Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 April 2009
It is well known that compact topological spaces are those space K for which given any point x0 in any topological space X, and a neighborhood H of the fibre -1 {x0}KXX, then there exists a neighborhood U of x0 such that -1UH. If now 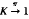 is an object in an arbitrary topos, in the internal logic of the topos this property means that, for any A inand B in K, we have (-1AB)=AB. We introduce this formula as a definition of compactness for objects in an arbitrary topos. Then we prove that in the gross topoi of algebraic, analytic, and differential geometry, this property characterizes exactly the complete varieties, the compact (analytic) spaces, and the compact manifolds, respectively.
is an object in an arbitrary topos, in the internal logic of the topos this property means that, for any A inand B in K, we have (-1AB)=AB. We introduce this formula as a definition of compactness for objects in an arbitrary topos. Then we prove that in the gross topoi of algebraic, analytic, and differential geometry, this property characterizes exactly the complete varieties, the compact (analytic) spaces, and the compact manifolds, respectively.