No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 July 2015
The generation and propagation of a small-amplitude Langmuir pulse excited by a planar grid electrode in a spatially uniform collisionless plasma with a constant flow velocity is studied by solving the linearized Vlasov–Poisson equations. The electrode is transparent to the flow of particles, like a screen or a wire mesh. The particles are assumed to have a Kappa velocity distribution, a reasonable approximation for electron distribution functions in the solar wind. Exact, closed-form solutions are obtained for 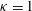 ${\it\kappa}=1$ , the Lorentzian distribution, and for
${\it\kappa}=1$ , the Lorentzian distribution, and for 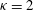 ${\it\kappa}=2$ . The explicit form of the solution in the case
${\it\kappa}=2$ . The explicit form of the solution in the case 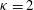 ${\it\kappa}=2$ has not, to our knowledge, appeared in the literature before. The properties of the solutions are investigated and a practical technique for measuring the bulk flow velocity in plasma experiments is proposed that may be useful for high-accuracy, high-time-resolution measurements of the bulk flow velocity in the solar wind.
${\it\kappa}=2$ has not, to our knowledge, appeared in the literature before. The properties of the solutions are investigated and a practical technique for measuring the bulk flow velocity in plasma experiments is proposed that may be useful for high-accuracy, high-time-resolution measurements of the bulk flow velocity in the solar wind.