Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 October 2015
The Sun is a giant particle accelerator. During solar flares, magnetic field energy stored in the corona is suddenly released and transferred to local heating of the coronal plasma, mass motions (e.g. jets) and the generation of energetic particles, i.e. electrons, protons and heavy ions. Basically, a flare occurs as a local enhancement of the emission of electromagnetic radiation from the radio up to the 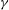 ${\it\gamma}$ -ray range on the Sun. That indicates the production of energetic electrons during flares. NASA’s RHESSI mission has the aim to investigate electron acceleration processes by studying the Sun’s X-ray and
${\it\gamma}$ -ray range on the Sun. That indicates the production of energetic electrons during flares. NASA’s RHESSI mission has the aim to investigate electron acceleration processes by studying the Sun’s X-ray and 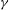 ${\it\gamma}$ -ray emission with high spatial, temporal and spectral resolution, i.e. by means of imaging spectroscopy. A substantial part of the energy released during a flare is carried by these energetic electrons. Apart from them, solar energetic particles, i.e. protons and heavy ions, and coronal mass ejections play an important role in the energy budget of a flare. Here, we focus on electron acceleration. The way in which
${\it\gamma}$ -ray emission with high spatial, temporal and spectral resolution, i.e. by means of imaging spectroscopy. A substantial part of the energy released during a flare is carried by these energetic electrons. Apart from them, solar energetic particles, i.e. protons and heavy ions, and coronal mass ejections play an important role in the energy budget of a flare. Here, we focus on electron acceleration. The way in which  $10^{36}$ electrons are accelerated up to energies beyond 30 keV is one of the open questions in solar physics. A flare is considered as the manifestation of magnetic reconnection in the solar corona. Which mechanisms lead to the production of energetic electrons in the magnetic reconnection region is discussed in this paper. Two of them are described in more detail.
$10^{36}$ electrons are accelerated up to energies beyond 30 keV is one of the open questions in solar physics. A flare is considered as the manifestation of magnetic reconnection in the solar corona. Which mechanisms lead to the production of energetic electrons in the magnetic reconnection region is discussed in this paper. Two of them are described in more detail.