No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
COMPONENTS AND MINIMAL NORMAL SUBGROUPS OF FINITE AND PSEUDOFINITE GROUPS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 March 2019
Abstract
It is proved that there is a formula 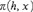 $\pi \left( {h,x} \right)$ in the first-order language of group theory such that each component and each non-abelian minimal normal subgroup of a finite group G is definable by
$\pi \left( {h,x} \right)$ in the first-order language of group theory such that each component and each non-abelian minimal normal subgroup of a finite group G is definable by 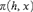 $\pi \left( {h,x} \right)$ for a suitable element h of G; in other words, each such subgroup has the form
$\pi \left( {h,x} \right)$ for a suitable element h of G; in other words, each such subgroup has the form 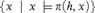 $\left\{ {x|x\pi \left( {h,x} \right)} \right\}$ for some h. A number of consequences for infinite models of the theory of finite groups are described.
$\left\{ {x|x\pi \left( {h,x} \right)} \right\}$ for some h. A number of consequences for infinite models of the theory of finite groups are described.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Association for Symbolic Logic 2019
References
REFERENCES
Aschbacher, M. and Guralnick, R., Some applications of the first cohomology group. Journal of Algebra, vol. 90 (1984), pp. 446–460.10.1016/0021-8693(84)90183-2CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Frink, O., Pseudo-complements in semi-lattices. Duke Mathematical Journal, vol. 29 (1962), pp. 505–514.10.1215/S0012-7094-62-02951-4CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Felgner, U., Pseudo-endliche Gruppen, Proceedings of the 8th Easter Conference on Model Theory (Dahn, B. and Wolter, H., editors), Humboldt–Universität, Berlin, 1990, pp. 82–96.Google Scholar
Gorenstein, D., Finite Simple Groups, An Introduction to their Classification, Plenum Press, New York, 1982.10.1007/978-1-4684-8497-7CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Isaacs, I. M., Finite Group Theory, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 2008.Google Scholar
Liebeck, M. W., O’Brien, E. A., Shalev, A., and Tiep, P. H., The Ore conjecture. Journal of the European Mathematical Society, vol. 12 (2010), pp. 939–1008.10.4171/JEMS/220CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Liebeck, M. W., O’Brien, E. A., Shalev, A., and Tiep, P. H., Commutators in finite quasisimple groups. Bulletin of the London Mathematical Society, vol. 43 (2011), pp. 1079–1092.10.1112/blms/bdr043CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Macpherson, D. and Tent, K., Stable pseudofinite groups. Journal of Algebra, vol. 312 (2007), pp. 550–561.10.1016/j.jalgebra.2005.07.012CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Ould Houcine, A. and Point, F., Alternatives for pseudofinite groups. Journal of Group Theory, vol. 16 (2013), pp. 461–495.10.1515/jgt-2013-0006CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Wilson, J. S., On simple pseudofinite groups. Journal of the London Mathematical Society (2), vol. 51 (1995), pp. 471–490.10.1112/jlms/51.3.471CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Wilson, J. S., First-order characterization of the radical of a finite group, this Journal, vol. 74 (2009), pp. 1429–1435.Google Scholar
Wilson, J. S., The first-order theory of branch groups. Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society, vol. 102 (2017), pp. 150–158.Google Scholar


