. hispanica and L. pustulata. A dash indicates no genes were detected for that class
Synteny and orthology analysis
Based on RBH analysis, 6382 orthologous gene pairs were identified between L. hispanica and L. pustulata proteins (see Supplementary Material Table S5, available online). The 211 largest (i.e. >50 kb) L. hispanica scaffolds (representing 75·6% of the genome) were then aligned with the 31 largest L. pustulata scaffolds (99·5% of the genome) to find syntenic regions. The alignment produced 68% and 71% of syntenic coverage in L. hispanica and L. pustulata, respectively, with gene retention >80% for both species. The circle plot of this genome comparison shows a high degree of synteny conservation between L. hispanica and L. pustulata, with only a few rearrangements (Fig. 5).
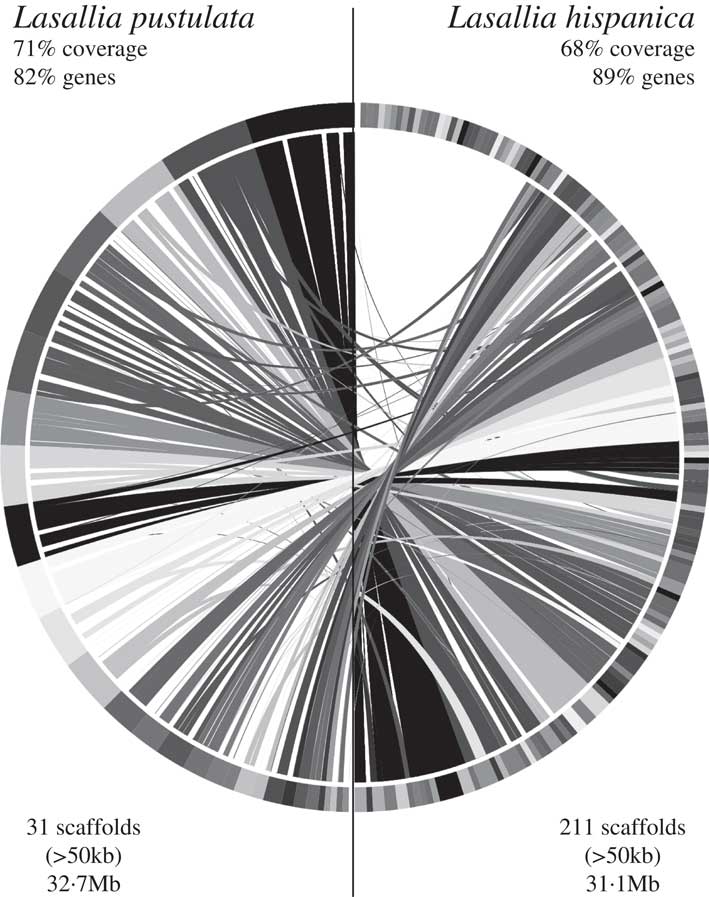

Fig. 5 Circle plot of the genome alignment between 31 L. pustulata (left) and 211 L. hispanica (right) scaffolds. Scaffolds of L. hispanica were ordered to align against the genome of L. pustulata using information from 202 syntenic blocks.
The draft genome of L. hispanica presented in this study sets the foundation for further research into speciation and niche evolution mechanisms in lichen-forming fungi. We believe that the L. hispanica-L. pustulata system is particularly suitable for this application owing to the ecological, reproductive and genetic differences between the species. In addition, the annotated draft genome serves as a resource for developing molecular markers, targeting specific functional genes and analysing repetitive elements in the context of population studies.
Data accessibility
This Whole Genome Shotgun project has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the Accession PKMA00000000. The raw sequence reads are available under the Accession number SRP127347.
This manuscript is dedicated to our friend and mentor Ana Crespo on the occasion of her 70th birthday. We honour her invaluable contributions to lichenology.
We thank Pradeep K. Divakar and Ana Crespo (Madrid) for support with fieldwork, and Véronique Jamilloux, Nathalie Choisne and Joelle Amselem (INRA - URGI, Versailles) for training and support in the use of REPET. Some analyses were performed on the FUCHS cluster of the Center for Scientific Computing (CSC) at Goethe University in Frankfurt am Main. This research was funded by Landes-Offensive zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-Oekonomischer Exzellenz (LOEWE) of Hesse’s Ministry of Higher Education, Research and the Arts through the Senckenberg Biodiversity and Climate Research Centre (SBiK-F).
Supplementary Material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S002428291800021X









