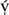The Ersu language (/
![]() -
-
![]()
![]() xò/, 尔苏语 ěrsūyǔ, ISO-639 code ers) is spoken by approximately 16,800 people who reside in five counties in Sichuan Province (四川省) in the People's Republic of China: (i) Ganluo (甘洛县), and (ii) Yuexi (越西县) counties of Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture (凉山彝族自治州), (iii) Shimian (石棉县) and (iv) Hanyuan (汉源县) counties of Ya’an Municipality (雅安市), and (iv) Jiulong (九龙县, Written Tibetan, hereafter WT brgyad zur) county of Ganzi (甘孜, WT dkar mdzes) Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture.Footnote
1
Ersu has two closely related sister languages: Lizu (/li
55-zu
55-hũ55/ or /ly
55-zu
55-hũ55/, 里汝语 lǐrǔyǔ or 栗苏语 lìsūyǔ) and Duoxu (/do
33-ɕu
33-na
31/, 多续语 duōxùyǔ or 多须语 duōxūyǔ).Footnote
2
Lizu is spoken in the neighbouring counties of (i) Muli Tibetan Autonomous County (木里藏族自治县, WT smi li rang skyong rdzong), (ii) Mianning (冕宁县), and (iii) Jiulong; whereas Duoxu is spoken in the county of Mianning, all in Sichuan province (see the map in Figure 1).
xò/, 尔苏语 ěrsūyǔ, ISO-639 code ers) is spoken by approximately 16,800 people who reside in five counties in Sichuan Province (四川省) in the People's Republic of China: (i) Ganluo (甘洛县), and (ii) Yuexi (越西县) counties of Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture (凉山彝族自治州), (iii) Shimian (石棉县) and (iv) Hanyuan (汉源县) counties of Ya’an Municipality (雅安市), and (iv) Jiulong (九龙县, Written Tibetan, hereafter WT brgyad zur) county of Ganzi (甘孜, WT dkar mdzes) Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture.Footnote
1
Ersu has two closely related sister languages: Lizu (/li
55-zu
55-hũ55/ or /ly
55-zu
55-hũ55/, 里汝语 lǐrǔyǔ or 栗苏语 lìsūyǔ) and Duoxu (/do
33-ɕu
33-na
31/, 多续语 duōxùyǔ or 多须语 duōxūyǔ).Footnote
2
Lizu is spoken in the neighbouring counties of (i) Muli Tibetan Autonomous County (木里藏族自治县, WT smi li rang skyong rdzong), (ii) Mianning (冕宁县), and (iii) Jiulong; whereas Duoxu is spoken in the county of Mianning, all in Sichuan province (see the map in Figure 1).

Figure 1 Distribution of the Ersu, Lizu, and Duoxu languages.
In present classifications of Tibeto-Burman languages spoken in Southwest China, Ersu, Lizu, and Duoxu are viewed as three dialects of one Ersu language. The Ersu language is, in turn, classified as a member of the Qiangic subgroup of the Tibeto-Burman language family (for more details, see Bradley Reference Bradley and Bradley1997: 36–37; H. Sun Reference Sun2001; Chirkova Reference Chirkova2012). In this conception, Lizu is the western dialect of the Ersu language, Duoxu is its central dialect, and Ersu proper is the eastern dialect of the Ersu language. In contrast to this received view and in accordance with the fact that differences between Lizu, Duoxu, and Ersu surpass the limit of mutual intelligibility (H. Sun Reference Sun1982, Chirkova Reference Chirkova2014), we consider Lizu, Duoxu, and Ersu as separate languages, and not as dialects of one Ersu language (Yu Reference Yu2012: 1). The phonological, lexical, and morphosyntactic differences between Ersu, Lizu, and Duoxu are likely to be in part due to the competing influences of the languages with which they are in contact. More specifically, Ersu has been historically influenced by Pumi (普米), Nuosu (Northern Ngwi or Yi 彝), and Mandarin Chinese (the local variety of Southwest Mandarin, hereafter SW Mandarin) (Wu Da 2010: 3). By contrast, Lizu has been influenced by Tibetan, Pumi, and Namuzi (纳木兹) languages (Chirkova & Chen Reference Chirkova and Chen2013). Finally, Duoxu has been essentially influenced by SW Mandarin as well as by Nuosu (Chirkova Reference Chirkova2014).
The main focus of this illustration is on a synchronic analysis of Ersu proper. (For more comparatively- and diachronically-oriented studies of Ersu, Lizu, and Duoxu, the interested reader is referred to Yu Reference Yu2012, Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013a, Chirkova Reference Chirkova2014.)
Ersu is relatively little researched, but the group and its language and culture have been receiving increasing attention in recent years (e.g. Wang Reference Wang2010, Wu Da 2010, Schmidt Reference Schmidt2011, Zhang Reference Zhang2013, Reference Zhang, Aikhenvald and Dixon2014). Early linguistic accounts include H. Sun (Reference Sun1982, Reference Sun1983) and Liu (Reference Shaoming and Junbo2007 [1983]), which focus on the Ersu as spoken in Ganluo county.
Ersu is an endangered language. It is essentially used as the primary language of oral communication in family and community events. Older Ersu speakers (typically above their sixties) are mostly trilingual (Ersu, SW Mandarin, Nuosu). Over the last three decades, most Ersu speakers have been bilingual using SW Mandarin in daily life. The current trend for the school-going generation is to become practically monolingual in Mandarin. Ersu has its own pictographic writing system, known as shaba 沙巴 (Ersu /ṣàpá/`ritual priest') writing, which is chiefly used by Bon priests (e.g. H. Sun Reference Sun2009, Wang Reference Wang2011).
The present illustration provides a preliminary description of Ersu on the basis of data from three speakers: two male speakers in their early sixties and one female speaker in her early forties, all born and raised in Ganluo county (Zela Township 则拉, Liangshan group 凉山组, Mofanggou village 磨坊沟村 /
![]()
![]()
![]() ɬá lò,
ɬá lò,
![]() ákáɽ
ákáɽ
![]() ɡ
ɡ
![]() f
f
![]() , nóN
, nóN
![]()
![]()
![]() pá/). Given the phonetic complexity of the consonant and vowel sounds of Ersu (including a number of typologically uncommon trilled retroflex sounds and phonemic fricative vowels), further research, based on more speakers, is required for a comprehensive analysis of this language. In the present Illustration, the basic phonetic characteristics of Ersu are described through acoustic, palatographic, aerodynamic, electroglottographic, and video data. We have chosen to illustrate the discussion with audio files (the word list and the text provided in the present paper) as read by the second author, a male native speaker of Ersu. This is because we were in the fortunate position of recording him in a phonetics laboratory, yielding high quality audio recordings. Conversely, palatographic images in the text are from the female speaker. This is because, as the youngest speaker among our language consultants, her dental and palatal condition yielded the clearest images.
pá/). Given the phonetic complexity of the consonant and vowel sounds of Ersu (including a number of typologically uncommon trilled retroflex sounds and phonemic fricative vowels), further research, based on more speakers, is required for a comprehensive analysis of this language. In the present Illustration, the basic phonetic characteristics of Ersu are described through acoustic, palatographic, aerodynamic, electroglottographic, and video data. We have chosen to illustrate the discussion with audio files (the word list and the text provided in the present paper) as read by the second author, a male native speaker of Ersu. This is because we were in the fortunate position of recording him in a phonetics laboratory, yielding high quality audio recordings. Conversely, palatographic images in the text are from the female speaker. This is because, as the youngest speaker among our language consultants, her dental and palatal condition yielded the clearest images.
Consonants
The Ersu consonant inventory consists of 38 phonemes. There is a general three-way manner distinction in stops and affricates: voiceless unaspirated, voiceless aspirated, and voiced. Ersu has an extensive system of coronal consonant contrasts in affricates at the dental, alveolar, alveolopalatal, and retroflex places of articulation. Alveolopalatals are marginal. They mainly occur in (recent) loanwords from Mandarin Chinese, such as /kʰà-tɕà-tɕá/ ‘to pick up with chopsticks’ (Chinese jiā 夹, SW Mandarin /tɕia⁴⁴/), /kòtɕó/ ‘legging, puttee’ (Chinese guǒjiǎo 裹脚, SW Mandarin /ko 53 tɕio 21/), /ɕá/ ‘incense’ (Chinese xiāng 香, SW Mandarin /ɕiaŋ⁴⁴/).Footnote 3 In the native vocabulary, alveolopalatals have a restricted distribution, co-occurring only with the vowels /i o a/. Examples include /tɕí-tɕí/ ‘to squeeze, to pick up with chopsticks; to cut with scissors’ (possibly, a loanword from Chinese jiǎn 剪 ‘to cut with scissors’, SW Mandarin /tɕian 53/), /tɕó/ ‘to wrap, to bind’, /ódʑá/ ‘pear’ (see below on vowels).
We studied the four-way contrast in coronals using palatographic analysis techniques (as described in Marchal Reference Marchal1988, Ladefoged Reference Ladefoged2003: 36–42, and Anderson Reference Anderson2008). The list of words used in the palatographic study consisted of monosyllabic words in common use in the language, each of which included only one coronal consonant. The palatography procedures were to paint the tip, blade, and front of the tongue with a solution of one part olive oil and one part of finely ground activated charcoal. After each word was pronounced, a mirror was placed in the speaker's mouth, resting against the lower teeth and the reflection of the upper palate and teeth was recorded using a video camera.
Stops and affricates
Ersu dental stops and affricates are both produced in the dental region. Dental stops involve contact on both the teeth and most of the alveolar ridge, making them (laminal) denti-alveolar. By contrast, dental affricates involve a smaller contact area, which includes the upper front teeth and the front part of the alveolar ridge. This is illustrated in Figure 2, with the words /d
![]() / ‘to weave’ and /
/ ‘to weave’ and /
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘rooster (zodiac sign)’.
/ ‘rooster (zodiac sign)’.

Figure 2 Palatograms of the words /d
![]() / ‘to weave’ and /
/ ‘to weave’ and /
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘rooster (zodiac sign)’.
/ ‘rooster (zodiac sign)’.
Alveolar affricates are produced with the tongue touching the middle of the alveolar ridge (laminal flat alveolar). The contrast between dental and alveolar affricates is illustrated in Figure 3, with the minimal pair /
![]()
![]() ó/ ‘to lay bricksʼ and /ḍẓó/ ‘water’.
ó/ ‘to lay bricksʼ and /ḍẓó/ ‘water’.

Figure 3 Palatograms of the words /
![]()
![]() ó/ ‘to lay bricks’ and /ḍẓó/ ‘water’.
ó/ ‘to lay bricks’ and /ḍẓó/ ‘water’.
Alveolopalatal affricates are produced with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge and the body of the tongue raised towards the palate, thus involving simultaneous alveolar and palatal articulation (compare ‘laminal palatalized post-alveolar’, as described in Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 153–154). The contrast between alveolar and alveolopalatal affricates is illustrated in Figure 4, with the words /ḍẓó/ ‘water’ and /dʑó/ ‘to push’.

Figure 4 Palatograms of the alveolar and alveolopalatal affricates in the words /ḍẓó/ ‘water’ and /dʑó/ ‘to push’.
Ersu retroflex affricates are produced with the point of contact on the roof of the mouth, that is, in the hard palate. The contact is made with the underside of the tongue (subapical). The articulation of retroflex affricates involves lateral bracing of the tongue against the teeth, so that the tongue tip is free to move to and from the hard palate. Figure 5 contains palatograms of the words /ʈɽò/ ‘gallbladder’ and /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’. As we did not paint the underside of the tongue with a mixture of olive oil and activated charcoal powder, the area of contact is not visible on the image.

Figure 5 Palatograms of the words /ʈɽò/ ‘gallbladder’ and /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’.
Ersu retroflex affricates have a trill release. They involve an aerodynamically induced movement of the tip of the tongue, causing intermittent contact between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth. Ersu retroflex affricates are typically single-contact trills. This is illustrated in Figure 6, with the words /ʈɽò/ ‘gallbladder’ and /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’. A contact, that is, a moment of closure of the oral cavity, is reflected on the spectrograms by a period of white space.

Figure 6 Waveforms and spectrograms of /ʈɽò/ ‘gallbladder’ and /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’ (arrows indicate contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth).
When retroflex affricates are followed by fricative vowels, the number of contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth may be increased to three. This is illustrated in Figure 7, with the words /ʈɽ
![]() / ‘sweat’ and /Nɖɽ
/ ‘sweat’ and /Nɖɽ
![]() / ‘tile’.
/ ‘tile’.

Figure 7 Waveforms and spectrograms of /ʈɽ
![]() / ‘sweat’ and /Nɖɽ
/ ‘sweat’ and /Nɖɽ
![]() / ‘tile’ (arrows indicate contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth).
/ ‘tile’ (arrows indicate contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth).
Fricatives
Ersu contrasts fricatives at five places of articulation: (i) labiodental, (ii) dental, (iii) alveolar, (iv) alveolopalatal (palatalized laminal post-alveolar), and (v) velar. All but velar show a two-way contrast between voiceless and voiced: /f
v/ (e.g. /fí/ ‘mildew’, /ví/ ‘tinder’), /
![]()
![]() / (e.g. /
/ (e.g. /
![]()
![]() / ‘air’, /
/ ‘air’, /
![]()
![]() / ‘wife’), /ṣ ẓ/ (e.g. /ṣò/ ‘blood’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debtʼ), /ɕ ʑ/ (e.g. /ɕó/ ‘to sweep’, /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’), /x/ (e.g. /xì/ ‘bamboo’).
/ ‘wife’), /ṣ ẓ/ (e.g. /ṣò/ ‘blood’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debtʼ), /ɕ ʑ/ (e.g. /ɕó/ ‘to sweep’, /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’), /x/ (e.g. /xì/ ‘bamboo’).
The voiced labiodental fricative /v/ is contrastive with the voiced labial-velar approximant /w/ before /a/ and /o/, as in /vá/ ‘net’, /wá/ ‘to be full, satisfied’. /f/ has a restricted distribution, occurring only before /i/ (as above) and /
![]() / (as in /f
/ (as in /f
![]() / ‘garlic’). In the latter environment, /f/ can be alternatively regarded as the allophone of /x/, as is also the case in SW Mandarin, with which Ersu is in close contact. Consider, for example, the Ersu word for ‘kettle’: /f
/ ‘garlic’). In the latter environment, /f/ can be alternatively regarded as the allophone of /x/, as is also the case in SW Mandarin, with which Ersu is in close contact. Consider, for example, the Ersu word for ‘kettle’: /f
![]() -f
-f
![]() /, which is a loanword from SW Mandarin /fu
21-fu⁴⁴/, corresponding to Standard Mandarin hú 壶 [xu
35].
/, which is a loanword from SW Mandarin /fu
21-fu⁴⁴/, corresponding to Standard Mandarin hú 壶 [xu
35].
Ersu exploits contrasts between grooved fricatives at the dental place of articulation and flat fricatives at the alveolar place of articulation. Figure 8 illustrates the three-way contrast between the dental, alveolar, and alveolopalatal places of articulation in fricatives with the words /
![]()
![]() / ‘wife’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debtʼ, and /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’.
/ ‘wife’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debtʼ, and /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’.

Figure 8 Palatograms of the words /
![]()
![]() / ‘wife’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debt’, and /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’.
/ ‘wife’, /ẓó/ ‘to scold; to be in debt’, and /ʑó/ ‘to soften (skin)’.
Before /o/, /x/ has an allophone [ç], which we analyse phonemically as a sequence of /x/ and the palatal approximant /j/, e.g. /xjó/ [çó] ‘to cry out’ (see below on clusters with approximants).
Nasals
Ersu has nasals at three places of articulation: (i) bilabial (/m/), (ii) dental (denti-alveolar) (/n/) (see Figure 9), and (iii) velar (/ŋ/).

Figure 9 Palatogram of the word /n
![]() / ‘you, thou’.
/ ‘you, thou’.
Ersu has one syllabic nasal, /
![]() /, as in /
/, as in /
![]()
![]() -
-
![]() / ‘seven’, /lwá
/ ‘seven’, /lwá
![]() ká/ ‘ridge of a building’, /
ká/ ‘ridge of a building’, /
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘satin, silkʼ (possibly from Chinese língzi 绫子 ‘damask silk’, SW Mandarin /nin
53tsɿ53/).
/ ‘satin, silkʼ (possibly from Chinese língzi 绫子 ‘damask silk’, SW Mandarin /nin
53tsɿ53/).
Liquids
Ersu laterals are made with an occlusion in the alveolar region extending back to the back molars. This is illustrated in Figure 10, with the minimal pair /lá/ ‘fertilizer, manure’ and /ɬá/ ‘month’.

Figure 10 Palatograms of the words /lá/ ‘fertilizer, manure’ and /ɬá/ ‘month’.
Similar to retroflex affricates, the Ersu retroflex trill (/ɽ/) is produced with the point of contact on the roof of the mouth in the hard palate and with the tongue body braced against the sides of the teeth to allow for an aerodynamically induced movement of the tongue tip (see McGowan Reference McGowan1992: 2903, Spajić, Ladefoged & Bhaskararao Reference Spajić, Ladefoged and Bhaskararao1996: 3; see Figure 11). Similar to the retroflex trill in Toda (Spajić et al. Reference Spajić, Ladefoged and Bhaskararao1996: 13), the first contact of the tongue tip is made at the back of the alveolar ridge, whereas subsequent contacts are made slightly further forward near or at the alveolar ridge, so that the trill is realized as [ɽr].

Figure 11 Palatogram of the word /ɽ
![]() / ‘earth, soil’.
/ ‘earth, soil’.
Ersu trill typically has two contacts. However, similar to trilled retroflex affricates, a trill followed by a fricative vowel may have a larger number of contacts (four to five). This is illustrated in Figure 12.

Figure 12 Waveforms and spectrograms of the words /ɽá/ ‘chicken’, /ɽó/ ‘bone; horn’, and /ɽ
![]() / ‘to laugh’ (arrows indicate contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth).
/ ‘to laugh’ (arrows indicate contacts between the tip of the tongue and the roof of the mouth).
Clusters
Ersu has a rich inventory of clusters, including (i) clusters with approximants, (ii) prenasalized clusters, and (iii) clusters with a schwa-like segment.
Clusters with approximants
The approximants /w/ and /j/ may occur after a broad range of initials and may be realized as secondary labialization or palatalization of the first position consonant. Of the two approximants, /w/ has the broadest distribution, occurring after bilabial, dental, and velar stops, dental affricates, and laterals. However, most of these clusters with /w/ can only be followed by /a/ (as in /kwá/ ‘to take off’, compare to /ká/ ‘to be stupid’). In addition, clusters with velar stops and /w/ can also be followed by /a˞/ (as in /nà-kw
![]() / ‘to put inside’, compare to /
/ ‘to put inside’, compare to /
![]()
![]() -ẓ
-ẓ
![]() -kà˞/ ‘to bear a grudge’).
-kà˞/ ‘to bear a grudge’).
/j/ has a more restricted distribution, occurring only after (bilabial and dental) nasals and laterals, and it can only be followed by the vowels /o/ and /a/. (/j/ may also occur after /x/, which combination can only be followed by /o/. The cluster /xjo/ is realized as [ç], as in /xjó/ [çó] ‘to cry out’, see above). Consider the following (near) minimal pairs: /má/ ‘mother, female’ vs. /mjá
bó/ ‘tear’; /nà-ná/ ‘to occupy’ vs. /njá/ ‘child’; /lá/ ‘fertilizer, manure’ vs. /ljá/ ‘to paint’; and /N
![]()
![]() ʰòɬó/ ‘flea’ vs. /m
ʰòɬó/ ‘flea’ vs. /m
![]() -ɬjó/ ‘lightning’.
-ɬjó/ ‘lightning’.
It is important to note that the realization of /w/ and /j/ in clusters ranges between a separate segment with a clear segmental boundary (mostly before /a/) and a segment with a secondary articulation, that is, a segment with a lesser degree of stricture that accompanies a primary articulation of a higher degree (mostly before /o/) (see Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 354). Examples include /njá/ [njá] ‘child’, /ljá/ [ljá] ‘to paint’, /njó/ or /nʲó/ [ɲó] ‘day’, /ljò/ or /lʲò/ [ʎò] ‘arm spread (measure of length)’. We note that the addition of the lip rounding gesture (in the case of /w/) and raising of the body of the tongue (in the case of /j/) have a strong acoustic effect on both the preceding consonant and the following vowel. Overall, compared to clusters with /w/ and /j/ in the closely related Lizu and Duoxu languages, Ersu medials /w/ and /j/ exhibit stronger assimilatory influence on neighboring segments (see Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013b for a detailed discussion).
In light of the above, Ersu alveolopalatal affricates and fricatives, which only occur in native vocabulary before the vowels /i o a/, can be alternatively analysed as palatalized allophones of dentals, alveolars and/or velars, followed by the high front vowel or the palatal approximant /j/.
Prenasalized clusters
Prenasalization in Ersu is contrastive and occurs not only before voiced stops and affricates, but also before voiceless aspirated ones. Prenasalized stops and affricates are found in all places of articulation. The place of articulation is always homorganic with that of the obstruent in the cluster. Thus, we use the archiphoneme N to refer to the homorganic nasal in prenasalized clusters. Compare the contrast between plain onsets in the following minimal pairs: /bò/ ‘string’ vs. /Nbò/ ‘horse’, /pʰó/ ‘to escape’ vs. /Npʰó/ ‘to steal’, /
![]()
![]() à/ ‘fodder’ vs. /N
à/ ‘fodder’ vs. /N
![]()
![]() à/ ‘Chinese people’, /
à/ ‘Chinese people’, /
![]()
![]() ʰá/ ‘hot’ vs. /N
ʰá/ ‘hot’ vs. /N
![]()
![]() ʰá/ ‘mark, sign’, /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’ vs. /Nɖɽò/ ‘dirt, filth’, /(m
ʰá/ ‘mark, sign’, /ɖɽò/ ‘pot, pan’ vs. /Nɖɽò/ ‘dirt, filth’, /(m
![]() lí) t
lí) t
![]() ʈɽʰó/ ‘one piece (of land)’ vs. /t
ʈɽʰó/ ‘one piece (of land)’ vs. /t
![]() Nʈɽʰó/ ‘one handful (e.g. of rice)’.
Nʈɽʰó/ ‘one handful (e.g. of rice)’.
In prenasalized voiceless aspirated stops and affricates, we observe regular glottal pulsing during the nasal section but not during the voiceless stop, as detailed in Figure 13. This figure shows that the nasal section is produced with a complete closure within the oral tract (no oral airflow) and with air moving through the nasal cavity (nasal airflow for the entire duration of the segment). It is therefore a characteristic nasal.

Figure 13 Audio waveforms, spectrograms, electroglottograph waveforms (EGG), nasal airflows (NAF), and oral airflows (OAF) for the pairs /pʰó/ ‘to escape’ vs. /N pʰó/ ‘to steal’ and /tʰwá/ ‘mule’ vs. /Ntʰwá/ ‘to be sharp’.
Clusters with a schwa-like segment
Ersu has seven voiceless (unaspirated) stops, affricates, and fricatives (/əp ət ək ə
![]()
![]() əṭṣ ətɕ əx/) and seven voiced stops, fricatives, and nasals (/əb əd əɡ ə
əṭṣ ətɕ əx/) and seven voiced stops, fricatives, and nasals (/əb əd əɡ ə
![]() əm ən əŋ/) that can be preceded by a segment with a schwa-like formant structure. Compare the minimal pairs /ə
əm ən əŋ/) that can be preceded by a segment with a schwa-like formant structure. Compare the minimal pairs /ə
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘interest’ vs. /
/ ‘interest’ vs. /
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘cloud’, and /ən
/ ‘cloud’, and /ən
![]() / ‘to be heavy; to be deep’ vs. /n
/ ‘to be heavy; to be deep’ vs. /n
![]() / ‘two’ in Figures 14 and 15.
/ ‘two’ in Figures 14 and 15.

Figure 14 Waveforms and spectrograms for the minimal pair /ə
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘interest’ vs. /
/ ‘interest’ vs. /
![]()
![]()
![]() / ‘cloud’.
/ ‘cloud’.

Figure 15 Waveforms and spectrograms for the minimal pair /ən
![]() / ‘to be heavy; to be deep’ vs. /n
/ ‘to be heavy; to be deep’ vs. /n
![]() / ‘two’.
/ ‘two’.
Clusters with a schwa-like segment can be tentatively identified with earlier consonant clusters. Independent evidence for such clusters can be found in Ersu words that etymologically correspond to Proto-Lolo-Burmese and Proto-Tibeto-Burman forms with initial clusters (see Bradley Reference Bradley1979: 144, Reference Bradley, Ratanakul and Thomas1985: 242; Matisoff Reference Matisoff2003:37). For example, Ersu /ən
![]() / ‘to be deep’ corresponds to Proto-Loloish *ʔ-nakᴸ ‘deep’ (Matisoff Reference Matisoff2003: 37) (see Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013a for a detailed discussion). Clusters with a schwa-like segment are in the process of disappearing from this language, merging with corresponding simple onsets.Footnote
4
/ ‘to be deep’ corresponds to Proto-Loloish *ʔ-nakᴸ ‘deep’ (Matisoff Reference Matisoff2003: 37) (see Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013a for a detailed discussion). Clusters with a schwa-like segment are in the process of disappearing from this language, merging with corresponding simple onsets.Footnote
4
In addition to clusters with a schwa-like segment, Ersu also marginally has preaspirated clusters, which are restricted to loanwords from Tibetan. Examples include /htóNbá/ ‘to be empty’ (WT stong pa), /hkwàɽá/ ‘to turn, to circle’ (WT skor ba). In these words, preaspiration diachronically derives from stop clusters with the preradical s- in Old Tibetan. The acoustic quality of Ersu preaspirated clusters is different from voiceless segments preceded by a schwa-like segment. The main differences include (i) the longer duration, and (ii) the clear formant structure of the schwa-like segment, as compared to preaspiration. These differences are illustrated in Figure 16, with the pair /ətó/ ‘to jump’ vs. /htóNbá/ ‘to be empty’.

Figure 16 Waveforms and spectrograms for the pair /ətó/ ‘to jump’ vs. /htó N bá/ ‘to be empty’.
Vowels
Ersu has eight vowel phonemes, of which four are plain (/i ɛ a
o/), two are fricative (/
![]()
![]() /), and two are rhotacized (/ə˞ a˞/). See the vowel chart plotted on the relative F1/F2 formant values.
/), and two are rhotacized (/ə˞ a˞/). See the vowel chart plotted on the relative F1/F2 formant values.
Plain vowels
/i/ has a fairly broad range of realizations. It ranges from [i] (essentially in loan vocabulary from SW Mandarin and Nuosu) to [j
![]() ] (mostly after bilabial initials) and [e] (mostly after dental, alveolar, and alveolopalatal initials). The value range for F1 is between 264 and 347 Hz, and for F2 between 1920 and 2274 Hz. Examples include: /ɕíkwá/ [ɕíkwá] ‘watermelon’ (Chinese xīguā 西瓜, SW Mandarin /ɕi⁴⁴kua⁴⁴/), /í
] (mostly after bilabial initials) and [e] (mostly after dental, alveolar, and alveolopalatal initials). The value range for F1 is between 264 and 347 Hz, and for F2 between 1920 and 2274 Hz. Examples include: /ɕíkwá/ [ɕíkwá] ‘watermelon’ (Chinese xīguā 西瓜, SW Mandarin /ɕi⁴⁴kua⁴⁴/), /í
![]()
![]() ʰ
ʰ
![]() / [
/ [
![]()
![]()
![]() ʰ
ʰ
![]() ] ‘ladle, a long handled spoon, generally made of wood’ (Nuosu it chyp [i
55
tʂʰʅ21]);Footnote
5
/pí/ [pj
] ‘ladle, a long handled spoon, generally made of wood’ (Nuosu it chyp [i
55
tʂʰʅ21]);Footnote
5
/pí/ [pj
![]() ] ‘dregs’, /mí/ [mj
] ‘dregs’, /mí/ [mj
![]() ] ‘monkey’, and /
] ‘monkey’, and /
![]() í/ [
í/ [
![]() é] ‘wood’ (compare to /
é] ‘wood’ (compare to /
![]()
![]() / ‘air’).
/ ‘air’).
After alveolar affricates, dental and alveolar fricatives, and velar stops, /ɛ/ may be realized as retroflex (characterized by lowered F3 values). For example, in the sound files compare the realization of the word /ẓ
![]() / ‘to crawl, to climb’ in isolation and the three repetitions of that word in the compound /Nbí ẓ
/ ‘to crawl, to climb’ in isolation and the three repetitions of that word in the compound /Nbí ẓ
![]() / ‘to climb mountains’.
/ ‘to climb mountains’.
Fricative vowels
Fricative vowels (Ersu /
![]() / and /
/ and /
![]() /) are defined as vowels that are produced with the tongue in essentially the same position as in the corresponding fricatives (Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1990: 117, Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 314). The constriction of the tongue tip or lips produces alveolar and labiodental frication, respectively.
/) are defined as vowels that are produced with the tongue in essentially the same position as in the corresponding fricatives (Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1990: 117, Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 314). The constriction of the tongue tip or lips produces alveolar and labiodental frication, respectively.
The two fricative vowels in Ersu (/
![]()
![]() /) are independent phonemes that co-occur with a broad range of initials. Therefore, they are distinct from the known cases of fricative vowels in Mandarin or Nuosu (see e.g. Chao Reference Chao1972 [1948]; Li & Ma Reference Ming1983: 36; Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 314), where syllabic fricatives can be viewed as conditioned variants of other (high) vowels.
/) are independent phonemes that co-occur with a broad range of initials. Therefore, they are distinct from the known cases of fricative vowels in Mandarin or Nuosu (see e.g. Chao Reference Chao1972 [1948]; Li & Ma Reference Ming1983: 36; Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 314), where syllabic fricatives can be viewed as conditioned variants of other (high) vowels.
Ersu fricative vowels display periodic vocal fold vibration and clear formant structure, as is typical of vowels. The two are differentiated by the configuration of the lips: spread for /
![]() / and rounded for /
/ and rounded for /
![]() /. /
/. /
![]() / is produced with a pronounced lip compression, whereby the lower lip is raised, while the upper lip remains in a static position (as characteristic for the articulation of labiodental fricatives, see Laver Reference Laver1994: 250). Examples include /
/ is produced with a pronounced lip compression, whereby the lower lip is raised, while the upper lip remains in a static position (as characteristic for the articulation of labiodental fricatives, see Laver Reference Laver1994: 250). Examples include /
![]() / ‘snow’, /
/ ‘snow’, /
![]() / ‘wine’, /
/ ‘wine’, /
![]()
![]() / ‘shoe’, and /
/ ‘shoe’, and /
![]()
![]() / ‘oil’ (see also video clips ‘shoe’ and ‘oil’). Ersu fricative vowels are accompanied by fricative noise: the high-frequency energy noise in the 3000–6000 Hz region for /
/ ‘oil’ (see also video clips ‘shoe’ and ‘oil’). Ersu fricative vowels are accompanied by fricative noise: the high-frequency energy noise in the 3000–6000 Hz region for /
![]() /, and a relatively flat spectrum for /
/, and a relatively flat spectrum for /
![]() / (as typical of labiodental fricatives) (see Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 173–176). The fricative noise is more diffuse and weaker in intensity than that found for other fricatives (see Figure 17).
/ (as typical of labiodental fricatives) (see Ladefoged & Maddieson Reference Ladefoged and Maddieson1996: 173–176). The fricative noise is more diffuse and weaker in intensity than that found for other fricatives (see Figure 17).

Figure 17 Acoustic spectra and waveforms and spectrograms of the words /
![]() / ‘snow’, /
/ ‘snow’, /
![]() / ‘wine’ (an arrow indicates high-frequency noise in the 3000–6000 Hz region).
/ ‘wine’ (an arrow indicates high-frequency noise in the 3000–6000 Hz region).
The vowel /
![]() / may occur after bilabial stops, dental and alveolar affricates and fricatives, retroflex affricates, /ɽ/, and, in a very few cases, also after the voiced velar initials /ɡ Nɡ ŋ/. It has a broad range of realization:
/ may occur after bilabial stops, dental and alveolar affricates and fricatives, retroflex affricates, /ɽ/, and, in a very few cases, also after the voiced velar initials /ɡ Nɡ ŋ/. It has a broad range of realization:
-
(i) After bilabial stop initials, /
 / is realized as [z
/ is realized as [z
 ] after non-aspirated initials and as devoiced, [
] after non-aspirated initials and as devoiced, [
 ], after aspirated stop initials. Examples include /b
], after aspirated stop initials. Examples include /b
 / [bz
/ [bz
 ] ‘bee’, /p
] ‘bee’, /p
 -p
-p
 / [pz
/ [pz
 -pz
-pz
 ] ‘to be flat’, /pʰ
] ‘to be flat’, /pʰ
 pó/ [p
pó/ [p
 pó] ‘wood shavings’.
pó] ‘wood shavings’. -
(ii) After dental and alveolar affricates and fricatives, retroflex affricates and /ɽ/, /
 / is realized as homorganic to the preceding consonant onset. Examples include /
/ is realized as homorganic to the preceding consonant onset. Examples include /

 / ‘matter, affair’ (Chinese shì 事, SW Mandarin /sɿ213/), /
/ ‘matter, affair’ (Chinese shì 事, SW Mandarin /sɿ213/), /

 / ‘shoe’, /
/ ‘shoe’, /


 / ‘to feed’, /
/ ‘to feed’, /

 ʰ
ʰ
 / ‘salt’, /ṣ
/ ‘salt’, /ṣ
 / [ṣ
/ [ṣ
 ] ‘meat’, /ẓ
] ‘meat’, /ẓ
 / [ẓ
/ [ẓ
 ] ‘to wear, to put on’, /ʈɽ
] ‘to wear, to put on’, /ʈɽ
 / [ʈɽ
/ [ʈɽ
 ] ‘star’, /ʈɽʰ
] ‘star’, /ʈɽʰ
 / [ʈɽʰ
/ [ʈɽʰ
 ] ‘to cut with a sickle’, /ɖɽ
] ‘to cut with a sickle’, /ɖɽ
 / [ɖɽ
/ [ɖɽ
 ] ‘glutinous rice’, /ɽ
] ‘glutinous rice’, /ɽ
 / [ɽ
/ [ɽ
 ] ‘to laugh’.
] ‘to laugh’. -
(iii) After velar initials, /
 / is realized close to [ɤ], as in /ɡ
/ is realized close to [ɤ], as in /ɡ
 ɽóə
ɽóə


 / [ɡ
/ [ɡ
 ɽóə
ɽóə


 ] ‘spine, backbone’ (compare to /ɡ
] ‘spine, backbone’ (compare to /ɡ
 / ‘boat’, /ɡó-ɡó/ ‘light (adj)’).
/ ‘boat’, /ɡó-ɡó/ ‘light (adj)’).
/
![]() / has a broader distribution and may occur after bilabial and velar stops; dental, alveolar and retroflex affricates; nasals; and dental and alveolar fricatives. It may be realized as [
/ has a broader distribution and may occur after bilabial and velar stops; dental, alveolar and retroflex affricates; nasals; and dental and alveolar fricatives. It may be realized as [
![]() ] or [ⱱ
] or [ⱱ
![]() ] in free variation (compare the two realizations of the word /ɡ
] in free variation (compare the two realizations of the word /ɡ
![]() / ‘boat’). Similar to /
/ ‘boat’). Similar to /
![]() /, /
/, /
![]() / has a fairly broad range of realization:
/ has a fairly broad range of realization:
-
(i) After bilabial stop initials and retroflex affricates, /
 / is realized close to [
/ is realized close to [
 ]. This is similar to its realization in the closely related Lizu language. Examples include /p
]. This is similar to its realization in the closely related Lizu language. Examples include /p
 / [p
/ [p
 ] ‘potato’, /tʰ
] ‘potato’, /tʰ
 -pʰ
-pʰ
 / [tʰ
/ [tʰ
 -pʰ
-pʰ
 ] ‘to change, to turn into, to transform’, /b
] ‘to change, to turn into, to transform’, /b
 / [
/ [
 ] ‘wild cat’, /ʈɽ
] ‘wild cat’, /ʈɽ
 / ‘sweat’, /ʈɽʰ
/ ‘sweat’, /ʈɽʰ
 / ‘six’, /Nɖɽ
/ ‘six’, /Nɖɽ
 / ‘tile’ (see also Figure 7 above and video clips ‘potato’, ‘to change, to turn into, to transform’, ‘wild cat’). The bilabial trill is particularly evident in the minimal contrastive pair /b
/ ‘tile’ (see also Figure 7 above and video clips ‘potato’, ‘to change, to turn into, to transform’, ‘wild cat’). The bilabial trill is particularly evident in the minimal contrastive pair /b
 / [
/ [
 ] ‘wild cat’ vs. /bó/ [bó] ‘to have, to possess’.
] ‘wild cat’ vs. /bó/ [bó] ‘to have, to possess’. -
(ii) After /m/, /
 / is realized as a voiced syllabic bilabial nasal ([
/ is realized as a voiced syllabic bilabial nasal ([
 ]). For example, /m
]). For example, /m



 / [
/ [



 ] ‘carpenter’, /m
] ‘carpenter’, /m



 / [
/ [



 ] ‘cat’.Footnote
6
] ‘cat’.Footnote
6
Rhotacized vowels
Ersu has two rhotacized vowels: /ə˞/ (as in /
![]() / ‘ashes; year; to be white; to bark’, /x
/ ‘ashes; year; to be white; to bark’, /x
![]() mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’, reportedly from Nuosu (yyx) hmy [(ʑɿ3⁴)
mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’, reportedly from Nuosu (yyx) hmy [(ʑɿ3⁴)
![]() ɿ33] ‘south’) and /a˞/ (as in /v
ɿ33] ‘south’) and /a˞/ (as in /v
![]() / ‘slave’, /x
/ ‘slave’, /x
![]() / ‘bear; needle’). Compared to their oral counterparts (/
/ ‘bear; needle’). Compared to their oral counterparts (/
![]() / and /a/, respectively), /ə˞/ and /a˞/ have a lowered frequency of the third formant. This is illustrated in Figure 18, with the minimal pair /vá/ ‘net’ vs. /v
/ and /a/, respectively), /ə˞/ and /a˞/ have a lowered frequency of the third formant. This is illustrated in Figure 18, with the minimal pair /vá/ ‘net’ vs. /v
![]() / ‘slave’.
/ ‘slave’.

Figure 18 Spectrograms of /vá/ ‘net’ vs. /v
![]() / ‘slave’ (arrows indicate F3).
/ ‘slave’ (arrows indicate F3).
/a˞/ has a broad distribution and co-occurs with bilabial and velar stops, /m/, /ŋ/, /v/, and /x/. (After bilabial initials, /a˞/ may be realized as the sequence [ɹa], e.g. /b
![]() / [bɹá] ‘to be full’, /m
/ [bɹá] ‘to be full’, /m
![]() / [mɹá] ‘to sleep’.) Conversely, /ə˞/ mostly occurs in isolation (as in /
/ [mɹá] ‘to sleep’.) Conversely, /ə˞/ mostly occurs in isolation (as in /
![]() / ‘ashes; year; to be white; to bark’). In addition, /ə˞/ also occurs after bilabial stops and /x/ (as in /x
/ ‘ashes; year; to be white; to bark’). In addition, /ə˞/ also occurs after bilabial stops and /x/ (as in /x
![]() mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’). After bilabial stops /ə˞/ is realized with frication. This is similar to the realization of /
mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’). After bilabial stops /ə˞/ is realized with frication. This is similar to the realization of /
![]() / after bilabial stops. However, in contrast to /
/ after bilabial stops. However, in contrast to /
![]() /, /ə˞/ is pronounced with the tongue curved in a convex shape. Examples include /b
/, /ə˞/ is pronounced with the tongue curved in a convex shape. Examples include /b
![]() / [b
/ [b
![]() ] ‘crown of a head’, /p
] ‘crown of a head’, /p
![]() / [p
/ [p
![]() ] ‘thin rope’, /pʰ
] ‘thin rope’, /pʰ
![]() / [p
/ [p
![]() ] ‘Tibetan’.
] ‘Tibetan’.
Overall, Ersu can be said to have an unbalanced vowel system in that it has a high front vowel /i/ without a corresponding high back vowel /u/; a back close-mid vowel /o/ without a corresponding front close-mid vowel /e/; and an open-mid low vowel /ɛ/ without a corresponding back open-mid vowel /ɔ/. In our analysis, this may be due to an ongoing realignment of the vowel system of Ersu, following the development of the fricative vowels /
![]() / and /
/ and /
![]() / from the high vowels /i/ and /u/ in this language. The development of the fricative vowels from /i/ and /u/ is suggested, on the one hand, by the synchronic distributional evidence, considered in the light of aerodynamic constraints outlined in Ohala (Reference Ohala and MacNeilage1983) and, on the other hand, by comparative evidence from the closely related Lizu and Duoxu languages. We note that Ersu /
/ from the high vowels /i/ and /u/ in this language. The development of the fricative vowels from /i/ and /u/ is suggested, on the one hand, by the synchronic distributional evidence, considered in the light of aerodynamic constraints outlined in Ohala (Reference Ohala and MacNeilage1983) and, on the other hand, by comparative evidence from the closely related Lizu and Duoxu languages. We note that Ersu /
![]() / does not co-occur with (dental and velar) stop initials, but it co-occurs with affricate initials instead. The vowel /
/ does not co-occur with (dental and velar) stop initials, but it co-occurs with affricate initials instead. The vowel /
![]() / does not co-occur with dental stop initials, but it co-occurs with alveolar affricate initials. This complementary distribution can be explained as an outcome of sound change whereby dental and velar stops developed an affricated release when followed by high vowels. This is due to the fact that the high velocity of the airflow created upon release of a stop lasts longer when the stop precedes a close vowel as opposed to an open vowel (Ohala Reference Ohala and MacNeilage1983: 204–205). From a comparative perspective, Ersu /
/ does not co-occur with dental stop initials, but it co-occurs with alveolar affricate initials. This complementary distribution can be explained as an outcome of sound change whereby dental and velar stops developed an affricated release when followed by high vowels. This is due to the fact that the high velocity of the airflow created upon release of a stop lasts longer when the stop precedes a close vowel as opposed to an open vowel (Ohala Reference Ohala and MacNeilage1983: 204–205). From a comparative perspective, Ersu /
![]() / has multiple correspondences in Lizu and Duoxu, including /i/ (as in ‘bee’: Ersu /b
/ has multiple correspondences in Lizu and Duoxu, including /i/ (as in ‘bee’: Ersu /b
![]() /, Lizu /R
bi/, Duoxu /bi
31/; ‘shoe’: Ersu /
/, Lizu /R
bi/, Duoxu /bi
31/; ‘shoe’: Ersu /
![]()
![]() /, Duoxu /ʑi
33/), /e/ (as in ‘hair’: Ersu /
/, Duoxu /ʑi
33/), /e/ (as in ‘hair’: Ersu /
![]()
![]() í/, Lizu /Ftɕe/) as well as non-high vowels preceded by the palatal approximant /j/ (as in ‘mountain’: Ersu /Nbí/ [Nbj
í/, Lizu /Ftɕe/) as well as non-high vowels preceded by the palatal approximant /j/ (as in ‘mountain’: Ersu /Nbí/ [Nbj
![]() ], Lizu /RNbje/) (see Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013b). These correspondence patterns reveal complex developments, which contribute to a realignment of the vowel system of Ersu, whereby the earlier phoneme /e/ is moving into the vacated /i/ space.
], Lizu /RNbje/) (see Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013b). These correspondence patterns reveal complex developments, which contribute to a realignment of the vowel system of Ersu, whereby the earlier phoneme /e/ is moving into the vacated /i/ space.
Nasalized vowels
Ersu marginally has a set of nasalized vowels. Nasalized vowels are generally restricted to recent loanwords from Mandarin Chinese, where the donor language has the nasal codas /n/ or /ŋ/ (as in /k
![]() / ‘steel’, Chinese gāng 钢, SW Mandarin /kaŋ⁴⁴/). (In addition, nasalized vowels are attested in two native Ersu words in our corpus, /
/ ‘steel’, Chinese gāng 钢, SW Mandarin /kaŋ⁴⁴/). (In addition, nasalized vowels are attested in two native Ersu words in our corpus, /
![]()
![]() / ‘goose’ and /
/ ‘goose’ and /
![]()
![]() / ‘duck’.) For that reason, vowel nasalization in Ersu must be regarded as subphonemic, and only needs to be marked in those cases where it is unpredictable (i.e. in recent loanwords). It is interesting to note that in older loanwords, where the original nasal coda is followed by a syllable that begins with a vowel or a nasal or when it is word-final, the original nasal element is in most cases lost without compensation, as in /ṭṣwá/ ‘brick’ from zhuān (SW Mandarin 砖 /tʂuan⁴⁴/), /p
/ ‘duck’.) For that reason, vowel nasalization in Ersu must be regarded as subphonemic, and only needs to be marked in those cases where it is unpredictable (i.e. in recent loanwords). It is interesting to note that in older loanwords, where the original nasal coda is followed by a syllable that begins with a vowel or a nasal or when it is word-final, the original nasal element is in most cases lost without compensation, as in /ṭṣwá/ ‘brick’ from zhuān (SW Mandarin 砖 /tʂuan⁴⁴/), /p
![]() tì/ ‘silver’ from báidìng 白锭 ‘white ingot’ (SW Mandarin /pei
21
tin
213/). This is similar to the situation in the closely related Lizu and Duoxu languages (Chirkova & Chen Reference Chirkova and Chen2013, Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013b).
tì/ ‘silver’ from báidìng 白锭 ‘white ingot’ (SW Mandarin /pei
21
tin
213/). This is similar to the situation in the closely related Lizu and Duoxu languages (Chirkova & Chen Reference Chirkova and Chen2013, Chirkova & Handel Reference Chirkova and Handel2013b).
Vowel harmony
In disyllabic domains, we observe regressive vowel assimilation. The vowel qualities can be divided into two sets: (i) the low vowels /a a˞/, and (ii) the remaining, non-low vowels, that is, /i ɛ o
![]()
![]() /. Vowel harmony appears to only apply to directional prefixes and the number ‘one’ (that is, it is restricted to high frequency morphemes). Consider expressions consisting of the numeral ‘one’ (/t
/. Vowel harmony appears to only apply to directional prefixes and the number ‘one’ (that is, it is restricted to high frequency morphemes). Consider expressions consisting of the numeral ‘one’ (/t
![]() / in isolation) followed by various nouns: /tá
/ in isolation) followed by various nouns: /tá
![]() á/ ‘one hundred’, /tá ká/ ‘one strip’, /Nṭṣʰ
á/ ‘one hundred’, /tá ká/ ‘one strip’, /Nṭṣʰ
![]() tà p
tà p
![]() / ‘one grain of rice’, /t
/ ‘one grain of rice’, /t
![]() pʰó/ ‘one set (of clothing)’, /t
pʰó/ ‘one set (of clothing)’, /t
![]() p
p
![]() / ‘one tree; ten cents’, /t
/ ‘one tree; ten cents’, /t
![]() ḍẓ
ḍẓ
![]() / ‘one sentence’. Like many languages that display vowel harmony in polysyllabic lexical items Ersu has two forms for affixes, such as verbal directional affixes, e.g. /kʰá-lá/ ‘to come in (in the direction to the speaker)’ vs. /kʰ
/ ‘one sentence’. Like many languages that display vowel harmony in polysyllabic lexical items Ersu has two forms for affixes, such as verbal directional affixes, e.g. /kʰá-lá/ ‘to come in (in the direction to the speaker)’ vs. /kʰ
![]() -jí/ ‘to enter (in the direction away from the speaker)’.
-jí/ ‘to enter (in the direction away from the speaker)’.
Syllable structure
The canonical Ersu syllable minimally consists of an obligatory nucleus and a tone. It may also contain up to three optional elements in the following linear structure: (C1)(C2)(C3)V, where C1 can be nasal (/N/) or a schwa-like segment (/ə/); C2 can be any consonant; C3 can be either /w/ or /j/; and V stands for vowel, and parentheses indicate optional constituents. Zero-initial words can be preceded by a non-phonemic glottal stop (e.g. /
![]()
![]() / [ʔ
/ [ʔ
![]()
![]() ] ‘goose’, /ódʑá/ [ʔódʑá] ‘pear’).
] ‘goose’, /ódʑá/ [ʔódʑá] ‘pear’).
-
(1)

-
(2)

-
(3)

-
(4)

In addition, (recent) loanwords may have the following structures:
-
(5)

-
(6)

Loanwords from Tibetan may also have /h/ in the C1 slot, as in /hkwàɽá/ ‘to turn, to circle’.
Similar to its linguistic neighbours, Ersu is phonologically monosyllabic with a strong tendency towards disyllabicity in its lexicon. Trisyllabic and quadrisyllabic words are mostly composite, e.g. /l
![]() má
ká/ ‘thumb’ (< /l
má
ká/ ‘thumb’ (< /l
![]() / ‘hand’), /
/ ‘hand’), /
![]()
![]() Nb
Nb
![]() əp
əp
![]() ək
ək
![]() / ‘nostril’ (< /
/ ‘nostril’ (< /
![]()
![]() Nb
Nb
![]() / ‘nose’, /əp
/ ‘nose’, /əp
![]() ək
ək
![]() / ‘hole, cavity’), although a handful of trisyllabic monomorphemic words (both native and loanwords) do exist (e.g. /x
/ ‘hole, cavity’), although a handful of trisyllabic monomorphemic words (both native and loanwords) do exist (e.g. /x
![]() mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’).
mìNtɕʰí/ ‘south’).
In disyllabic composite forms, where the second syllable has zero initial, the two adjacent vowels merge into one vowel or a diphthong, a process that typically results in a tone change. This change characteristically occurs when the perfective marker /á/ (which has an etymological high-register tone) is added to a verb stem. For example, compare the realization of the verb /d
![]() -pʰwá/ [dà-pʰʷá] ‘to smash’ in isolation and when followed by the perfective marker /á/, i.e. /d
-pʰwá/ [dà-pʰʷá] ‘to smash’ in isolation and when followed by the perfective marker /á/, i.e. /d
![]() -pʰwà-á/ ‘have smashed’.
-pʰwà-á/ ‘have smashed’.
The diminutive morpheme /ji/ often fuses with the preceding vowel resulting in a diphthong that combines the original vowel with the offglide [j]. Examples include ‘armpit’, which is /jíbá-jì/ in careful pronunciation and /jíbá
j/ in a more rapid speech tempo (note a clear falling tone contour on the second syllable of the fused form, resulting from the low tone of /jì/ being conjoined with the high tone of /bá/); and ‘lamb’, which is /lá
b
![]() -jì/ in careful pronunciation and /lá
b
-jì/ in careful pronunciation and /lá
b
![]() j/ in a more rapid speech tempo.
j/ in a more rapid speech tempo.
Prosodic organization
Ersu is a register tone language with two registers: Low and High (hereafter L and H), thus bearing resemblance to the tonal system of Tibetan (see e.g. J. Sun Reference Sun1997). In polysyllabic domains, there is tone reduction in non-initial syllables, resulting in highly restricted tone patterns in polysyllabic words.
Monosyllabic words and compounds
The register contrast in Ersu can be exemplified with the following minimal pairs: /b
![]() / ‘to plough’ vs. /b
/ ‘to plough’ vs. /b
![]() / ‘wild cat’, /là/ ‘musk deer’ vs. /lá/ ‘fertilizer, manure’, /Nɖɽò/ ‘dirt, filth’ vs. /Nɖɽó/ ‘leather, skin’, /ʈɽʰò/ ‘dog’ vs. /ʈɽʰó/ ‘sound, melody’. While the register contrast is fundamental in this language, surface pitch contours are subject to variation in both registers (as illustrated in Figure 19).
/ ‘wild cat’, /là/ ‘musk deer’ vs. /lá/ ‘fertilizer, manure’, /Nɖɽò/ ‘dirt, filth’ vs. /Nɖɽó/ ‘leather, skin’, /ʈɽʰò/ ‘dog’ vs. /ʈɽʰó/ ‘sound, melody’. While the register contrast is fundamental in this language, surface pitch contours are subject to variation in both registers (as illustrated in Figure 19).

Figure 19 Pitch contours of the low and high register tones by a male speaker illustrated with the minimal pairs /b
![]() / ‘to plough’ vs. /b
/ ‘to plough’ vs. /b
![]() / ‘wild cat’, and /ʈɽʰò/ ‘dog’ vs. /ʈɽʰó/ ‘sound, melody’. The low tone contour is represented by a solid line, the high tone contour is represented by a dotted line.
/ ‘wild cat’, and /ʈɽʰò/ ‘dog’ vs. /ʈɽʰó/ ‘sound, melody’. The low tone contour is represented by a solid line, the high tone contour is represented by a dotted line.
We note that monosyllabic words that are rarely used in isolation (such as verbs and measure words) and loanwords are often realized in the context of elicitation in the high register, which we, for that reason, regard as the unmarked register in this language.
Polysyllabic words and compounds
In disyllabic domains (both compounds and composite lexical words), the domain-initial syllable retains its tone whereas the non-initial syllable does not. Disyllabic words and compounds that begin with a morpheme or a word in the high register are invariably realized with H tone on both syllables. Conversely, in the case of disyllabic words and compounds that begin with a morpheme or a word in the low register, two tonal patterns are possible: (i) L tone on both syllables, and (ii) L tone on the domain-initial syllable and H on the second syllable. The two patterns are in free variation, as is the case in the word /
![]() ɽà/ ‘cloth’: [ⱱ
ɽà/ ‘cloth’: [ⱱ
![]() 33ɽra⁴⁴] or [ⱱ
33ɽra⁴⁴] or [ⱱ
![]() 33ɽra
31]. Examples of the tonal patterns on disyllabic domains include (i) the compounds /ŋw
33ɽra
31]. Examples of the tonal patterns on disyllabic domains include (i) the compounds /ŋw
![]() -dʑí/ ‘cow shed’ and /Nbò-dʑí/ ‘horse pen’, which begin each with a L register word (/ŋw
-dʑí/ ‘cow shed’ and /Nbò-dʑí/ ‘horse pen’, which begin each with a L register word (/ŋw
![]() / ‘cow’ and /Nbò/ ‘horse’, respectively; the word ‘shed, pen’ has an etymological low-register tone, i.e. /dʑì/); and (ii) the compounds /v
/ ‘cow’ and /Nbò/ ‘horse’, respectively; the word ‘shed, pen’ has an etymological low-register tone, i.e. /dʑì/); and (ii) the compounds /v
![]() -dʑí/ ‘pig shed’ and /jó-dʑí/ ‘sheep pen’, which begin each with an H register word (/v
-dʑí/ ‘pig shed’ and /jó-dʑí/ ‘sheep pen’, which begin each with an H register word (/v
![]() / ‘pig’ and /jó/ ‘sheep’, respectively).
/ ‘pig’ and /jó/ ‘sheep’, respectively).
The same two patterns are attested in composite lexical words. Examples of minimal pairs for the two tonal patterns include: /Ndʑó-Ndʑó/ ‘to make friends’, /Ndʑò-Ndʑó/ ‘ear of millet’ (see Figure 20); /njó-njó/ ‘milk; breast’, /njò-njó/ ‘to be soft’; /tɕó-tɕó/ ‘to wrap, to bind’, /tɕò-tɕó/ ‘maternal uncle’ (Chinese jiùjiu 舅舅, SW Mandarin /tɕiəu
213
tɕiəu⁴⁴/); /kʰ
![]() -jí/ ‘to enter’, /kʰ
-jí/ ‘to enter’, /kʰ
![]() -jí/ ‘to go live (inside)’.
-jí/ ‘to go live (inside)’.

Figure 20 Illustration of the H vs. L contrast in disyllabic items /N dʑó-N dʑó/ ‘to make friends’ and /N dʑò-N dʑó/ ‘ear of millet’ by a male speaker.
In addition, Ersu disyllabic words marginally have a third tonal pattern, in which the high f0 peak is realized before the end of the first syllable, where the pitch starts to fall already and continues to fall in the second syllable. Perceptually, the second syllable of these words sounds much less prominent than the first syllable, giving rise to the impression that it is unstressed. This tonal pattern is essentially observed in Chinese loanwords, in fusions as well as in a handful of native Ersu words. Examples include /f
![]() tʰiào/ ‘rice noodle’, /p
tʰiào/ ‘rice noodle’, /p
![]() tʰa
tʰa
![]() / ‘crystal sugar’, /
/ ‘crystal sugar’, /
![]()
![]() ʰálà/ ‘tomb’, /
ʰálà/ ‘tomb’, /
![]()
![]() t
t
![]() / ‘who’.
/ ‘who’.
The same three tonal patterns are observed in trisyllabic compounds. These include:
-
(i) H tone on all syllables within the domain, for those domains that begin with an H tone word (HHH), as in:
-
/

 / ‘fish’ + /m
/ ‘fish’ + /m
 Nṭṣʰ
Nṭṣʰ
 / ‘tail’ > /z
/ ‘tail’ > /z
 m
m
 Nṭṣʰ
Nṭṣʰ
 / ‘fish tail’
/ ‘fish tail’ -
/jó/ ‘sheep’ + /Nɖɽ
 pí/ ‘skin, leather’ > /jó Nɖɽ
pí/ ‘skin, leather’ > /jó Nɖɽ
 pí/ ‘sheep skin’
pí/ ‘sheep skin’
-
-
(ii) L tone on all syllables of the domain, for those compounds that begin with an L tone word (optionally, with the H tone on the last syllable of the domain) (LLL/H), as in:
-
/Nbò/ ‘horse’ + /m
 Nṭṣʰ
Nṭṣʰ
 / ‘tail’ > /Nbò m
/ ‘tail’ > /Nbò m
 Nṭṣʰ
Nṭṣʰ
 / ‘horse tail’
/ ‘horse tail’ -
/ŋw
 / ‘cow’ + /Nɖɽ
/ ‘cow’ + /Nɖɽ
 pí/ ‘skin, leather’ > /ŋw
pí/ ‘skin, leather’ > /ŋw
 Nɖɽ
Nɖɽ
 pí/ ‘cowhide’
pí/ ‘cowhide’
-
-
(iii) The third, less frequent, tonal pattern is that in which the domain of tone change appears to be restricted to the first two syllables, whereas the remaining syllable(s) is realized with a low tone (HHL), as in:
-
/ṣ
 / ‘iron’ + /N
/ ‘iron’ + /N


 -N
-N


 / ‘button’ > /ṣ
/ ‘button’ > /ṣ
 N
N


 -N
-N


 / ‘iron button’
/ ‘iron button’ -
/əm
 / ‘soldier’ + /N
/ ‘soldier’ + /N

 òmó/ ‘official’ > /əm
òmó/ ‘official’ > /əm
 N
N

 ómò/ ‘general’
ómò/ ‘general’ -
/
 -
-

 / ‘the Ersu people’ + /xó/ ‘language’ > /
/ ‘the Ersu people’ + /xó/ ‘language’ > /
 -
-

 xò/ ‘the Ersu language’
xò/ ‘the Ersu language’
-
Ersu function words and discourse particles (e.g. the genitive particle /i/, the focus particle /
![]() ɛ/ in the recorded text) are never pronounced in isolation. Their surface tone realization depends on the tone of the preceding (host) lexical word (as in tonal contours in compounds).
ɛ/ in the recorded text) are never pronounced in isolation. Their surface tone realization depends on the tone of the preceding (host) lexical word (as in tonal contours in compounds).
Transcription of the recorded text: ‘The North Wind and the Sun’
The original audio and video recordings (made with a Digidesign 003 Rack soundcard, Pro Tools LE software for iMac, an AKG C520L headset microphone, and video cameras Sony HDR-XR 520E and Sony HDR-PJ650) have been made available to the JIPA along with this analysis.
Semi-narrow phonetic transcription
Interlinear morphemic glossing
Abbreviations used in the gloss below follow the Leipzig Glossing Rules (LGR, http://www.eva.mpg.de/lingua/resources/glossing-rules.php). Non-standard abbreviations (those not included in the LGR) are: anm = animate, cmpr = comparative.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our Ersu language consultants, Mrs. Wang Ying 王英 (Jiman Keli 吉满柯莉) and Mr. Chen Guofu 陈国富 for their patience and assistance. We are grateful to the Laboratoire de Phonétique et Phonologie (LPP) of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) for making their phonetic laboratory available to us through the operation ‘Phonetic and Phonological Complexity’ of the project LabEx-EFL (Laboratoire d’excellence ‘Fondements Empiriques de la Linguistique – Empirical Foundations of Linguistics’). We are also grateful to Jacqueline Vaissière, Zev Handel, and the two anonymous reviewers of this Illustration for helpful comments and suggestions, and to Matthew Faytak for a discussion on fricative vowels. Thanks are also due to Jos Pacilly (Leiden University) for helping us with PRAAT scripts, to Franz Huber (ETH Zürich) for creating the map in this paper, and to Wang Ke 王轲 (Jiman Shalima 吉满莎丽玛) and Gu Tao 古涛 for help with the recording of palatograms. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche of France (grant number ANR-07-JCJC-0063) and LabEx-EFL (axe PPC2) to Katia Chirkova, Dehe Wang, and Tanja Kocjančič Antolík; of the Endangered Languages Documentation Programme (ELDP, grant number MPD0257) to Katia Chirkova, Dehe Wang, and Yiya Chen; and of the European Research Council (ERC-Starting Independent Researcher Grant, 206198) to Yiya Chen.


 -
-