Article contents
WHITTAKER PERIODS, MOTIVIC PERIODS, AND SPECIAL VALUES OF TENSOR PRODUCT  $L$-FUNCTIONS
$L$-FUNCTIONS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 March 2015
Abstract
Let 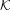 ${\mathcal{K}}$ be an imaginary quadratic field. Let
${\mathcal{K}}$ be an imaginary quadratic field. Let 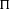 ${\rm\Pi}$ and
${\rm\Pi}$ and 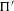 ${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$ be irreducible generic cohomological automorphic representation of
${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$ be irreducible generic cohomological automorphic representation of 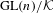 $\text{GL}(n)/{\mathcal{K}}$ and
$\text{GL}(n)/{\mathcal{K}}$ and 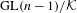 $\text{GL}(n-1)/{\mathcal{K}}$, respectively. Each of them can be given two natural rational structures over number fields. One is defined by the rational structure on topological cohomology, and the other is given in terms of the Whittaker model. The ratio between these rational structures is called a Whittaker period. An argument presented by Mahnkopf and Raghuram shows that, at least if
$\text{GL}(n-1)/{\mathcal{K}}$, respectively. Each of them can be given two natural rational structures over number fields. One is defined by the rational structure on topological cohomology, and the other is given in terms of the Whittaker model. The ratio between these rational structures is called a Whittaker period. An argument presented by Mahnkopf and Raghuram shows that, at least if 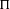 ${\rm\Pi}$ is cuspidal and the weights of
${\rm\Pi}$ is cuspidal and the weights of 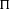 ${\rm\Pi}$ and
${\rm\Pi}$ and 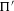 ${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$ are in a standard relative position, the critical values of the Rankin–Selberg product
${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$ are in a standard relative position, the critical values of the Rankin–Selberg product 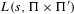 $L(s,{\rm\Pi}\times {\rm\Pi}^{\prime })$ are essentially algebraic multiples of the product of the Whittaker periods of
$L(s,{\rm\Pi}\times {\rm\Pi}^{\prime })$ are essentially algebraic multiples of the product of the Whittaker periods of 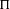 ${\rm\Pi}$ and
${\rm\Pi}$ and 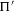 ${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$. We show that, under certain regularity and polarization hypotheses, the Whittaker period of a cuspidal
${\rm\Pi}^{\prime }$. We show that, under certain regularity and polarization hypotheses, the Whittaker period of a cuspidal 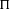 ${\rm\Pi}$ can be given a motivic interpretation, and can also be related to a critical value of the adjoint
${\rm\Pi}$ can be given a motivic interpretation, and can also be related to a critical value of the adjoint  $L$-function of related automorphic representations of unitary groups. The resulting expressions for critical values of the Rankin–Selberg and adjoint
$L$-function of related automorphic representations of unitary groups. The resulting expressions for critical values of the Rankin–Selberg and adjoint  $L$-functions are compatible with Deligne’s conjecture.
$L$-functions are compatible with Deligne’s conjecture.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 15 , Issue 4 , October 2016 , pp. 711 - 769
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2015
References
- 10
- Cited by


