Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 September 2009
One of the questions that has prompted this study is
this: despite the fact that various Xiongnu
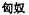 and Xianbei
and Xianbei
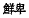 groups
dominated the political arena in Northern China for
almost 300 years between the collapse of the Western
Jin
groups
dominated the political arena in Northern China for
almost 300 years between the collapse of the Western
Jin 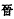 and the
founding of the Sui
and the
founding of the Sui 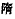 , and the
usually unacknowledged fact that their descendants
continued to do so for several hundreds more
years,1 why is it that one could learn
so little about their cultural heritage in
traditional historiography?2 Even the
linguistic affinity of the Tuoba
, and the
usually unacknowledged fact that their descendants
continued to do so for several hundreds more
years,1 why is it that one could learn
so little about their cultural heritage in
traditional historiography?2 Even the
linguistic affinity of the Tuoba  Xianbei
remains to this day a matter of
controversy.3
Xianbei
remains to this day a matter of
controversy.3
The author would like to thank several colleagues and friends for their help and comments. In particular, he thanks Professor Samuel Adshead of the University of Canterbury for furnishing him with a copy of the late Joseph Fletcher's unpublished article on blood tanistry, and Dr Chungmo Kwok for extensive editorial and other help.
1
Guang, Sima
et al. , ![]() Zizhi tongjian
Zizhi tongjian
![]() (Beijing,
1956; hereafter
ZZhTJ), 108.3429, comments by Hu
Sanxing
(Beijing,
1956; hereafter
ZZhTJ), 108.3429, comments by Hu
Sanxing ![]() .Google Scholar
.Google Scholar
2 Even on those external “barbarians” who might be considered China's primary “security concern”, the records were still astonishingly meagre, as observed bySinor, Denis, “Central Eurasia”in Central Eurasia, in Orientalism and History, ed. Sinor, D. (Bloomington, 1970), pp. 93–119.Google Scholar
3 Chen, S., “A-gan revisited – the Tuoba's cultural and political heritage”, Journal of Asian History, forth-coming.Google Scholar
4 Morgan, David, Medieval Persia, 1040–1797 (London, 1988), p. 22.Google Scholar See also Bosworth, C. E., The Ghaznavids (Edinburgh, 1963), p. 56.Google Scholar
5 Franke, Herbert, From Tribal Chieftain to Universal Emperor and God: The Legitimation of the Yüan Dynasty (Munich, 1978), p. 609.Google Scholar
6 See Bosworth, , op. cit., p. 3.Google Scholar
7 See for examples Fairbank, John King, “Synarchy under the Treaties”, in Chinese Thought and Institutions, ed. Fairbank, J. K. (Chicago, 1957), pp. 204–31Google Scholar, in particular p. 204, and Wittfogel, Karl A., Oriental Despotism; a Comparative Study of Total Power (New Haven, 1957), p. 182.Google Scholar
8 Honey, David, “Stripping off felt and fur: an essay on nomadic sinification”, Papers on Inner Asia. Ancient Inner Asia, XXI (1992),Google Scholar seems, the only exception in trying to include the Tang in the “conquest dynasties”. Yet in addition to his very curious exclusion of the preceding Sui, he still considers the Tang house “basically sinified” (p. 2). Therefore in his otherwise colourful essay on nomadic sinicization covering the entire Chinese history from the late Shang to the Qing, not a single item or case pertaining to the Tang was found.
9 Crossley, Pamela K., “Thinking about ethnicity in early modern China”, Late Imperial China, XI (1990), pp. 1–34.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
10 For the etymology Xianbei < *Sarbi, see for example Golden, Peter B., An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples (Wiesbaden, 1992), p. 69.Google Scholar
11 Honey, “Stripping off felt and fur”, p. 2.
12
They are “Li-Tang shizu zhi tuice wenti ![]() “, “Li-Tang
shizu zhi tuice houji
“, “Li-Tang
shizu zhi tuice houji ![]() ”. “San lun
Li-Tang shizu wenti
”. “San lun
Li-Tang shizu wenti ![]() ”, and
“Li-Tang Wu-Zhou xianshi shiji zakao
”, and
“Li-Tang Wu-Zhou xianshi shiji zakao ![]() “. All can
be found in his collected works Chen Yinke xiansheng
lunwenji
“. All can
be found in his collected works Chen Yinke xiansheng
lunwenji
![]() (Taipei,
1974).Google Scholar
(Taipei,
1974).Google Scholar
13
Rulei, Hu,
Li Shimin zhuan
![]() (Beijing,
1984), p.
2.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1984), p.
2.Google Scholar
14
Bowuguan, Ningxia
Zizhiqu
![]() ,“Mu fajue
jianbao
,“Mu fajue
jianbao ![]() ”,
Wenwu
”,
Wenwu
![]() (1985.11), pp.
1–20Google Scholar.
This implication of Li Xian's newly unearthed tomb
inscription on the ethnic origin of the Tang
imperial family was pointed out to me by Dr Chungmo
Kwok via private communications.
(1985.11), pp.
1–20Google Scholar.
This implication of Li Xian's newly unearthed tomb
inscription on the ethnic origin of the Tang
imperial family was pointed out to me by Dr Chungmo
Kwok via private communications.
15 S. Chen, “A-gan revisited”.
16
Pansui, Lui
![]() , “Li-Tang
wei fanxing kao”,
, “Li-Tang
wei fanxing kao”,![]() Nü shida xueshu jikan
Nü shida xueshu jikan
![]() I.4 (no
date), pp.
1–5,Google Scholar
first made this important discovery based on an
entry in Xiu, Ouyang
et al. ,
I.4 (no
date), pp.
1–5,Google Scholar
first made this important discovery based on an
entry in Xiu, Ouyang
et al. , ![]() Xin Tang shu
Xin Tang shu
![]() (Beijing,
1975; hereafter XTSh),
44.1160.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1975; hereafter XTSh),
44.1160.Google Scholar
17
Zhitui, Yan
![]() ,
Yanshi jiaxun, edition used:
Liqi, Wang
,
Yanshi jiaxun, edition used:
Liqi, Wang
![]() ,
Yanshi jiaxun jijie
,
Yanshi jiaxun jijie
![]() ,
rev. ed.
(Beijing,
1993),
1.50–1.Google Scholar For an English
translation of the passage, see for example
Wright, Arthur
F., The Sui
Dynasty (New
York, 1978), p.
36.Google Scholar
,
rev. ed.
(Beijing,
1993),
1.50–1.Google Scholar For an English
translation of the passage, see for example
Wright, Arthur
F., The Sui
Dynasty (New
York, 1978), p.
36.Google Scholar
18
See the list in Pu, Wang
![]() ,
Tang hui yao
,
Tang hui yao
![]() (Taipei,
1963; hereafter
THY), 6.75.Google Scholar More
extensive lists were given in Tongling, Wang
(Taipei,
1963; hereafter
THY), 6.75.Google Scholar More
extensive lists were given in Tongling, Wang
![]() ,
‘Yang-Sui Li-Tang xianshi xitong
kao
,
‘Yang-Sui Li-Tang xianshi xitong
kao
![]() ,
Nüshida xueshu jikan,
II.2 (no date),
pp.
1–23.Google Scholar
,
Nüshida xueshu jikan,
II.2 (no date),
pp.
1–23.Google Scholar
19 Gökalp, Ziya (translated by Devereux, R.), The Principles of Turkism (Leiden, 1968), p. 110.Google Scholar
20
XTSh 119.4306, 172.5205ȓ06,
ZZhTJ 248.8036 and Fang, Li
![]() ,
Taiping guangji
,
Taiping guangji
![]() (Beijing,
1961), 184.1379.Google Scholar Read also
Yinke, Chen,
Tangdai zhengzhishi shulun gao
(Beijing,
1961), 184.1379.Google Scholar Read also
Yinke, Chen,
Tangdai zhengzhishi shulun gao
![]() (Chongqing/Shanghai,
1944)/1947, pp.
57–9.Google Scholar
(Chongqing/Shanghai,
1944)/1947, pp.
57–9.Google Scholar
21 Tongling, Wang, op. cit., pp. 20–3,Google Scholar has a rather extensive table on this issue. Still the important Kirghiz case is missing in that table.
22 See for example ZZhTJ 172.8879, Hu Sanxing's notes.
23 XTSh 217b.6150.
24 ZZhTJ 195.6135ȓ36, 200.6138.
25
Read for instance Da, Xiang
![]() ,
Tangdai Chang'an yu Xiyu wenming
,
Tangdai Chang'an yu Xiyu wenming
![]() (Beijing,
1957)Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1957)Google Scholar
26
Zhen, Yuan
![]() 's poem
Faqu
's poem
Faqu
![]() (Quan Tangshi
(Quan Tangshi
![]() [Shanghai,
1986], 419.1025) may serve as a
succinct review of the fad.Google Scholar
[Shanghai,
1986], 419.1025) may serve as a
succinct review of the fad.Google Scholar
27
Shou, Wei
![]() ,
Wei shu
,
Wei shu
![]() (Beijing,
1974) 19.469 and 21.536 (also
ZZhTJ 140.4357 and
142.4434).Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1974) 19.469 and 21.536 (also
ZZhTJ 140.4357 and
142.4434).Google Scholar
28
Xu, Liu
![]() Jiu Tang shu
Jiu Tang shu
![]() (Beijing,
1975; hereafter
JTSh), 45.1938, 1951,
XTSh, 24.527–28, and
THY 31.577–78.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1975; hereafter
JTSh), 45.1938, 1951,
XTSh, 24.527–28, and
THY 31.577–78.Google Scholar
29 XTSh 34.878.
30
Dang, Wang
![]() ,
Tang yulin
(Changsha,
1939), 4.101.Google Scholar This was
corroborated by XTSh 125.4407.
,
Tang yulin
(Changsha,
1939), 4.101.Google Scholar This was
corroborated by XTSh 125.4407.
31 Pansui, Liu, op. cit.,Google Scholar was the first to point out that both were non-Chinese etiquettes, though Liu's citations were far from complete.
32 “A-gan revisited”.
33
“Tang Ashina Zhong mu fajue jianbao ![]() ”,
Kaogu
”,
Kaogu
![]() (1977.2),
reprinted in Tujue yu Huihe lishi lunwen
xuanji
(1977.2),
reprinted in Tujue yu Huihe lishi lunwen
xuanji
![]() , ed. Gan, Lin
(Beijing,
1987), ii, pp.
408–19.Google Scholar
, ed. Gan, Lin
(Beijing,
1987), ii, pp.
408–19.Google Scholar
34
Xi, Zhu
![]() ,
Zhuzi yulei
,
Zhuzi yulei
![]() (Beijing,
1986), 136.3245.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1986), 136.3245.Google Scholar
35
Wendi's childhood name was Nanluoyan ![]() See
Daoxuan,
See
Daoxuan,
![]() , XU
gaoseng zhuan
, XU
gaoseng zhuan
![]() (Taipei,
1988), 26.900. Yangdi's was Ame
(Taipei,
1988), 26.900. Yangdi's was Ame
![]() See for
example ZZhTJ
179.5577.Google Scholar
See for
example ZZhTJ
179.5577.Google Scholar
36
Yang Yong's childhood name was Gandifa ![]() (ZZhTJ 179.5575). As we have
pointed out in “A-gan revisited”, this name can be
identified with a similar childhood name Qizhifa
(ZZhTJ 179.5575). As we have
pointed out in “A-gan revisited”, this name can be
identified with a similar childhood name Qizhifa
![]() of the
“Xianbei-ized” warlord Feng Ba
of the
“Xianbei-ized” warlord Feng Ba ![]() . See
Wei shu, 97.2126. Li Jiangcheng's
childhood name was Pishamen
. See
Wei shu, 97.2126. Li Jiangcheng's
childhood name was Pishamen ![]() (XTSh 79.3540).
(XTSh 79.3540).
37 ZZhTJ 212.6735.
38 JTSh 64.2415.
39 For this childhood name, see for example ZZhTJ 197.6206.
40 ZZhTJ 197.6208.
41
This term was well attested as the clan name Chinu
![]() , which
became Lang
, which
became Lang ![]() , “wolf”, in
Emperor Xiaowen's sinicization drive (Wei
shu, 113.3013). As Peter Boodberg pointed
out in his “The language of the T'o-pa
Wei”, HJAS,
I (1936), pp.
167–85.Google Scholar another likely
attestation was the popular personal name Chounu
, “wolf”, in
Emperor Xiaowen's sinicization drive (Wei
shu, 113.3013). As Peter Boodberg pointed
out in his “The language of the T'o-pa
Wei”, HJAS,
I (1936), pp.
167–85.Google Scholar another likely
attestation was the popular personal name Chounu
![]() .
.
42
Zheng, Wei
et al. , ![]() Sui shu
Sui shu
![]() (Beijing,
1974), 15.397.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1974), 15.397.Google Scholar
43 JTSh 62.2375–76, 74.2614–15, XTSh 98.3897, 99.3907–08, and ZZhTJ 186.5834, 194.6095.
44 XTSh 201.5728.
45
See for example Daoxun, Xu
![]() and Keyao, Zhao
and Keyao, Zhao
![]() ,
Tang Xuanzong zhuan
,
Tang Xuanzong zhuan
![]() (Beijing,
1993), p.
409Google Scholar and
passim.
(Beijing,
1993), p.
409Google Scholar and
passim.
46 See for example ZZhTJ 272.8904.
47 See for example Tekin, Talat, A Grammar of Orkhon Turkic (Bloomington, 1968), pp. 373–4.Google Scholar
48 Sui shu 52.1341.
49 al-Kāšγarī, Maḥmūd, Compendium of the Turkic Dialects (Türk Şiveleri Lügati), edited and translated by Dankoff, Robert and Kelly, James (Cambridge, Mass., 1982–1985), i, p. 341.Google Scholar
50 ZZhTJ 190.5959.
51 JTSh 64.2415–16.
52
Su, Liu,
![]() ,
Sui Tang jiahua
,
Sui Tang jiahua
![]() (Beijing,
1979), 1.7;Google Scholar
Su, Liu
(Beijing,
1979), 1.7;Google Scholar
Su, Liu
![]() , Da
Tang xinyu
, Da
Tang xinyu
![]() (Beijing,
1984), 1.13.Google Scholar
Guang, Again
Sima edited it to a mere
tianshe weng
(Beijing,
1984), 1.13.Google Scholar
Guang, Again
Sima edited it to a mere
tianshe weng
![]() – “old
house-owning peasant” in ZZhTJ
194.6096.Google Scholar
– “old
house-owning peasant” in ZZhTJ
194.6096.Google Scholar
53
Read for example Yuan, Chen
![]() ,
Tongjian Huzhu biaowei
,
Tongjian Huzhu biaowei
![]() (Beijing,
1958), pp.
323–4,Google Scholar though Chen
quoted only a small number of cases.
(Beijing,
1958), pp.
323–4,Google Scholar though Chen
quoted only a small number of cases.
54
Zhuo, Zhang
![]() ,
Chaoye qianzai
(Beijing,
1979), 4.89.Google Scholar
,
Chaoye qianzai
(Beijing,
1979), 4.89.Google Scholar
55 Twitchett, Denis Crispin (ed.), The Cambridge History of China (London, 1979), iii, p. 236.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
56 Wright, Arthur, “T'ang T'ai-tsung and Buddhism”, in Perspectives on the T'ang, ed. Wright, A. F. and Twitchett, D. (New Haven, 1973), pp. 239–63.Google Scholar The particular comment is on p. 253.
57 Pulleyblank, Edwin G., “The An Lu-shan rebellion and the origins of chronic militarism in late T'ang China” in Essays on T'ang Society, ed. Perry, J. C. and Smith, B. L. (Leiden, 1976), pp. 32–60.Google Scholar See p. 37.
58
See, e.g., ZZhTJ 192.6034, Quan Tang wen
![]() (Beijing,
1983) 9.106,Google Scholar
THY 26.506, Da Tang
xinyu 9.133, etc. For continuing his old
habit while an emperor, see ZZhTJ
192.6021–22, 192.6042.
(Beijing,
1983) 9.106,Google Scholar
THY 26.506, Da Tang
xinyu 9.133, etc. For continuing his old
habit while an emperor, see ZZhTJ
192.6021–22, 192.6042.
59 “A-gan revisited”.
60
They include Tuli ![]() (Tölis)
Qaghan of the Eastern Turk (ZZhTJ
191.5992), the loyal Turk general Simo, Ashina
(Tölis)
Qaghan of the Eastern Turk (ZZhTJ
191.5992), the loyal Turk general Simo, Ashina
![]() (Cefu yuangui
(Cefu yuangui
![]() [Beijing,
1960], 980.11516Google Scholar) who was
given the imperial clan name Li
(JTSh 194.5156,
XTSh 215.6037), and the Western
Turk prince, later Duolu
[Beijing,
1960], 980.11516Google Scholar) who was
given the imperial clan name Li
(JTSh 194.5156,
XTSh 215.6037), and the Western
Turk prince, later Duolu ![]() Qaghan
(JTSh 194.5183).
Qaghan
(JTSh 194.5183).
61
Zhongmian, Cen
![]() ,
Sui Tang shi
,
Sui Tang shi
![]() (Beijing.
1957), PP. 140 and
142,Google Scholar has claimed that
certain features of Tang Taizong's mausoleum were
imitative of Turkish burial custom, a notion
followed by Wechsler, Howard
J., Offerings of Jade
and Silk (New
Haven, 1985), p.
81.Google Scholar We contend that,
rather than mere imitation, it in fact reflected the
Tang imperial house's steppe background. The Tang's
respect for non-Han burial customs both within and
without the Chinese heartland was reflected in Tang
Taizong's condemnation of the Eastern Turks'
adoption of the (Han) tomb burials in violation of
their ancestral customs (Cefu
yuangui, 125.1501; see also Ecsedy, Ilkidó,
“Ancient Turk [T'u-chüeh] burial
customs”, AOH,
XXXVIII [1984], pp.
263–87;Google Scholar the particular
passages are found on pages 276–7) and Tang
Xuanzong's edict allowing a surrendered Turk
official to “be buried according to the native
[Turkish] customs” (Cefu yuangui,
974.11446).
(Beijing.
1957), PP. 140 and
142,Google Scholar has claimed that
certain features of Tang Taizong's mausoleum were
imitative of Turkish burial custom, a notion
followed by Wechsler, Howard
J., Offerings of Jade
and Silk (New
Haven, 1985), p.
81.Google Scholar We contend that,
rather than mere imitation, it in fact reflected the
Tang imperial house's steppe background. The Tang's
respect for non-Han burial customs both within and
without the Chinese heartland was reflected in Tang
Taizong's condemnation of the Eastern Turks'
adoption of the (Han) tomb burials in violation of
their ancestral customs (Cefu
yuangui, 125.1501; see also Ecsedy, Ilkidó,
“Ancient Turk [T'u-chüeh] burial
customs”, AOH,
XXXVIII [1984], pp.
263–87;Google Scholar the particular
passages are found on pages 276–7) and Tang
Xuanzong's edict allowing a surrendered Turk
official to “be buried according to the native
[Turkish] customs” (Cefu yuangui,
974.11446).
62 ZZhTJ 196.6191.
63 Schafer, Edward H., The Golden Peaches of Samarkand: a Study of T'ang Exotics (Berkeley, 1963), p. 65.Google Scholar
64 Boodberg, Peter A., “The language of the T'o-pa Wei”, HJAS, I (1936), pp. 167–85.Google Scholar
65
See Taizong's, Emperor
essay “Liumatu zan ![]() ”. in
Quan Tang wen,
10.124.Google Scholar
”. in
Quan Tang wen,
10.124.Google Scholar
66 Wu, Silas H. L., Passage to Power: K'ang-hsi and His Heir Apparent, 1661–1772 (Cambridge, Mass., 1979), pp. 133–6.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
67 THY 55.943–44, XTSh 199.5661, ZZhTJ 201.6363.
68 XTSh 80.3565.
69 THY 27.521.
70 Wei shu, 22.558.
71
Zixian, Xiao
![]() ,
Nan Qi shu
(Beijing,
1972), 57.996.Google Scholar
,
Nan Qi shu
(Beijing,
1972), 57.996.Google Scholar
72
See for example Qiaoyi, Chen
![]() , Li
Daoyuan yu Shujing zhu
, Li
Daoyuan yu Shujing zhu
![]() (Shanghai,
1987), PP. 31,
34–5.Google Scholar
(Shanghai,
1987), PP. 31,
34–5.Google Scholar
73 Yinke, Chen, Tangdai zhengzhishi, pp. 52–3.Google Scholar
74 Yuan, Chen op. cit., p. 252.Google Scholar
75 Jin shu (Beijing, 1974), 101.2648Google Scholar and passim.
76 Fletcher, Joseph, “The Mongols: ecological and social perspectives”, HJAS, XLVI (1986), pp. 11–50.Google Scholar
77 Fletcher, Joseph, “Turco-Mongolian monarchic tradition in the Ottoman Empire”, Harvard Ukrainian Studies, III/IV (1979–1980), pp. 236–51.Google Scholar
78 Boodberg, Peter A., “Marginalia to the histories of the Northern dynasties”, HJAS, IV (1939), pp. 230–83,Google Scholar in particular p. 266.
79 Fletcher, Joseph, “Blood tanistry: authority and succession in the Ottoman, Indian Muslim, and later Chinese empires”, The Conference on the Theory of Democracy and Popular Participation,Bellagio, Italy,1978.Google Scholar
80
Yi, Zhao,
Nian'ershi Zhaji
![]() , annotated
by Weiyun, Du
, annotated
by Weiyun, Du
![]() (Taipei,
1975), 19.410.Google Scholar
(Taipei,
1975), 19.410.Google Scholar
81 ZZhTJ 197.6197, 199.6280–81.
82 ZZhTJ 197.6195.
83 ZZhTJ 202.6377, 203.6419.
84
For example, see Hu
ji,
![]() Wu Zetian benzhuan
Wu Zetian benzhuan
![]() (Xi'an,
1986), pp.
60–1.Google Scholar
(Xi'an,
1986), pp.
60–1.Google Scholar
85 ZZhTJ 199.6286–87, 204.6467, 207.6557.
86 JTSh 7.135, ZZhTJ 204.6473, 205.6490.
87 ZZhTJ 204.6474–75, 206.6526–27.
88 Alderson, Anthony D., The Structure of the Ottoman Dynasty (Oxford, 1956), pp. 32–6;Google Scholar Goody, Jack (ed.), Succession to High Office (Cambridge, 1966), pp. 20–1.Google Scholar For a detailed description of this part of the Ottoman palace, see Penzer, Norman Mosley, The Harem (London, 1936), pp. 197–201.Google Scholar
89 ZZhTJ 244.7886. We may also note that the Ottoman Kafes was hardly unique in the Turkic political sphere: the later Ghaznavids in Afghanistan and Northern India also developed a similar policy after incessant succession struggles among the Sultan's family members. See Bosworth, C. E., The Later Ghaznavids: Splendour and Decay (Edinburgh, 1977), p. 38.Google Scholar Corresponding to the “birth control” measures in the Kafes, a remarkable episode was Xuanzong's repeated attempts in aborting his consort's pregnancy for fear of further antagonizing Princess Taiping (JTSh 52.2184). One notes that the incident was recorded due largely to the fact that the pregnancy Xuanzong (then the crown prince) tried to terminate produced in the end none other than the future emperor Suzong.
90 ZZhTJ 208.6611–12.
91 ZZhTJ 209.6641–42.
92 ZZhTJ 209.6650.
93 ZZhTJ 210.6656–57.
94 See for example the story in ZZhTJ 210.6673–74, JTSh 97.3051 and XTSh 125.4406.
95 JTSh 45.1957–58.
96 See Silas Wu, Passage to Power.
97 ZZhTJ 214.6829.
98
Zuyu, Fan,
Tang jian
![]() (Shanghai,
1937), 9.78.Google Scholar
(Shanghai,
1937), 9.78.Google Scholar
99 On November 20, 1514. See Alderson, , op. cit., p. 30.Google Scholar
100 XTSh 82.3608, ZZhTJ 216.6916.17.
101 ZZhTJ 218.6975–76, 218.6982.
102 ZZhTJ 221.7094–95.
103 ZZhTJ 218.6983, 219.7007.
104
Li Bai signed on with the losing side of this
fratricidal struggle for the throne, for which he
almost received a death sentence. He was eventually
exiled to Yelang ![]() , which was
by far the most serious crisis in Li's life. See for
example XTSh 202.5763. This in turn
led Du Fu to write several immortal poems on his
deep concern over his friend's fate.
, which was
by far the most serious crisis in Li's life. See for
example XTSh 202.5763. This in turn
led Du Fu to write several immortal poems on his
deep concern over his friend's fate.
105 ZZhTJ 219.7013.
106 ZZhTJ 222.7123–24.
107 Wright, Arthur, “Sui Yang-ti: personality and stereotype”, in Confucianism and Chinese Civilization, ed. Wright, A. (New York, 1964), pp. 158–87.Google Scholar
108 Xiong, Victor Cunrui, “Sui Yangdi and the building of Sui-Tang Luoyang”, The Journal of Asian Studies, LII (1993), PP. 66–89.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
109 Bosworth, , The Ghaznavids, pp. 230–4.Google Scholar
110
Erkang, Feng
![]() Yongzheng zhuan
Yongzheng zhuan
![]() (Beijing,
1985), pp.
555–9.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1985), pp.
555–9.Google Scholar
111 Winstanley, Lilian, Hamlet and the Scottish Succession (Cambridge, 1921)Google Scholar and, much more recently, Kurland, Stuart M., “Hamlet and the Scottish succession?” Studies in English Literature, 1500–1900, XXXIV (1994), pp. 279–300.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
112
Defen, Linghu,
Zhou shu
(Beijing,
1971) 50.909;Google Scholar also
Li Yanshou,
![]() Bei shi
Bei shi
![]() (Beijing,
1974), 99.3287,Google Scholar and
You, Du
(Beijing,
1974), 99.3287,Google Scholar and
You, Du
![]() Tong dian
Tong dian
![]() (Shanghai,
1935), 197.1068.Google Scholar
(Shanghai,
1935), 197.1068.Google Scholar
113 SirFrazer, James G., “The killing of the Khazar kings”, Folklore, XXVIII (1917), pp. 382–407;CrossRefGoogle Scholar Dunlop, D. M., The History of the Jewish Khazars (Princeton, 1954), p. 97.Google Scholar An extensive exposition of ritual regicide can be found in SirFrazer, James G., The Golden Bough, 3rd ed. (New York, 1935), iv, pp. 9–119.Google Scholar
114 A comprehensive summary of most such “retired emperors” can be found in Yi, Zhao, op. cit., 13.281–6.Google Scholar
115 See for instance Hummel, Arthur William (ed.), Eminent Chinese of the Ch'ing period (1644–1912) (Washington, D.C., 1943–1944), P. 372.Google Scholar
116 ZZhTJ 134.4187, 137.4302.
117
Fan Ye,
![]() Hou Han shu
(Beijing,
1965), 90.2979.Google Scholar
Hou Han shu
(Beijing,
1965), 90.2979.Google Scholar
118 Yanshi jiaxun jijie, 1.48. Wright, Arthur (The Sui Dynasty, p. 35)Google Scholar has also noted Yan's observation.
119
The case of Lady Gouyi ![]() of the Han,
from which the Tuoba custom had allegedly taken its
cue, was evidently an exceptional, ad
hoc measure.
of the Han,
from which the Tuoba custom had allegedly taken its
cue, was evidently an exceptional, ad
hoc measure.
120 ZZhTJ 152.4739.
121 See for example Fletcher, Joseph, “Turco-Mongol monarchic tradition in the Ottoman Empire”.Google Scholar
122 Yinke, Chen, Tangdai zhengzhi shi, pp. 41–4.Google Scholar
123 XTSh79. See also Wechsler, Howard J., Mirror to the Son of Heaven: Wei Cheng at the Court of T'ang T'ai-tsung (New Haven, 1974), p. 71.Google Scholar
124 THY 73.1311; ZZhTJ 193.6098.
125
Li Duozuo ![]() (JTSh 109.3296–97) was a typical
case.
(JTSh 109.3296–97) was a typical
case.
126
See for example Yinke, Chen,
“Lun Tangdai zhi Fanjiang yu
fubing
![]() ”,
Chen Yinke xiansheng lunwenji,
i, pp.
665–77,Google Scholar and Qun, Zhang
”,
Chen Yinke xiansheng lunwenji,
i, pp.
665–77,Google Scholar and Qun, Zhang
![]() ,
“Tangdai Fanjiang
chutan
,
“Tangdai Fanjiang
chutan
![]() ”,
Journal of Oriental Studies,
XIX (1981), pp.
1–38.Google Scholar
”,
Journal of Oriental Studies,
XIX (1981), pp.
1–38.Google Scholar
127 See for example Tekin, Talat, op. cit., p. 264.Google Scholar
128
For example, in Emperor Xuanzong's military move to
eliminate Princess Taiping's supporters, which
culminated in the princess's suicide and Emperor
Ruizong's final “retirement”, two important players
were Wang Maozhong ![]() , a family
slave of Korean descent, and Gao Lishi it
, a family
slave of Korean descent, and Gao Lishi it
![]() , a eunuch.
See ZZhTJ 210.6683,
JTSh 106.3252.
, a eunuch.
See ZZhTJ 210.6683,
JTSh 106.3252.
129 Pulleyblank, (“The An-Lu-shan rebellion”, p. 40)Google Scholar seems the only author to have noted this Turco-Chinese partnership, albeit failing to recognize the crucial Xianbei factor which, like the Manchus, was the key element binding the steppe and the agrarian communities into a true empire.
130 See Yinke, Chen, Tangdai zhengzhishi, pp. 50–1.Google Scholar
131 Jackson, Peter and Lockhart, Laurence(ed.), The Cambridge History of Iran VI (Cambridge, 1986), p. 366;CrossRefGoogle Scholar Lockhart, Laurence, The Fall of the Safavi Dynasty and the Afghan occupation of Persia (Cambridge, 1958), pp. 17, 29–32.Google Scholar
132 ZZhTJ 254.8237.
133
For example, Lin, Zhao
![]() , Yinhua lu
, Yinhua lu
![]() , in
Tang Guoshi bu deng bazhong
, in
Tang Guoshi bu deng bazhong
![]() , ed. Jialuo, Yang
, ed. Jialuo, Yang
![]() (Taipei,
1962),Google Scholar 5.35, has a telling
story on the deplorable condition during the Yuanhe
(Taipei,
1962),Google Scholar 5.35, has a telling
story on the deplorable condition during the Yuanhe
![]() (806–820)
era of an originally prestigious imperial guard
office.
(806–820)
era of an originally prestigious imperial guard
office.
134 Read for example Wright, , “Sui Yang-Ti”, pp. 161–2.Google Scholar
135 See, e.g. Rulei, Hu, op. cit., pp. 78–9.Google Scholar
136 ZZhTJ 189.5931–2.
137 ZZhTJ 195.6150, 196.6174.
138 ZZhTJ 196.6168.
139 THY 4.44. The incident itself showed Chengqian's decent quality, something the official history was reluctant to admit.
140
Weijuan, Yao
![]() ,
Beichao huxing kao
,
Beichao huxing kao
![]() (Beijing,
1958), pp.
25–8.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1958), pp.
25–8.Google Scholar
141 It is interesting to note several cases of elder and more “militaristic” sons being passed over for succession in the Turco-Iranian realm which have puzzled early Muslim and later authors (Bosworth, , The Ghaznavids, pp. 45 and 228).Google Scholar Bosworth has suggested they might be a reminiscence of the steppe custom of ultimogeniture. However, as many Mongolists have pointed out, the Mongol practice of ochigin regarding the inheritance of property might not necessarily apply to political power (khanship). In the Sarbo-Chinese connection, the cultural aspect of these cases would also seem an interesting topic. One notes that, among the Ghaznavids for example, in contrast with the militarist elder brother Mas'ūd, the younger brother Muḥammad's tastes “were predominately literary and studious” (Bosworth, , Later Ghaznavids, p. 18).Google Scholar
142 Wei Zheng was noted for his loyalty to Emperor Gaozu's original heir apparent Prince Jiancheng. As shown by an interesting episode in JTSh 71.2559, he was still quite unwavering on the dizhang succession rule after many years of service under Emperor Taizong, whose accession to the throne represented a breach of this very principle.
143 Frye, Richard N. and Sayili, Aydin M., “Turks in the Middle East before the Saljuqs”, JAOS, LXII (1943), pp. 194–207.Google Scholar
144 Hummel, , op. cit., p. 94.Google Scholar
145 Li Xian's famed annotation of Hou Han shu has since become an integral part of that dynastic history.
146
Guodong, Sun
![]() ,
“Tang Zhenguan Yonghui jian
dangzheng shishi
,
“Tang Zhenguan Yonghui jian
dangzheng shishi
![]() ”,
Xinya Shuyuan xueshu niankan
”,
Xinya Shuyuan xueshu niankan
![]() ,
VII (1965), pp.
39–49,Google Scholar
did point out that Zhangsun Wuji, Li Zhi's decisive
backer, was not a man of letters while three major
supporters of Prince Wei, namely Liu Ji
,
VII (1965), pp.
39–49,Google Scholar
did point out that Zhangsun Wuji, Li Zhi's decisive
backer, was not a man of letters while three major
supporters of Prince Wei, namely Liu Ji
![]() , Cen Wenben
, Cen Wenben
![]() and Cui
Renshi
and Cui
Renshi ![]() all were,
and all had a rather miserable end.
all were,
and all had a rather miserable end.
147 See ZZhTJ 197.6195 and Quan Tang wen 161.1645.
148 Paraphrasing the title of David Honey's essay on sinicization. See note 8.
149 Barfield, Thomas J., The Perilous Frontier (Cambridge Mass., 1989), p. 197.Google Scholar
150 Tao, , Jing-Shen, , Jurchen in Twelfth-Century China (Seattle, 1976), pp. 42–7.Google Scholar
151
Baiyao, Li
![]() Bei Qi shu
(Beijing,
1972),
24.347–48.Google Scholar
Bei Qi shu
(Beijing,
1972),
24.347–48.Google Scholar
152 Meskoob, Shahrokh, Iranian Nationality and the Persian Language (Translation of Millilyat va zaban) (Washington, D.C., 1992), pp. 36–7.Google Scholar
153
Zhongluo, Wang
![]() Wei-Jin nanbeichao shi
Wei-Jin nanbeichao shi
![]() (Shanghai,
1980), ii, p.
983,Google Scholar discusses briefly
the savageries of the Northern Zhou army based on
some scattered data.
(Shanghai,
1980), ii, p.
983,Google Scholar discusses briefly
the savageries of the Northern Zhou army based on
some scattered data.
154 ZZhTJ 165.5121.
155
See for example Ciyuan
![]() (Beijing,
1988), p.
82Google Scholar quoting Shuo
fu
(Beijing,
1988), p.
82Google Scholar quoting Shuo
fu
![]()
156 Togan, Zeki Velidi, “Sur l'origine des Safavides”, in Mélanges Louis Massignon (Damascus, 1957), iii, PP. 345–57;Google Scholar Mazzaoui, Michael M., The Origins of the Ṣafawids: šīism, Ṣūfism, and the Ġulāt (Wiesbaden, 1972), pp. 47–8.Google Scholar
157 Braun, Hellmut, “Iran under the Safavids and in the 18th century”, in The Muslim World; a Historical Survey, ed. Spuler, B. (Leiden, 1969), iii, pp. 181–218, in particular p. 188.Google Scholar
158 Holt, Peter Malcolm et al. (ed.), The Cambridge History of Islam (Cambridge, 1970), i, p. 394;Google Scholar Mazzaoui, , op. cit., pp. 46–52.Google Scholar
159 Bawden, Charles R. (trans, and annotate), The Mongol Chronicle Altan Tobci (Wiesbaden, 1955), pp. 128–9;Google Scholar Franke, H. Franke, op. cit., pp. 64–9.Google Scholar
160 Wright, Arthur, “T'ang T'ai-tsung and Buddhism”, in Perspectives on the T'ang, ed. Wright, A. F. and Twitchett, D. (New Haven, 1973), pp. 239–63.Google Scholar
161
Yongtong, Tang,
Wangri zagao
![]() (Beijing,
1962), p.
10;Google Scholar
Sui-Tang Fojiao
shigao
(Beijing,
1962), p.
10;Google Scholar
Sui-Tang Fojiao
shigao
![]() (Beijing,
1982), p.
14.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1982), p.
14.Google Scholar
162 Weinstein, Stanley, Buddhism under the T'ang (Cambridge, 1987), pp. 11–12 and p. 155 n. 2.Google Scholar
163
Shiyan,
![]() ,
Tang hufa shamen Falin biezhuan
,
Tang hufa shamen Falin biezhuan
![]() in
Da zang jing
in
Da zang jing
![]() Zhi
Zhi
![]() No. 8,
(Shanghai,
1912), p.
10.Google Scholar
No. 8,
(Shanghai,
1912), p.
10.Google Scholar
164 JTSh 191.5089, 192.5125; XTSh 204.5804–05.
165 ZZhTJ 191.6009.
166
Minqiu, Song
![]() (comp.),
Tang da zhaoling ji
(comp.),
Tang da zhaoling ji
![]() (Beijing.
1959). 113.586.Google Scholar
(Beijing.
1959). 113.586.Google Scholar
167 See Pulleyblank, Edwin, “The Chinese and their neighbours in prehistoric and early historic times”, in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, ed. Keichtley, David N. (Berkeley, 1983), pp. 411–66, in particular pp. 414–15.Google Scholar
168 Middle Chinese pronunciation bit. For a dissenting view, see Sinor, Denis, “Altaica and Uralica”, in Studies in Finno-Ugric Linguistics in Honor of Alo Raun, ed. Sinor, D. (Bloomington, 1978), pp. 319–32.Google Scholar
169
Long-speculated existence of a Xianbei script (see, for
example, Mair, Victor
H., “Buddhism
and the rise of the written vernacular in East
Asia: the making of national
languages”, JAS,
LIII [1994], pp.
707–51CrossRefGoogle Scholar) can be largely
disregarded after the discovery of the Xianbei
cavern and even more because of other equally rich
collections of archaeological findings, especially
tomb inscriptions and other artifacts of this
period. See Yiliang, Zhou
![]() Wei-Jin nanbeichao shi lunji
xubian
Wei-Jin nanbeichao shi lunji
xubian
![]() (Beijing,
1991), pp.
179–80.Google Scholar
(Beijing,
1991), pp.
179–80.Google Scholar
170 Goody, Jack and Watt, Ian, “The consequence of literacy”, Comparative Studies in Society and History,V (1963), pp. 304–45.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
171 Zhou shu 36.643.
172
Shitong
![]() edition
used: Lüfu, Zhao
edition
used: Lüfu, Zhao
![]() Shitong xin jiaozhu
Shitong xin jiaozhu
![]() (Chongqing,
1990), pp. 457,
960.Google Scholar
(Chongqing,
1990), pp. 457,
960.Google Scholar
173 ZZhTJ 173.5382.
174 This distrust might have even contributed to the cause of the An Lushan rebellion. See Pulleyblank, Edwin, The Background of the Rebellion of An Lu-shan (London, 1955), pp. 75–81.Google Scholar
175 See for example Dien, Albert E., “Yen Chih-T'ui (531–91 +): His Life and Thought”, Diss. (University of California, 1962), p. 12,Google Scholar and Holmgren, Jennifer, “Politics of the inner court under the Hou-chu (Last Lord) of the Northern Ch'i (ca. 565–73)”, in State and Society in Early Medieval China, ed. Dien, A. E. (Stanford, 1990), pp. 269–330,Google Scholar though both have used the standard “exemplary history” arguments to explain this contrast.
176 Eberhard, Wolfram, A History of China, 4th ed. (London, 1977), p. 152.Google Scholar
177 Barfield, , op. cit., p. 126.Google Scholar