Article contents
Particle trajectories in Weibel filaments: influence of external field obliquity and chaos
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 May 2020
Abstract
When two collisionless plasma shells collide, they interpenetrate and the overlapping region may turn Weibel unstable for some values of the collision parameters. This instability grows magnetic filaments which, at saturation, have to block the incoming flow if a Weibel shock is to form. In a recent paper (Bret, J. Plasma Phys., vol. 82, 2016b, 905820403), it was found by implementing a toy model for the incoming particle trajectories in the filaments, that a strong enough external magnetic field 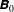 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D63D}_{0}$ can prevent the filaments blocking the flow if it is aligned with them. Denoting by
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D63D}_{0}$ can prevent the filaments blocking the flow if it is aligned with them. Denoting by  $B_{f}$ the peak value of the field in the magnetic filaments, all test particles stream through them if
$B_{f}$ the peak value of the field in the magnetic filaments, all test particles stream through them if 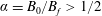 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}=B_{0}/B_{f}>1/2$. Here, this result is extended to the case of an oblique external field
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}=B_{0}/B_{f}>1/2$. Here, this result is extended to the case of an oblique external field 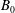 $B_{0}$ making an angle
$B_{0}$ making an angle 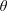 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ with the flow. The result, numerically found, is simply
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ with the flow. The result, numerically found, is simply 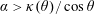 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}>\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})/\cos \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}>\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})/\cos \unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$, where 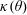 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})$ is of order unity. Noteworthily, test particles exhibit chaotic trajectories.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}(\unicode[STIX]{x1D703})$ is of order unity. Noteworthily, test particles exhibit chaotic trajectories.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2020
References
- 1
- Cited by


