Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zubkov, M. V.
Kalimullin, I. Sh.
Melnikov, A. G.
and
Frolov, A. N.
2019.
Punctual Copies of Algebraic Structures.
Siberian Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 6,
p.
993.
Downey, Rod
Melnikov, Alexander
and
Ng, Keng Meng
2019.
Categorical linearly ordered structures.
Annals of Pure and Applied Logic,
Vol. 170,
Issue. 10,
p.
1243.
Grädel, Erich
2020.
Automatic Structures.
p.
21.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
Kalimullin, Iskander
Melnikov, Alexander
and
Ng, Keng Meng
2020.
Online presentations of finitely generated structures.
Theoretical Computer Science,
Vol. 844,
Issue. ,
p.
195.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
2020.
Computer Science – Theory and Applications.
Vol. 12159,
Issue. ,
p.
142.
Bazhenov, N.
Greenberg, N.
Melnikov, A.
Miller, R.
and
Ng, K. M.
2021.
A Note on Computable Distinguishing Colorings.
Lobachevskii Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
693.
Greenberg, Noam
Harrison-Trainor, Matthew
Melnikov, Alexander
and
Turetsky, Dan
2021.
Non-density in punctual computability.
Annals of Pure and Applied Logic,
Vol. 172,
Issue. 9,
p.
102985.
Kalimullin, Iskander
Melnikov, Alexander
and
Montalban, Antonio
2021.
Punctual definability on structures.
Annals of Pure and Applied Logic,
Vol. 172,
Issue. 8,
p.
102987.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
Mustafa, Manat
and
Ospichev, Sergei
2022.
Rogers semilattices of punctual numberings.
Mathematical Structures in Computer Science,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 2,
p.
164.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
Mustafa, Manat
and
Nurakunov, Anvar
2022.
Theory and Applications of Models of Computation.
Vol. 13571,
Issue. ,
p.
79.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
and
Mustafa, Manat
2022.
Computable embeddability for algebraic structures.
Asian-European Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 07,
Kalimullin, I. Sh.
2022.
Punctual Structures and Primitive Recursive Reducibility.
Lobachevskii Journal of Mathematics,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 3,
p.
582.
Alaev, Pavel
2022.
Computer Science – Theory and Applications.
Vol. 13296,
Issue. ,
p.
35.
Dorzhieva, Marina
Melnikov, Alexander
Bazhenov, Nikolay
Kihara, Takayuki
and
Selivanova, Svetlana
2023.
Punctually presented structures I: Closure theorems.
Computability,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 4,
p.
323.
Lupini, Martino
Melnikov, Alexander
and
Nies, Andre
2023.
Computable topological abelian groups.
Journal of Algebra,
Vol. 615,
Issue. ,
p.
278.
Alaev, P. E.
2023.
The Complexity of Inversion in Groups.
Algebra and Logic,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 2,
p.
103.
Askes, Matthew
and
Downey, Rod
2023.
Online, computable and punctual structure theory.
Logic Journal of the IGPL,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 6,
p.
1251.
Hammatt, Ellen
2024.
Twenty Years of Theoretical and Practical Synergies.
Vol. 14773,
Issue. ,
p.
179.
Bazhenov, Nikolay
Mustafa, Manat
and
Nurakunov, Anvar
2024.
On Concept Lattices for Numberings.
Tsinghua Science and Technology,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 6,
p.
1642.
Kalmurzayev, Birzhan S
Bazhenov, Nikolay A
and
Iskakov, Alibek M
2025.
Computably enumerable equivalence relations via primitive recursive reductions.
Journal of Logic and Computation,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 2,
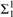 ${\rm{\Sigma }}_1^1 $-complete. We also use similar methods to show that there is no reasonable characterisation of the structures with a polynomial-time presentation in the sense of Nerode and Remmel.
${\rm{\Sigma }}_1^1 $-complete. We also use similar methods to show that there is no reasonable characterisation of the structures with a polynomial-time presentation in the sense of Nerode and Remmel.

