No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF HYPOELLIPTIC RANDOM WALKS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 May 2014
Abstract
We study the spectral theory of a reversible Markov chain This random walk depends on a parameter 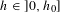 $h\in ]0,h_{0}]$ which is roughly the size of each step of the walk. We prove uniform bounds with respect to
$h\in ]0,h_{0}]$ which is roughly the size of each step of the walk. We prove uniform bounds with respect to 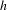 $h$ on the rate of convergence to equilibrium, and the convergence when
$h$ on the rate of convergence to equilibrium, and the convergence when 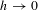 $h\rightarrow 0$ to the associated hypoelliptic diffusion.
$h\rightarrow 0$ to the associated hypoelliptic diffusion.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 14 , Issue 3 , July 2015 , pp. 451 - 491
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2014
References
Bismut, J.-M., Martingales, the Malliavin calculus and hypoellipticity under general Hörmander’s conditions, Z. Wahrsch. Verw. Geb. 56(4) (1981), 469–505.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Bally, V. and Talay, D., The Euler scheme for stochastic differential equations: error analysis with Malliavin calculus, Math. Comput. Simul. 38(1–3) (1995), 35–41.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Bally, V. and Talay, D., The law of the Euler scheme for stochastic differential equations. I. Convergence rate of the distribution function, Probab. Theory Related Fields 104(1) (1996), 43–60.Google Scholar
Chow, W.-L., Über Systeme von linearen partiellen Differentialgleichungen erster Ordnung, Math. Ann. 117 (1939), 98–105.Google Scholar
Diaconis, P., Lebeau, G. and Michel, L., Geometric analysis for the Metropolis algorithm on Lipschitz domains, Invent. Math. 185(2) (2011), 239–281.Google Scholar
Diaconis, P., Lebeau, G. and Michel, L., Gibbs/Metropolis algorithms on a convex polytope, Math. Z. 272(1–2) (2012), 109–129.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Diaconis, P. and Saloff-Coste, L., What do we know about the metropolis algorithm, J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 57(1) (1998), 20–36.Google Scholar
Folland, G. B., Subelliptic estimates and function spaces on nilpotent Lie groups, Ark. Mat 13 (1975), 161–207.Google Scholar
Goodman, R., Lifting vector fields to nilpotent Lie groups, J. Math. Pures Appl. (9) 57(1) (1978), 77–85.Google Scholar
Hörmander, L., The Analysis of Linear Partial Differential Operators. III: Pseudodifferential Operators, Grundl. Math. Wiss., Band 274, (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985).Google Scholar
Jerison, D., The Poincaré inequality for vector fields satisfying Hörmander’s condition, Duke Math. J. 53(2) (1986), 503–523.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Karatzas, I. and Shreve, S. E., Brownian Motion and Stochastic Calculus, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1988).Google Scholar
Nagel, A., Stein, E. and Wainger, S., Balls and metrics defined by vector fields. I. Basic properties, Acta Math. 155(1–2) (1985), 103–147.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Rothschild, L. P. and Stein, E. M., Hypoelliptic differential operators and nilpotent groups, Acta Math. 137(3–4) (1976), 247–320.CrossRefGoogle Scholar


