Introduction
Fossil Dasycladales are commonly preserved as external calcified molds of their soft parts. The way in which the calcium carbonate envelops the alga reflects the thallus anatomy. For such specimens, the calcareous skeleton constitutes the only information concerning the anatomical elements of the alga in fossil material. The moldic nature of dasycladalean calcification emphasizes the importance of correctly interpreting the origins of voids within the calcareous skeleton (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). A key question is whether cavities reflect original soft parts or result from a deficiency in calcification? This is especially important when such cavities involve reproductive organs obliterating the relationship between the reproductive organs and the laterals. This can significantly affect systematic determinations. The new taxa described here particularly illustrate the taxonomic problems related to the interpretation of skeletal cavities in calcified dasycladaleans.
Geological setting
The Perșani Mountains form the southwestern sector of the Eastern Carpathians, at their junction with the Southern Carpathians (Fig. 1.1). From a structural point of view, they belong to the Median Dacides (Săndulescu, Reference Săndulescu1984) and share similar structural characteristics with the Rarău and Hăghimaș massifs, two other units belonging to the Median Dacides of the Eastern Carpathians. Two main structural units are recognized in the Perșani Mountains: the Bucovinian and Transylvanian nappes. Upper Aptian Urgonian limestones and conglomerates cover the Bucovinian and Transylvanian units and form the first part of the post-nappe cover (Patrulius et al., Reference Patrulius, Popa-Dimian and Dimitriu-Popescu1966).
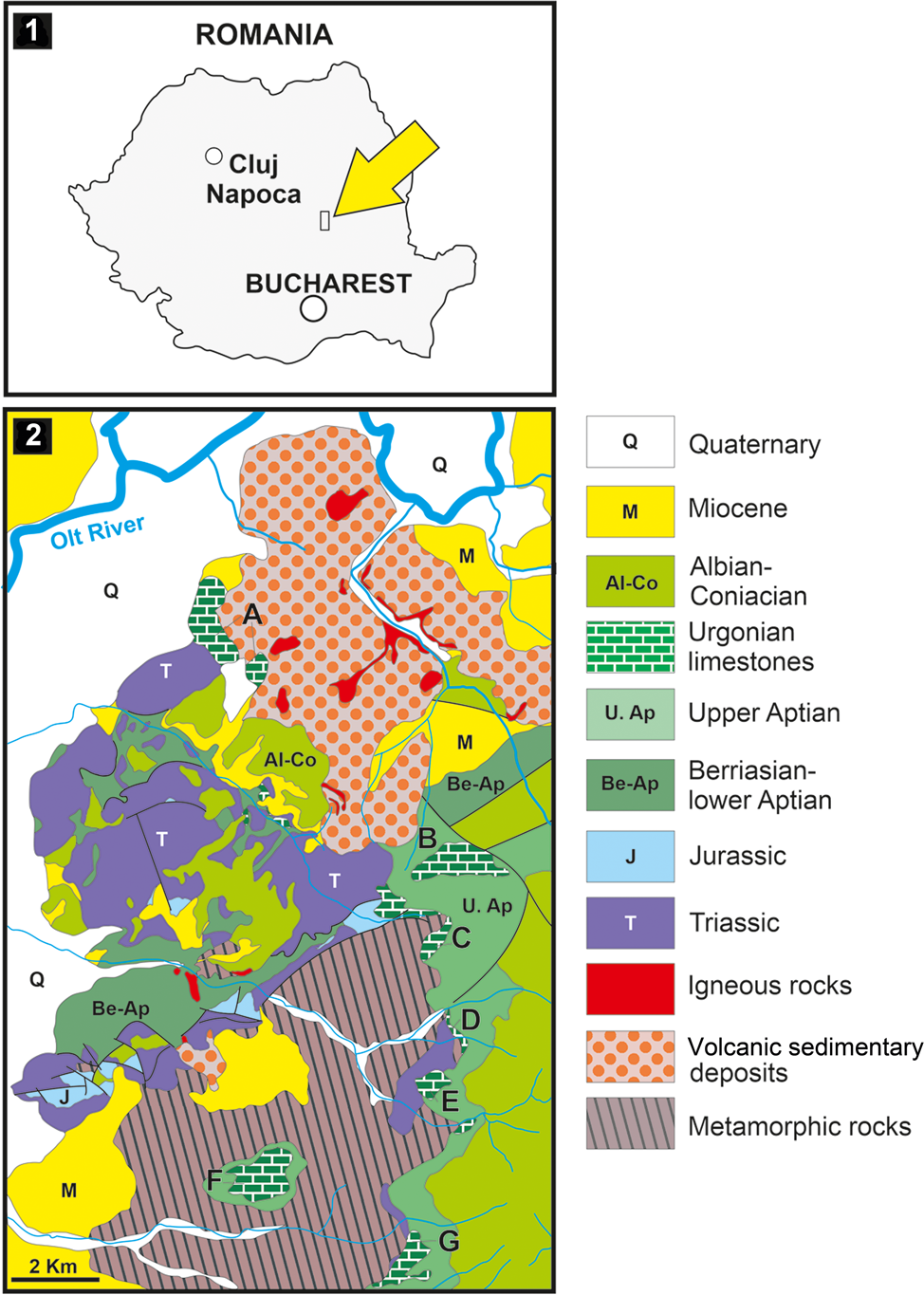
Figure 1. Location of the studied material. (1) Location of the Perşani Mountains within the Carpathian orogen (small rectangle indicated with yellow arrow); (2) geological map of the central-southern part of the Perşani Mountains; A–G, outcrops of Urgonian limestone; outcrop A corresponds to the location of the Fântâna area (modified after Popescu, Reference Popescu1970).
Upper Aptian limestones crop out in five areas in the central-southern sector of the Perșani Mountains (Fig. 1.2): Fântâna (A), Trestia (B, C), Comana (D, E), Gârbova (F), and Mănăstirii Valley (G). In the Fântâna area (Fig. 2), the carbonate rocks consist of a reddish to yellowish limestone covering red clays. A 70 m thick succession contains coral-rudist boundstone, orbitolinid-bearing wackestone–packstone, bioclastic packstone–floatstone with coral and rudist fragments, intraclastic bioclastic grainstone–rudstone, and partially fenestral bindstone–packstone. The fossil association comprises corals, calcareous algae, and benthic foraminifera (including Mesorbitolina texana [Roemer, Reference Roemer1849]), as well as encrusting organisms and incertae sedis.
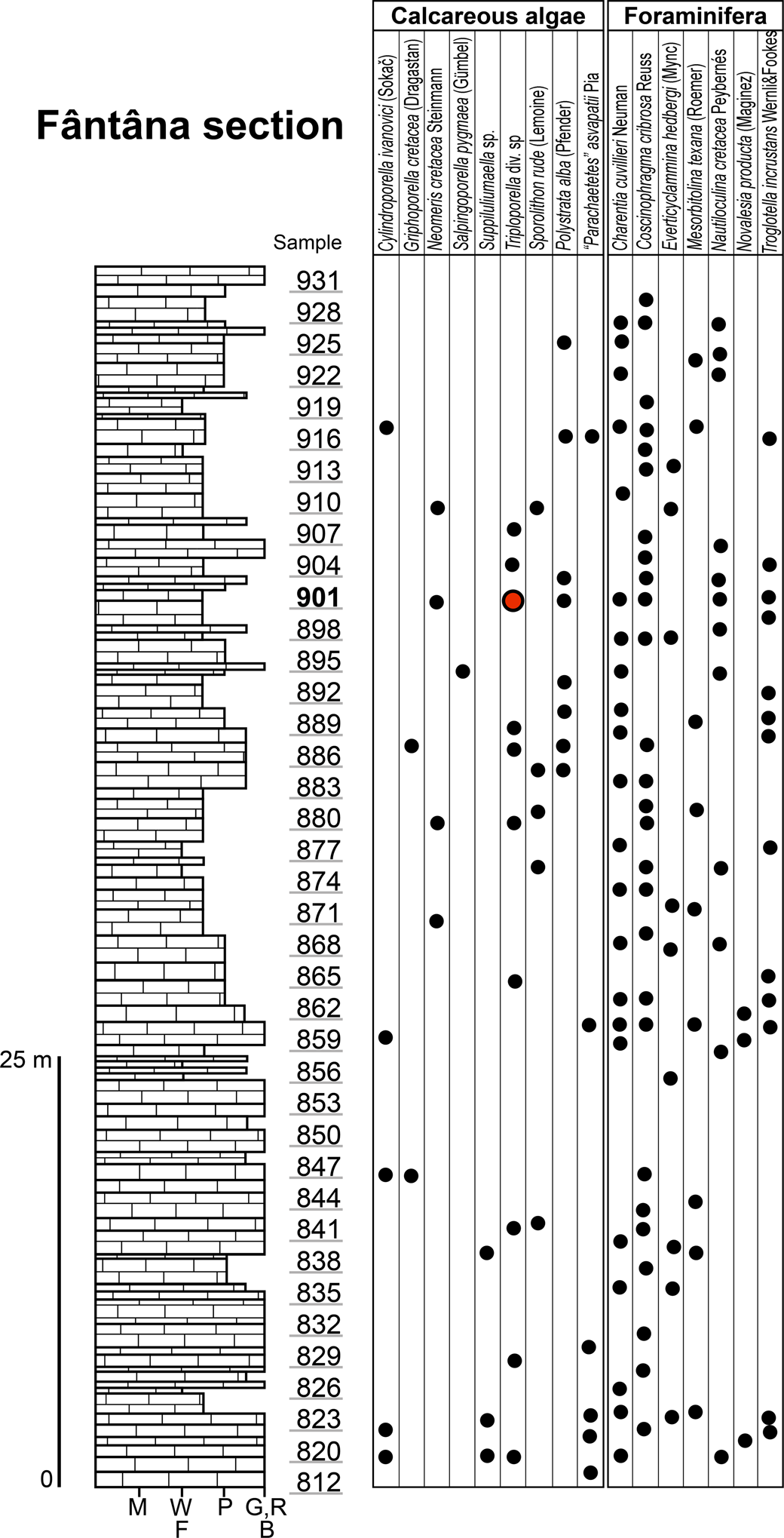
Figure 2. Succession of the upper Aptian limestone at Fântâna with ranges of the most important microfossils; M, mudstone; W, wackestone; F, floatstone; P, packstone; G, grainstone; R, rudstone; B, boundstone. Red circle, type horizon.
Sample 901 contains the majority of Triploporellaceae species presented in this study (Fig. 2). It also contains Neomeris cretacea Steinmann, Reference Steinmann1899, Polystrata alba (Pfender, Reference Pfender1936), Girvanella sp., Terquemella sp., Akcaya minuta (Hofker, Reference Hofker1965), Ammobaculites sp., Coscinophragma cribrosa (Reuss, Reference Reuss1846), Charentia cuvillieri Neumann, Reference Neumann1965, and “Coptocampylodon” fontis Patrulius, Reference Patrulius1965. The presence of the orbitolinid Mesorbitolina texana indicates a late Aptian age of these limestone deposits.
Material and methods
Most of the algal specimens obtained are contained in 155 thin sections of limestone labeled PSM 901-1 through 901-155. A few specimens are from samples 896 and F53. The algal specimens were observed by optical stereomicroscope and photographed and measured under a petrographic microscope. An identification number has been assigned to each of the 121 specimens.
Some values of the number of laterals in a whorl (w) have been estimated according to methods discussed in Barattolo et al. (Reference Barattolo, Carras, Conrad and Radoičić2019, supplemental data). The height between whorls (h) has been obtained through a procedure provided in the supplemental data.
Repositories and institutional abbreviations
PSM, Palaeontology-Stratigraphy Museum in the Geology Department of the Babeş-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca (Romania). DiSTAR, Department of Earth Sciences Environment and Resources, University of Naples Federico II.
Deciphering voids and taxonomic implication
The abundant algal material analyzed shows mineralized skeletons with a wide range of cavities whose shape could lead to differing interpretations. Some structural interpretations may be almost irrelevant to the systematics and are only part of a more complete understanding of the alga. Conversely, the adoption of other interpretations can have important implications for the taxonomic position of the alga, even at the family level. Here, we focus on the interpretation of voids that may have significant taxonomic implications. These mainly refer to primary-pore/reproductive-organ relationships and pores adjacent to the outer surface. Oblique and tangential-oblique sections often provide a key understanding of the structure of the alga (De Castro, Reference De Castro1997; Barattolo et al., Reference Barattolo2019). Serial sections of voids throw light on their nature and shape. Moreover, the transitional region encompassing the lower sterile and upper fertile parts can reveal how early reproductive elements were added to the basic vegetative framework of the alga. We therefore specifically chose two sections, one tangential-oblique (thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N122) and the other oblique (thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N089), cutting through or very close to the sterile-fertile boundary in the lower part of the thallus.
Primary laterals and reproductive organs
The tangential-oblique section (thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N122, Fig. 3.4) is clearly truncated downwards where two whorls of sterile laterals are intercepted (rows of circular pores). Around the periphery only single pores, not grouped in clusters, can be observed. They widen outwards, implying a phloiophorous shape. From the fourth to the eighth whorl, reproductive organs are clearly visible inside larger irregular voids. The third and the fourth whorls show irregularly shaped pores. Many of them, termed eight-shaped pores, are vertically elongated and separated by constrictions. These latter pores, combined with the larger irregular voids, can be variously interpreted. Here we consider three different interpretations (Fig. 3.1–3.3), and as many corresponding appearances in axial section (Figs. 4.1–4.3). For the sake of discussion, these are referred to as Hypothesis A, B, and C, respectively.
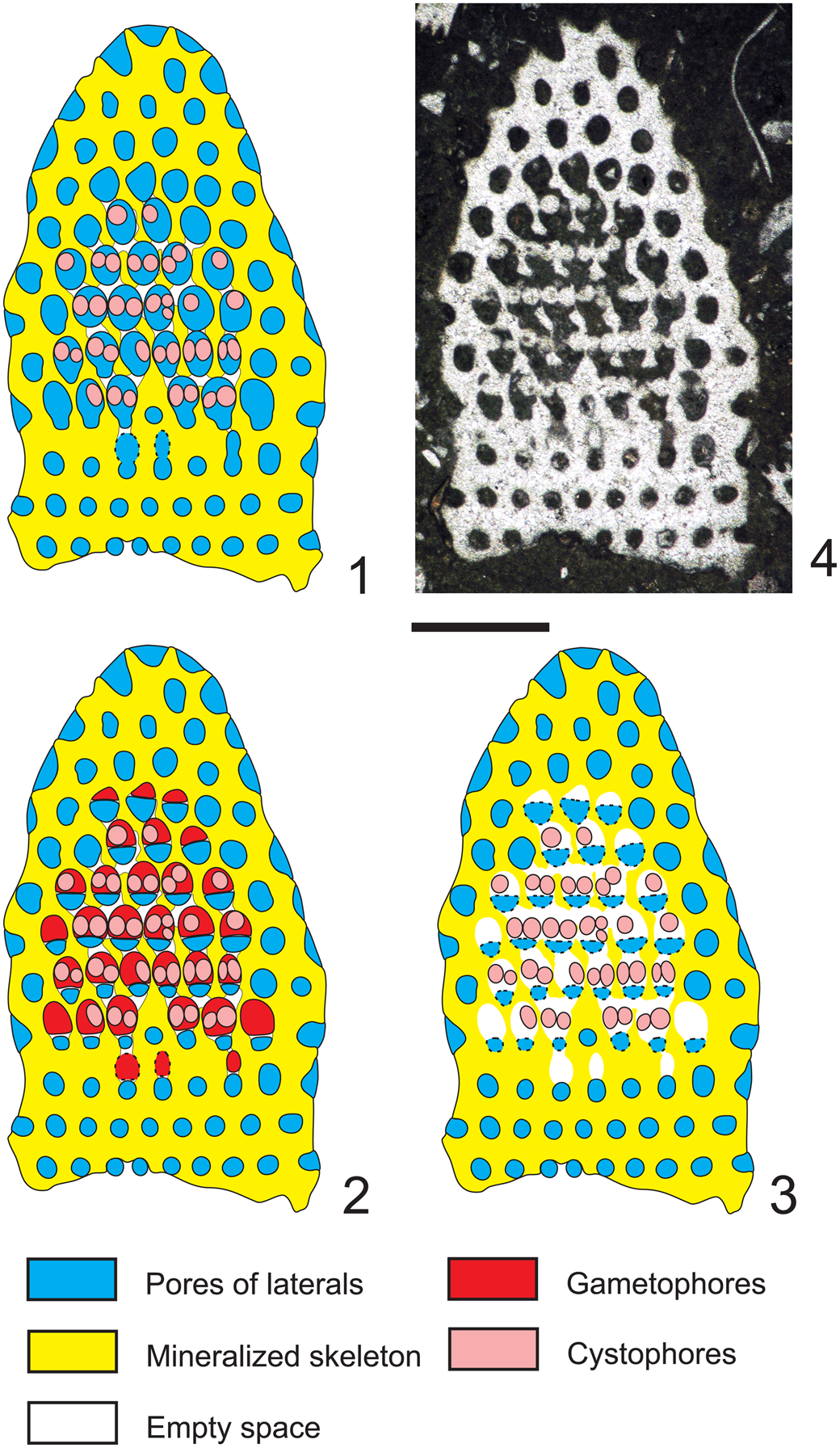
Figure 3. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. Different structural interpretations of the voids (pores and empty spaces) based on a tangential oblique section through the lower part of the biomineralized skeleton. In the analysis presented here: (1) voids are interpreted as pores (molds of primary laterals) and empty spaces as lack of calcification between them; (2) pores are interpreted as combinations of molds of primary laterals and external gametophores; empty spaces occur between them; (3) pores are partly interpreted as false pores (molds of primary laterals) and empty space between the cystophores; empty spaces occur between them; (4) tangential oblique section (thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N122). Presumed shape shown by dashed line. Scale bar represents 1.0 mm.
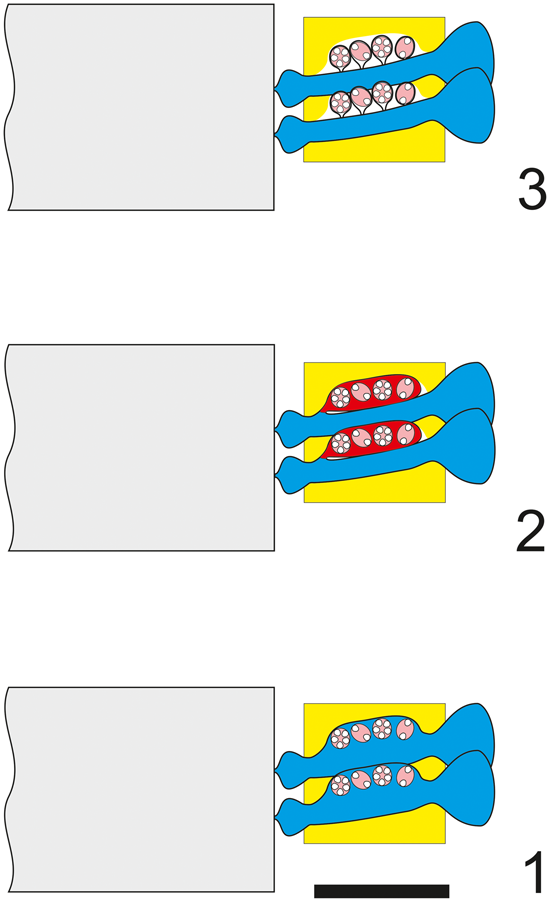
Figure 4. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; various structural interpretations of the alga. (1) Cladosporous primary lateral containing cystophores; (2) primary lateral bearing a single lateral gametophore (goniosporate type, as in primitive Dasycladaceae, e.g., Bakalovaella); (3) primary lateral bearing several lateral gametophores (goniosporate type, as in Bornetellaceae). Colors as in Figure 3; central stem in gray. Scale bar represents 1.0 mm.
Hypothesis A (Fig. 3.1)
Pores and voids are interpreted as molds of primary laterals (cladospore interpretation, Fig. 4.1). Eight-shaped pores, filled by micrite, are assumed to be the result of an incipient swelling that hosted reproductive organs. The middle widening of primary pores, together with the intervening deficiency in mineralization, gives the impression of large irregular voids. According to these attributes, the taxon must be attributed to the family Triploporellaceae.
Hypothesis B (Fig. 3.2)
Pores and voids are interpreted as molds of small primary laterals, each bearing a large lateral gametophore containing cystophores (goniospore interpretation, Fig. 4.2). Eight-shaped pores are assumed, corresponding to the stalks of gametophores proximally joined to the primary lateral. The dense package of primary laterals and gametophores produces compound pores (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). In this case, the specimen must be attributed to genus Bakalovaella, and referred to the family Dasycladaceae (Granier and Bucur, Reference Granier and Bucur2019).
Hypothesis C (Fig. 3.3)
Pores and voids are interpreted as molds of small primary laterals and empty spaces, respectively. Cystophores are thought to be external gametophores attached sideways to primary laterals (goniospore interpretation, Fig. 4.3). Eight-shaped pores are assumed to correspond to primary lateral adjacent to an empty space. The dense package of primary laterals and gametophores produces compound pores (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). The irregular large voids are the result of primary pores fused to cavities by a deficiency in calcification (annular channels; Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). Based on this hypothesis, the taxon should be assigned to the family Bornetellaceae (Granier and Bucur in Granier et al., Reference Granier, Dias-Brito, Bucur and Tibana2013).
The regular large elliptical pores joined by oblique channels, shown in the center of Figure 3.4, exclude Hypothesis C (Fig. 4.3). The eight-shaped pores tend to support Hypothesis B (Fig. 4.2), but the largest elliptical pores lack any sign of subdivision. In this view, Hypothesis A (Fig. 4.1) appears the most likely option and is therefore adopted here.
Secondary laterals versus asymmetry
The oblique section of thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N089 (Fig. 5.1), shows weak evidence of inner eight-shaped pores (right side of the fifth whorl). Conversely, eight-shaped pores frequently occur in the middle and outer part of the section (see second and third whorl). With respect to Figure 3.4, Figure 5.1 exhibits two pairs of pores at the lower margin (right side of first whorl; see also the interpretive drawing, Fig. 5.2). The intercepts of the sixth (Fig. 6.1, w1) and first (Fig. 6.1, w2) whorls in the corresponding transverse section are depicted in Figure 6.3 and Figure 6.4, respectively. The distal eight-shaped pores (Fig. 6.1), doubling the inner single pores (Fig. 6.5), are usually interpreted as the occurrence of secondary laterals (Fig. 6.7). In the systematics, such a choice between one or two orders of laterals has a genus level implication. In this case, the distal eight-shaped pores can be deciphered differently. The first and second whorls (Fig. 6.1) are atypical if compared with the symmetrical succeeding ones (e.g., third to sixth whorls). The latter whorls reflect the typical radial symmetry of dasycladaleans, even though the pores increase in size from left to right in the first two whorls. This could be interpreted as being a result of asymmetrical swelling of primary laterals within the whorl. This bulge is most likely reduced or absent in one sector, while gradually extending outwards in the adjacent one (Fig. 6.6, 6.8). This appears to occur in the whorls of the transitional band between the sterile and fertile region (Fig. 6.2, w2).

Figure 5. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; interpretation of pores in oblique section. (1) Oblique section (thin section PSM 901-104, specimen N089); (2) interpretative drawing of (1). Yellow, calcified skeleton; light gray/gray, pores of subsequent whorls (without cystophores). Presumed shape shown by dashed line. Scale bar represents 1.0 mm.
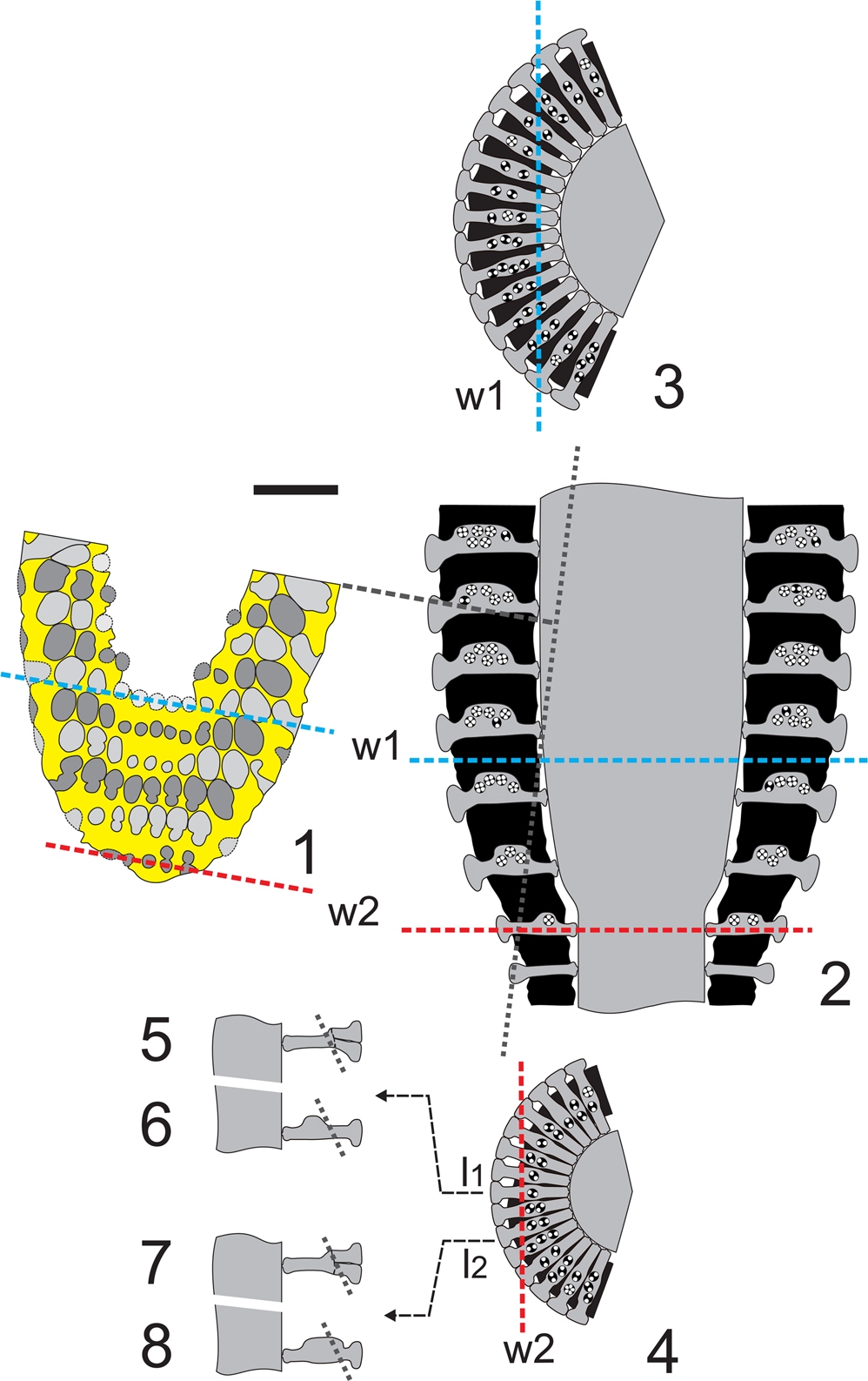
Figure 6. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; interpretation of sections. (1) Drawing of the oblique section (Fig. 5.1 = Fig. 11.6); w1, intercept of the innermost whorl; w2, intercept of the outermost whorl; (2) axial view of the corresponding part (lower part of the thallus) with w1 and w2 positions; gray dotted line, intercept of the oblique section (1); (3) transverse view (sector) of w1 with the intercept in (1); (4) transverse view (sector) of w2 with the intercept in (1); (5) axial view of the central lateral l1 with the hypothesis of two orders of laterals; (6) axial view of the central lateral l1 with the hypothesis of cladosporous primary lateral; (7) axial view of the second lateral at right l2 with the hypothesis of two orders of laterals; (8) axial view of the second lateral at right l2 with the hypothesis of cladosporous primary lateral in an asymmetrical whorl; dashed line, intercept of the oblique section (1). Black: mineralized skeleton. Scale bar represents 1.0 mm.
Asymmetrical whorls can be observed in extant and ancient taxa at the sterile/fertile boundary (e.g., Cymopolia barbata [Linnaeus, Reference Linnaeus1758] Lamouroux, Reference Lamouroux1816 [Berger and Kaever, Reference Berger and Kaever1992, fig. 2.25b]; Triploporella praturlonii Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1982b, pl. 3, fig.1, third whorl from below; Zittelina massei Bucur, Granier, and Săsăran, Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, fig. 5e, third whorl from below; Batophora oerstedii Agardh, Reference Agardh1854 [Berger, Reference Berger2006, p. 55, fig. 22; sketched in transverse view in Fig. 7.1]; and Cymopolia mayaense Johnson and Kaska, Reference Johnson and Kaska1965 [Fig. 7.2]). Most examples pertain to taxa with terminal gametophores (choristosporous taxa). Vegetative elements (laterals) maintain similar size all around the whorl, but only a few bear gametophores. Correspondingly, in cladosporous forms, some laterals can remain sterile while others may be variously swollen by hosting reproductive organs. Distal eight-shaped pores are observed in very few specimens, in comparison to the great majority of single, well-spaced pores. All of them can be due to the effect of asymmetry. Thus, we interpret the present taxon as shown in Figure 4.1.
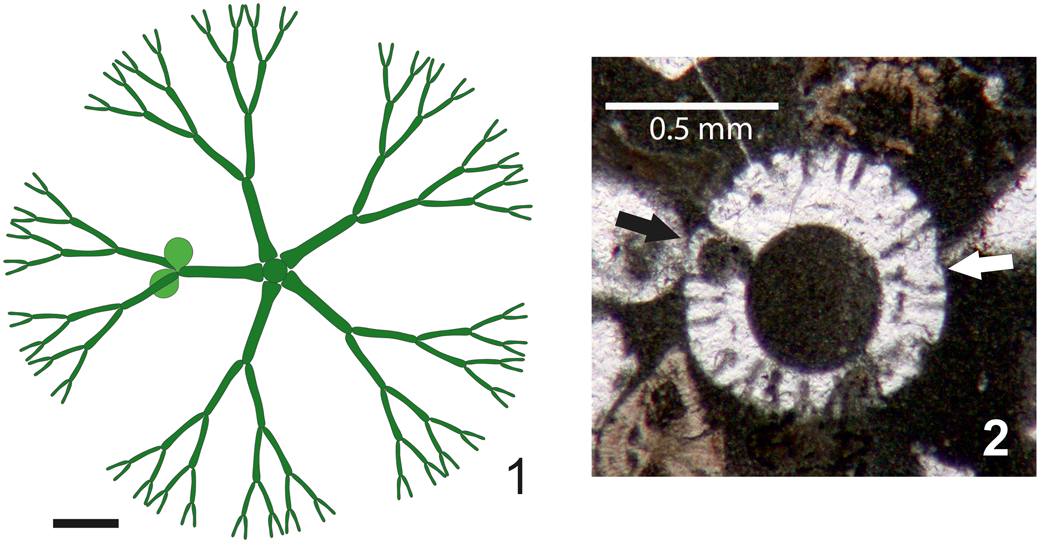
Figure 7. Examples of asymmetrical whorls. (1) Batophora oerstedii whorl amid the sterile and fertile regions; only one primary lateral out of five bears gametophores (drawing in transverse view from Berger, Reference Berger2006, p. 55, fig. 22); (2) Cymopolia mayaense oblique section in the lower part of an article; the primary lateral at left bears the gametophore (black arrow), the corresponding lateral at right (white arrow) lacks the gametophore (Selandian, environs of Sarakhs, NE Iran, DiSTAR-BA4249.1). Scale bars represent (1) 1.0 mm; (2) 0.5 mm.
Systematic paleontology
Order Dasycladales Pascher, Reference Pascher1931
Family Triploporellaceae (Pia, Reference Pia1920) Berger and Kaever, Reference Berger and Kaever1992
Tribe Salpingoporelleae Pia, Reference Pia1920
Genus Dragastanella new genus
Type species
Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; Aptian, Perşani Mountains (Braşov district, Romania).
Other species
Dragastanella hispanica (Masse, Arias, and Vilas, Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993) n. comb., Dragastanella massei (Bucur, Granier, and Săsăran, Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010) n. comb., Dragastanella matesina (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1980) n. comb.
Diagnosis
Cylindrical to club-shaped thallus. Euspondyl, phloiophorous primary laterals making cortex. Russoella-type reproductive organs (gametophores) inside primary laterals (cladosporous type).
Etymology
Dedicated to Prof. Ovidiu Dragastan for his important contributions to the study of fossil calcareous algae.
Remarks
The new genus Dragastanella shows the closest affinities with Triploporella Steinmann, Reference Steinmann1880 emend. Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1981. Dragastanella n. gen. has only first-order laterals, forming a cortex outward; thus, the primary laterals have both the reproductive and assimilative roles. Conversely, in Triploporella, there are two orders of laterals. This key difference between Triploporella and Dragastanella n. gen. is sufficient to separate the two genera. Pseudotriploporella Jaffrezo et al. (Reference Jaffrezo, Poisson and Akbulut1980) was also supposed to differ from the genus Triploporella Steinmann, Reference Steinmann1880 because it has only primary laterals. However, Granier and Deloffre (Reference Granier and Deloffre1993, p. 23–24) showed that Pseudotriploporella imecikae Jaffrezo, Poisson, and Akbulut, Reference Jaffrezo, Poisson and Akbulut1980, type species of the genus, and Triploporella sp., occurring in the same sample, belong to a single taxon. Therefore, Pseudotriploporella imecikae has primary and secondary laterals, and consequently Granier and Deloffre (Reference Granier and Deloffre1993, p. 24) transferred it to the genus Triploporella. As a result, the genus Pseudotriploporella is a junior synonym of Triploporella. The new genus Dragastanella, as herein established, includes characters earlier assigned to Pseudotriploporella.
Dragastanella n. gen. shares the occurrence of only phloiophorous primary laterals with Zittelina Morellet and Morellet (Reference Morellet and Morellet1913) and Salpingoporella Pia (Reference Pia1918). Zittelina has long and thin primary laterals that support external gametophores (gonioporate reproduction). On the other hand, Salpingoporella shows primary laterals that are thin and lack reproductive bodies; endosporate reproduction is inferred.
Based on the presence of phloiophorous primary laterals arranged in whorls, and containing mineralized lenticular Russoella-like cystophores (cladosporous type), Dragastanella n. gen. is assigned to the family Triploporellaceae.
Dragastanella transylvanica new species
Figures 3–6, 8–12
- Reference Bucur, Bruchental, Cociuba, Granier, Hebriştean, Lazar, Marian and Săsăran2013
Triploporella sp. 1; Bucur et al., fig. 8 a, b.
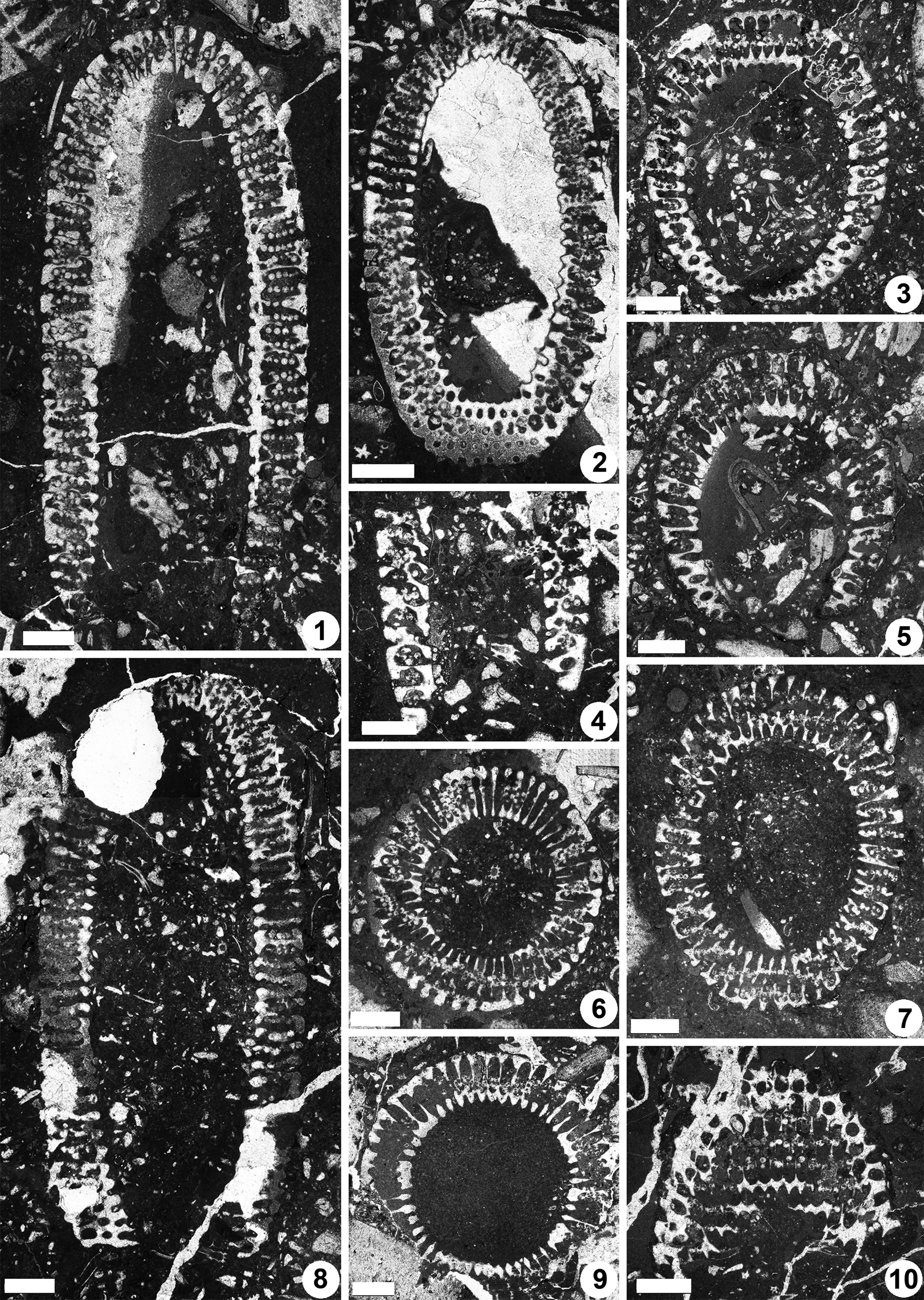
Figure 8. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., upper Aptian, central-southern part of the Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village (Braşov County, Romania). (1) Axial section, PSM 901-16, specimen N013, holotype; notice the tapered bottom (laterals reducing in size downwards), bottom laterals orthogonal to inclined, vertical laterals at top, and the outer tracts that are usually shifted downwards with respect to the primary lateral axis; (2) oblique section cutting the top and bottom of the thallus, PSM 901-37, specimen N033, paratype; bottom apparently not tapered, with laterals orthogonal to gently inclined upward, outer tract aligned along the lateral axis, occurrence of eight-shaped pores (third whorl from the bottom); (3) oblique section crossing the bottom of the thallus (inner ellipse of the section is eccentric, shifted downwards with respect to the outer ellipse), PSM 901-37, specimen N031, paratype; bottom tapered with sterile laterals orthogonal to gently inclined upward; (4) fragment of a calcareous skeleton in axial section, showing the tapered bottom of the thallus, PSM 901-62, specimen N053, paratype; (5) oblique section across the tapered bottom of the thallus, PSM 901-84, specimen N073, paratype; (6) transverse-oblique section, PSM 901-44, specimen N039, paratype; mineralization extends up to the cortex; (7) oblique section, PSM 901-15, specimen N012, paratype; calcareous skeleton extends up to the middle tract of laterals; (8) longitudinal section, PSM 901-48, specimen N043, paratype; bottom not tapered; (9) transverse section, PSM 901-73, specimen N063, paratype; notice the lateral fusion of pores (annular channel) and the swollen inner end of primary laterals resembling a countersink; (10) tangential section, PSM 901-116, specimen N092, paratype; occurrence of thin walls between the pores of the same whorl; eight-shaped pores are visible at the top of the photo. All scale bars represent 1.0 mm.

Figure 9. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., upper Aptian, central-southern part of the Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village (Braşov County, Romania). (1) Oblique section, PSM 901-17, specimen N014, paratype; calcareous skeleton coating only the inner and the middle tracts of the primary laterals; (2) oblique section through the lower part of the thallus (sterile laterals at bottom), PSM 901-21, specimen N018, paratype; calcareous skeleton reaches the cortex, first whorl in the bottom is sterile, second whorl is asymmetrical (last, but one pore on the right is fertile); (3) oblique section though top of the thallus (inner cavity apparently shifted upward, as in Fig. 9.4), PSM 901-18, specimen N015, paratype; annular, uncalcified channel as in the specimen in Figure 9.5; (4) oblique section though the upper part of the thallus, PSM 901-40, specimen N035, paratype; calcareous skeleton reaches to the cortex, outer tract aligned along the lateral axis; (5) oblique section, PSM 901-82, specimen N072, paratype; mineralized skeleton not reaching the outer tract, occasional interverticillar arrangement of the cystophores, shifted beyond the laterals; (6) oblique section, PSM 901-137, specimen N107, paratype; thin mineralized wall between pores of the same whorl (top of the picture); (7) oblique section, PSM 901-24, specimen N021, paratype; notice oblique, uncalcified channels (bottom of the picture), (8) tangential-oblique section, PSM 901-41, specimen N036, paratype; occurrence of oblique channels and vertical package of laterals between alternated whorls, external cortex. All scale bars represent 1.0 mm.

Figure 10. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., upper Aptian, central-southern part of Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village (Braşov County, Romania). (1) Oblique section, PSM 901-136, specimen N106, paratype; notice the remnants of mineralization between whorls (fertile middle tract of the primary laterals); (2) oblique section through the upper part of the thallus, PSM 901-125, specimen N097, paratype; primary laterals apparently form a sort of inner cortex (regular hexagonal meshes close to the central stem) in addition to the outer cortex (bottom of picture); the outer tract of the lateral is shifted downwards; (3) oblique section cutting the lower part of the thallus, PSM 901-24, specimen N021, paratype; bottom sterile laterals orthogonal to inclined upward; (4) tangential section, PSM 901-46, specimen N041p, paratype; regular hexagonal meshes close to the central stem, as in Figure 10.2, remnants of mineralization between alternating whorls, superior arrangement of the cystophores; (5) transverse section, PSM 901-123, specimen N095, paratype, the swollen inner end of primary laterals looks countersunk; (6) oblique section through the top of the thallus, PSM 901-142, specimen N112, paratype, orthogonal laterals in the lower part; (7) oblique section crossing the lower part of the thallus, PSM 901-150, specimen N116, paratype; the outer tract of the lateral is aligned along the main lateral axis (not shifted downwards); (8) transverse section, PSM 901-72, specimen N062, paratype, laterals are swollen inward like a countersink (top of the picture), their distal parts are not preserved. All scale bars represent 1.0 mm, except (4) = 0.5 mm.
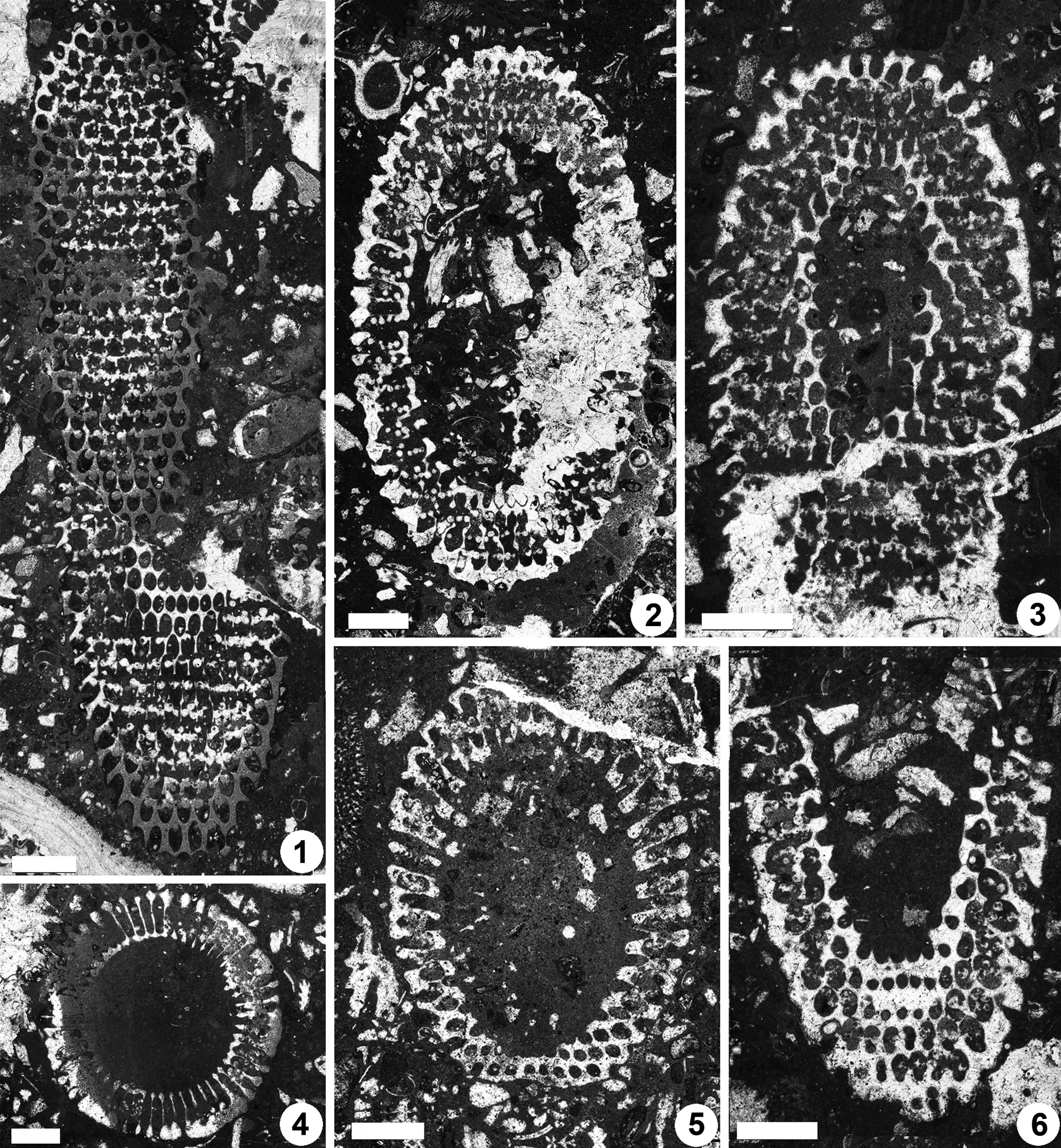
Figure 11. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., upper Aptian, central-southern part of Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village (Braşov County, Romania). (1) Tangential section, PSM 901-124, specimen N096, paratype; cystophores are inside (superior type) and outside the laterals (marginal) in the lower and upper part of the thallus, respectively; (2) oblique section, PSM 901-149, specimen N115, paratype; primary laterals are distally conspicuously flared outwards (cortex); (3) sub-tangential section, PSM 901-115, specimen N091, paratype; note how primary laterals (outer tract) distally shift downwards; (4) transverse section, PSM 901-88, specimen N077, paratype; laterals are clearly swollen outwards (upper part of the picture, cortex); (5) oblique section through the lower, partly sterile, part of the thallus, PSM 901-57, specimen N049, paratype; notice sterile whorls (bottom of the picture); (6) oblique section, PSM 901-113, specimen N089, paratype; see the eight-shaped pores (bottom of the picture) and the outer tract of primary laterals shifted downwards (right). All scale bars represent 1.0 mm.
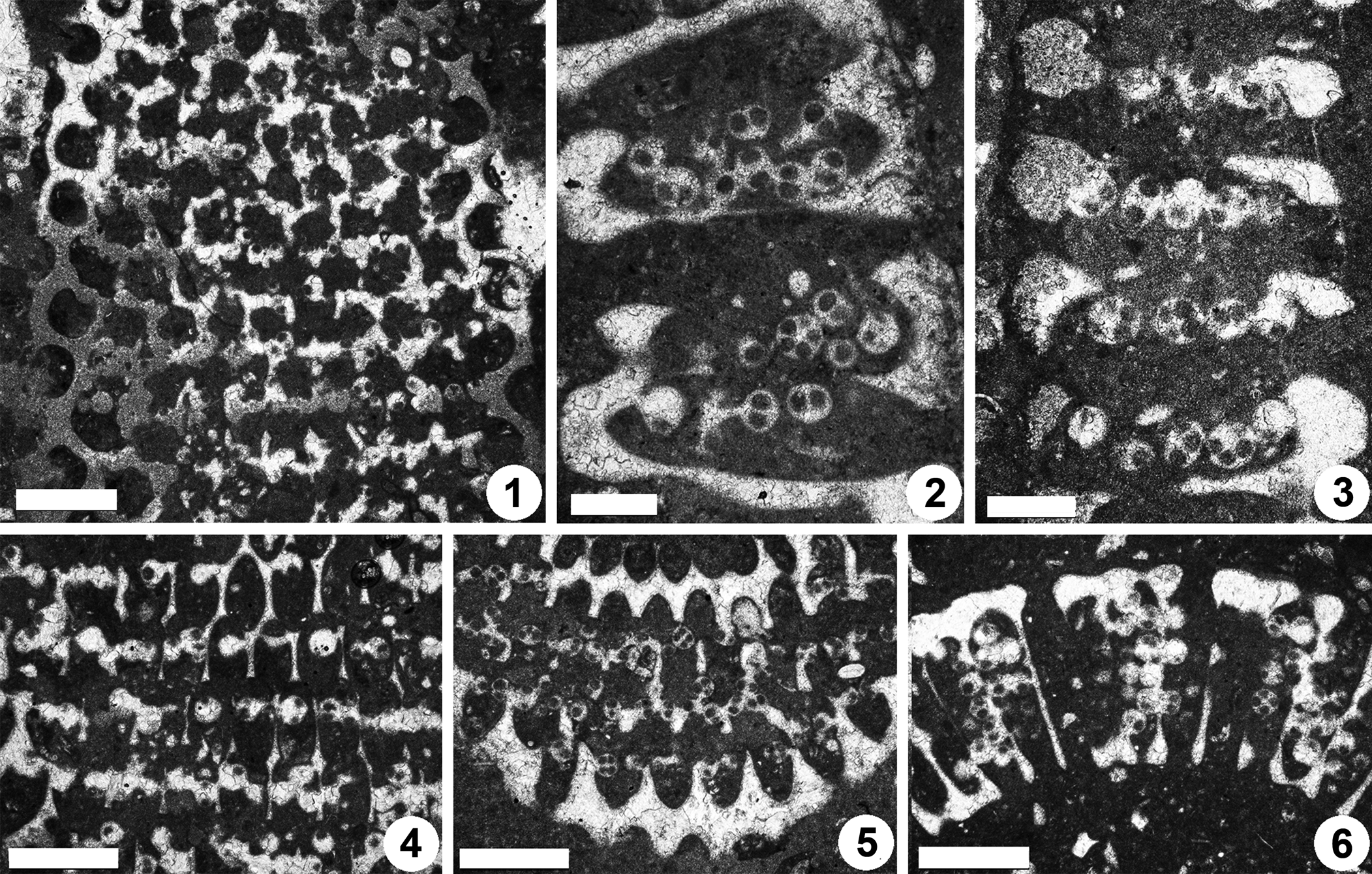
Figure 12. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., upper Aptian, central-southern part of the Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village (Braşov County, Romania). (1) PSM 901-124, detail of specimen N096 (see Fig. 11.1, upper part), paratype; peripheral arrangement of the cystophores; (2) PSM 901-147, specimen N113, paratype; cystophores generally cut along the axis; (3) PSM 901-152, detail of specimen N117, paratype; cystophores generally cut along the equatorial plane; (4) PSM 901-124, detail of specimen N096 (see Fig. 11.1, lower part), paratype; superior arrangement of the cystophores; (5) PSM 901-131, detail of specimen N102, oblique section (lower part), paratype; interverticillar arrangement of cystophores; (6) PSM 901-137, detail of specimen N108, transverse oblique section (right side), paratype; cystophores mainly set inside the laterals. Scale bars represent 0.5 mm in (1, 4–6) and 0.25 mm in (2, 3).
Type material
Holotype: axial section (Fig. 8.1), PSM 901-16. Paratypes: specimens contained in the thin sections, PSM 901-1 through PSM 901-155. Upper Aptian, reddish limestones with Mesorbitolina texana. The outcrop is located in the central-southern Perşani Mountains near Fântâna village, coordinates 45°57'32.89"N, 25°18'6.75"E (Fig. 1).
Diagnosis
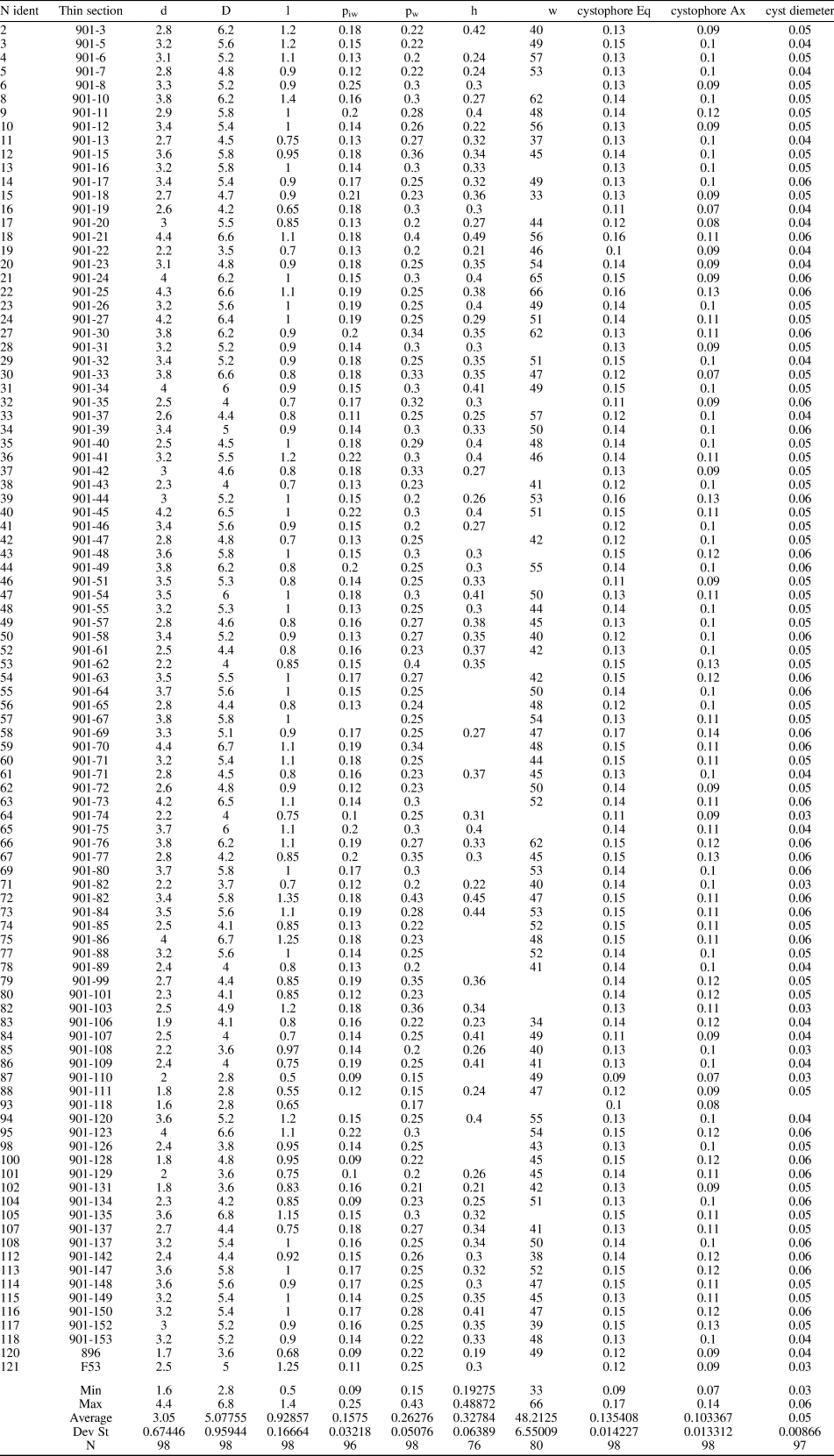
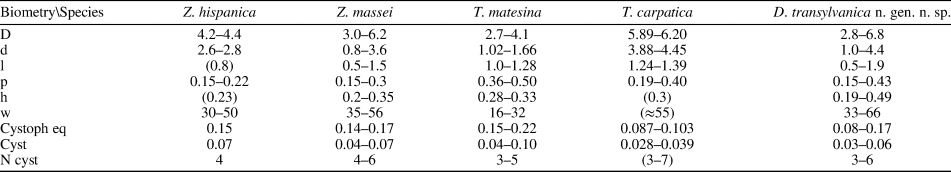
Simple, large, cylindrical to slightly club-shaped thallus, wide central cavity. The primary laterals are moderately long and phloiophorous. Each primary lateral can be subdivided into three parts: (1) inner subcylindrical tract, ~15–20% of the total length, markedly expanding inward; (2) middle, large fertile tract, ~65–70% of the total length, developing upward as a laterally compressed ellipsoidal bulge; and (3) outer tract, similar in size to the inner tract, flared outward and making a cortex distally. Primary laterals are arranged in close whorls (euspondyl), 33–66 per whorl, and alternating in position between subsequent whorls. The primary laterals are orthogonal in the lower part of the calcareous skeleton, but inclined at 80° in the middle and upper parts, with the inclination gradually decreasing so that they are upright at the top. Reproductive organs consist of mineralized gametophores located inside the primary laterals (cladosporous type), particularly confined in the upper part of the reproductive space. Cystophores are lenticular in shape and contain three to five, seldom six, cysts arranged in the equatorial plane. The calcified skeleton usually extends from next to the central stem to the distal outer part of the primary laterals before the cortical widening. Mineralization is reduced around the middle tract of primary laterals. Biometric data are shown in Table 1. Estimation of h from oblique sections is illustrated in the supplemental data.
Table 1. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. Table of main biometrical parameters: d, inner diameter; D, outer diameter; l, length of the primary lateral; piw, whorl width of the first tract of the primary lateral; pw, whorl width of the primary lateral (maximum diameter); h, height between whorls; w, number of laterals in a whorl; cystophore Eq., equatorial diameter of the cystophores; cystophore Ax, axial diameter of the cystophores; cyst diameter, axial diameter of cysts. Values of h and w from oblique sections are mathematically inferred. All dimensions are in millimeters.
Occurrence
Type locality and horizon only.
Description
The calcareous sleeve is simple, not articulated, closed at the top. The shape is roughly cylindrical, ~1.9–3.5 times longer than wide. The lower part may be tapered (Fig. 8.1, 8.3–8.5) or not (Fig. 8.2, 8.8).
The inner surface is slightly undulose, seemingly close to the central stem, but not touching it. The inner widening and lateral contact of the primary laterals prevented mineralization from extending farther inward. The inner cavity is quite large, which is augmented because the initial parts of the primary laterals are not mineralized.
The outer surface is regular, sometimes faintly undulose between whorls. Calcification encrusts the outer part of primary laterals, from the end of the middle tract (Figs. 8.7, 9.1) to the widening distal part (Figs. 8.6, 9.2, 9.4). Calcification is deficient in the mid part of the fertile tract. As a result, in this part, adjacent pores of the same whorl are often not separated by a mineralized wall (Figs. 8.9, 9.3–9.5), thus forming an annular channel (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019, fig. 7). Very occasionally a distinct thin wall can be observed (Figs. 8.10, 9.6). In the space between whorls, an oblique canal connects two pores of adjacent whorls, forming oblique channels (Fig. 9.7, 9.8). Remnants of mineralization persist in the spaces between whorls (Fig. 10.1, 10.4).
The primary laterals are set in close whorls (Figs. 8.1, 9.2), with 33–66 per whorl. The distance between whorls (h) is relatively low (0.19–0.49 mm) so that in the middle tract primary laterals appear vertically packed (e.g., Fig. 9.8). The arrangement is alternate in two subsequent whorls (Figs. 9.8, 10.4). In the lower part of the calcareous skeleton, primary laterals are orthogonal, or bent slightly upward, with respect to the vertical axis (Figs. 8.1–8.3, 9.2, 10.3). In the middle and upper parts, they are slightly inclined upward (75–80° to the axis), and inclination then decreases towards the top where they are arranged vertically (Figs. 8.1, 8.8, 10.6). The primary laterals are moderately long and phloiophorous. The primary lateral can be subdivided into three parts. The inner tract is subcylindrical, ~15–20% of total length. It opens widely inward (Figs. 8.9, 10.2, 10.5, 10.8); it is not clear whether this inner swelling is a primary character or is due to deficiency of calcification (countersinking, Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). The regular shape of the pores and reduction in size of the middle part of the first tract suggest that this is a primary character (Fig. 10.2, 10.4). The middle tract is the largest, and fertile, forming ~65–70% of the total length. The enlargement is not symmetrical relative to the primary lateral axis, but develops in the upper side as a laterally compressed ellipsoidal bulge. Gametophores are confined to this tract, especially to the bulge. In the lower part of the thallus, primary laterals are shorter and the bulge more globular. Here, primary laterals exhibit an eight-shaped transverse cut (see section on “Deciphering voids and taxonomic implication”). The outer tract is similar in size to the inner tract, is flared out and creates a distal cortex (Figs. 8.2, 9.8, 10.2, 11.2, 11.4). It is aligned parallel to the primary lateral axis (Figs. 8.2, 9.4, 10.4). Sometimes, in the middle–upper parts of the thallus, this tract is strikingly shifted downward (Figs. 8.1, 10.2, 11.3). A few whorls of sterile primary laterals can occasionally be observed at the base of the calcareous skeleton (Figs. 8.2, 8.3, 9.2, 10.3, 11.5). These laterals are thinner and shorter than fertile ones, akrophorous for most of their length, and flaring outward.
Small, flattened, ellipsoidal (oblate spheroid) sparry calcite bodies occur inside the primary laterals, and often contain cyst cavities (Fig. 12.2, 12.6). These cystophores (Barattolo et al., Reference Barattolo, Bucur, Kołodziej, Hoffmann and Skupien2013) can be considered a special type of gametophores. Cysts are arranged in the equatorial plane of the spheroid and number three to five, rarely six. No clear evidence has been found of seven cysts, although this cannot be excluded. The cystophores remain inside the middle tract of the primary laterals (Fig. 12.2, 12.6), noting that the equatorial planes are preferentially vertical. The cystophores rarely move peripherally into the space between the primary laterals (Fig. 12.5). In other cases, where the calcareous skeleton is reduced, isolated gametophores mark the boundary between two adjacent laterals (Fig. 12.1). The same is observed in Triploporella (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1982a, Reference Barattolob; Barattolo et al., Reference Barattolo, Bucur, Kołodziej, Hoffmann and Skupien2013). This arrangement may occur in the same specimen (e.g., upper region versus lower region, Figs. 11.1, 12.4).
Contiguous cystophores often become fused to each other, and to the calcareous skeleton, due to diagenetic conversion of the originally aragonitic skeleton (Fig. 12.3).
Etymology
From Transylvania, the region that includes the Perşani Mountains.
Remarks on thallus reconstruction
The mineralized skeleton coats most parts of the fertile region of the thallus. The middle tract of the calcareous sleeve is often poorly calcified, thus producing an intermediate empty space (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo2019). Consideration of the structures obliterated by the lack of mineralization have been discussed above (see section on “Deciphering voids and taxonomic implication”). All specimens can be referred to the apical fertile region of the thallus, and only a short length of the lower sterile part is preserved, making it difficult to estimate the total length of the thallus. Our reconstructions (Figs. 13, 14) assume that the primary laterals were prolonged inward, with a short uncalcified tract continuing the swollen inner part, and that the primary laterals likewise extended outward, forming a cortex.
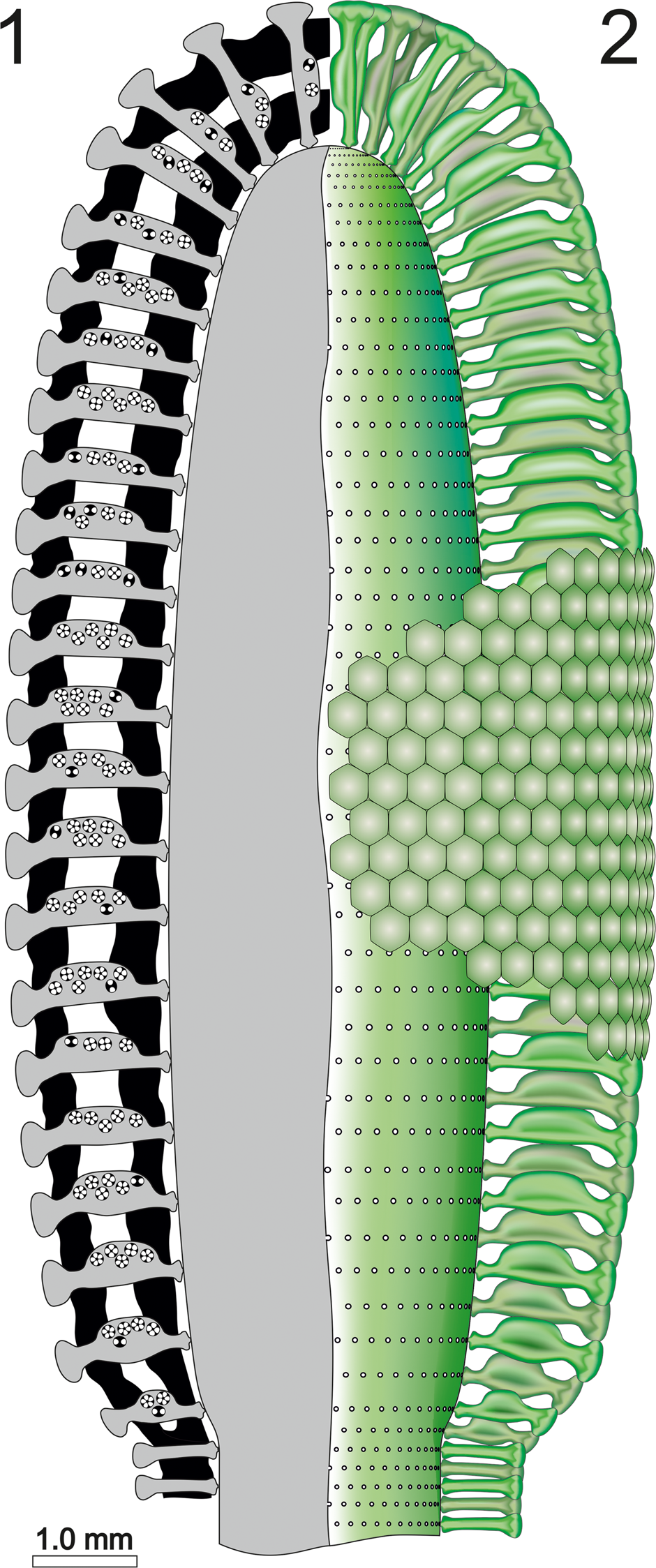
Figure 13. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. (1) Reconstruction of the alga in axial section; black, calcified skeleton; gray, soft parts; (2) axial view of the soft parts (green).
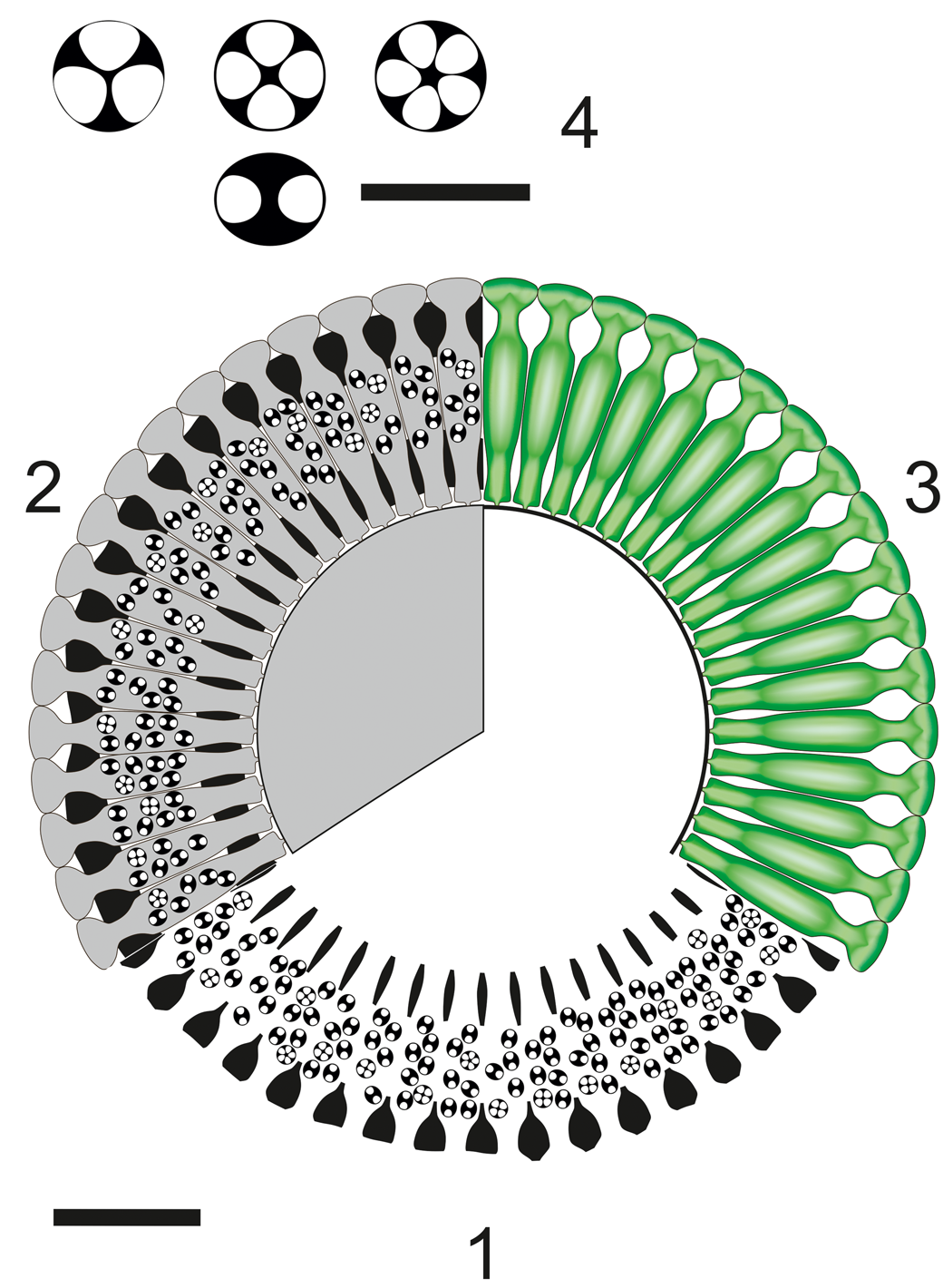
Figure 14. Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; reconstruction of the alga in transverse view. (1) Sector of a whorl in transverse section; black, extracellular and intracellular (cystophore) calcification; (2) sector of a whorl in transverse section; black, extracellular and intracellular (cystophore) calcification; gray, soft parts; (3), upper view of whorl, soft parts in green; (4) cystophores in equatorial section (up) and in axial section (down), usually containing 3–5 gametangia (cysts). Scale bar represents 1.0 mm (1–3) and 0.2 mm in (4).
The tapered lower part of the thallus suggests that the sterile uncalcified part probably continued downwards for only a short distance. This part has been not considered in the reconstruction (Figs. 13, 14).
Species assigned to Dragastanella n. gen. and comparison
The detection of species with one order or two orders of laterals is challenging when calcification does not extend beyond the primary laterals. In this situation, it is difficult to justify attribution of a species to Dragastanella n. gen. or Triploporella. For example, Triploporella carpatica Bucur, Reference Bucur1993 (Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Bruchental, Cociuba, Granier, Hebriştean, Lazar, Marian and Săsăran2013) resembles Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., but mineralization stops before the distal end of the primary laterals (Fig. 15.1, 15.2, 15.9, 15.10). In comparison with Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., its cystophores are smaller, the fertile part of the primary laterals is entirely enveloped by a thin mineralized wall, and the sterile part is poorly and irregularly mineralized. Despite this, the mineralized skeleton of Triploporella carpatica does not allow convincing assignment to either Triploporella or Dragastanella n. gen. Nonetheless, this species is provisionally retained in the genus Triploporella. Conversely, species such as Zittelina hispanica Masse et al., Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993, Zittelina massei Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, and Triploporella matesina Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1980, are here transferred to Dragastanella n. gen.
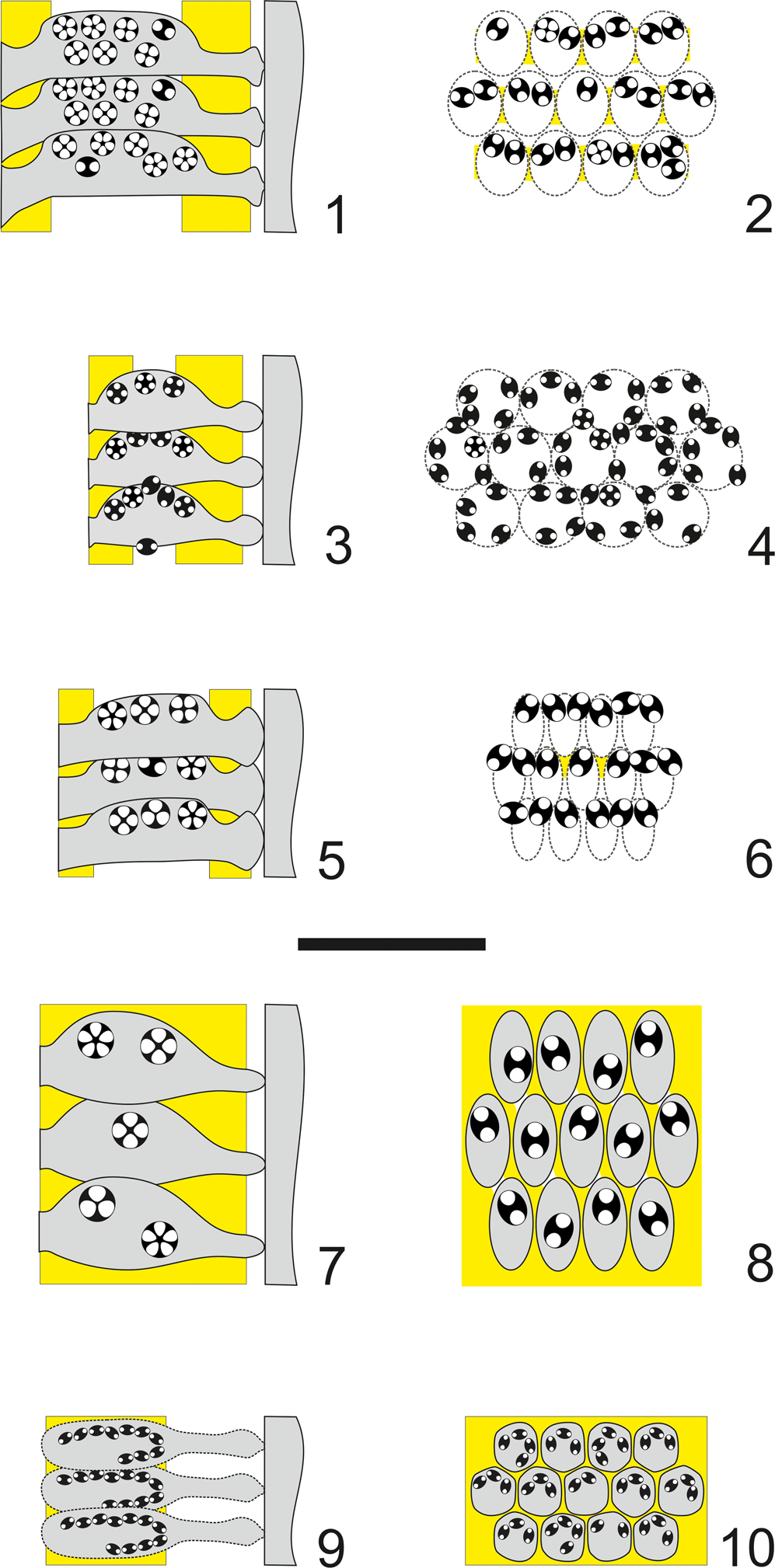
Figure 15. Algal structures compared. (1) Axial and (2) tangential section of Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.; (3) axial and (4) tangential section of Dragastanella hispanica n. comb.; (5) axial and (6) tangential section of Dragastanella massei n. comb.; (7) axial and (8) tangential section of Dragastanella matesina n. comb.; (9) axial and (10) tangential section of Triploporella carpatica. Extracellular calcification in yellow, intracellular calcification in black, presumed shape shown by dashed line. All figures: scale bar represents 1.0 mm.
Comparing the species assigned to Dragastanella n. gen., it seems evident that most of the biometrical range intervals overlap considerably (Table 2). Thus, simple traditional size parameters, such as outer (D) and inner (d) diameters, are insufficient to clearly distinguish species. Conversely, the thallus, laterals, cystophores, and mineralization, taken together, allow confident distinction among species. The overall appearance of the alga depends on a combination of biometric characters, such as size of the primary laterals (p, l), number of laterals in a whorl (w), and height between whorls (h). In contrast, the arrangement of reproductive organs within primary laterals is regulated by parameters related to the capacity of the primary laterals, such as size of primary laterals (p), size of cystophores (la, da), and number of cystophores per lateral. In this regard, at least three types of primary arrangement of cystophores have been observed (Fig. 16.1–16.3). Cystophores can occupy the upper part of the primary laterals (superior type, Fig. 16.1, e.g., Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp.), be more or less equally disseminated within the primary lateral (internal type, Fig. 16.2, e.g., Dragastanella matesina n. comb.), or be arranged close to the inner surface of the primary laterals (peripheral type, Fig. 16.3). Moreover, there is substantial evidence that, following decay of the alga, cystophores were released from the primary laterals. The secondary location of the cystophores can be inferred when, for example, cystophores are found half in and half out of the primary laterals that originally contained them or when, in the same specimen, they are totally inside laterals in one location, and outside in another. Two types of secondary location have been recorded (Fig. 16.4, 16.5). Cystophores can be totally or partly distributed between the whorls (interverticillar type, Fig. 16.4, e.g., Dragastanella massei n. comb.), or all around the laterals (marginal type, Fig. 16.5, e.g., Dragastanella hispanica n. comb.). The lack of cystophores, or the occurrence of one or two types of secondary location, seemingly depends on several factors, such as the presence, thickness, or lack of the calcified wall around primary laterals, and the accommodation space between laterals of the same whorl and between the whorls. Therefore, in the same species, by subtly varying these factors, it is possible to produce one or two types of placement, rarely three types.
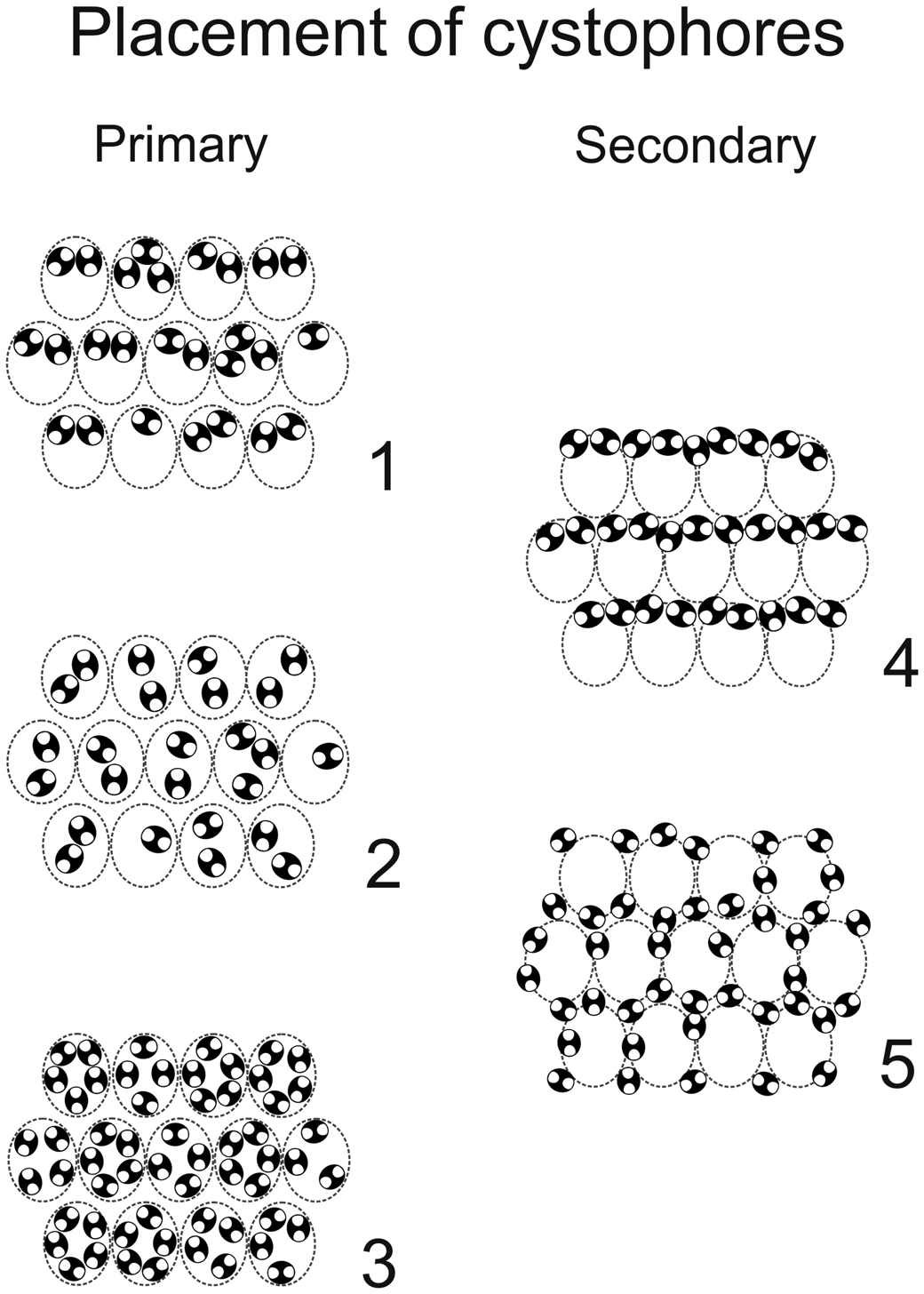
Figure 16. Primary (1–3) and secondary (4, 5) positions of cystophores in triploporellid species. (1) Superior; (2) internal; (3) peripheral; (4) interverticillar; (5) marginal. Intracellular calcification shown in black; presumed shape shown by dashed line.
Table 2. Biometrical dimensions compared. Symbols are the same as Table 1. Values in parentheses are estimated from original photographs. All dimensions are in millimeters.
Dragastanella hispanica (Masse, Arias, and Vilas, Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993) new combination
- Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993
Zittelina hispanica Masse, Arias, and Vilas, Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993, p. 294, pl. I.
Holotype
Longitudinal-oblique section from the Sierra de la Oliva, Caudete (Albacete Province, Spain), thin section 11695-9, Centre de sédimentologie-paléontologie, Université de Provence (Marseille, France), J. P. Masse collection. Illustrated in Masse et al. (Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993, pl. I, fig. 1).
Remarks
As described by Masse et al. (Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993), primary laterals are only enveloped by calcification in their proximal and distal parts. In the middle part, primary laterals are not calcified. However, rarely, calcified walls are visible between laterals of the same whorl (Masse et al., Reference Masse, Arias and Vilas1993, pl. I, figs. 4, 5, central and middle-right parts, respectively). This suggests that the middle parts of primary laterals could have been relatively strong and laterally closely packed (Fig. 15.3, 15.4). Cystophores are secondarily shifted, producing a marginal arrangement (Fig. 15.4). Dragastanella hispanica n. comb. (Fig. 15.3, 15.4) differs from Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. by having a stronger and less elongate shape of the primary laterals, and by having peripheral to marginal cystophores. Most specimens (95%) of Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. (Fig. 15.1, 15.2) show a primary location of the cystophores (superior type), and only a few show a secondary location (interverticillar type, 4%, and marginal type, 1%).
Dragastanella massei (Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010) new combination
- Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010
Zittelina massei Bucur, Granier and Săsăran, p. 445, fig. 4f, g, figs. 5–8.
Holotype
Longitudinal-oblique section from Subpiatră Quarry, near Aleşd (Pădurea Craiului Massif, Northern Apuseni Mountains, Romania), thin section 10209(1), deposited in the Department of Geology, Babeş-Bolyai University, Ioan I. Bucur collection. Figured in Bucur et al. (Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, fig. 5b).
Remarks
As in Dragastanella hispanica n. comb., this species has an inner calcified wall close to the axial stem and an outer sub-cortical calcified wall. The middle part of the primary laterals is not calcified; a thin wall is occasionally present between laterals of a whorl (Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, fig. 5e), and rarely in the space between whorls (Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, fig. 7i). The first tract of primary laterals displays an outward eight shape (8) in transverse section (Bucur et al., Reference Bucur, Granier and Săsăran2010, fig. 5e [middle part], fig. 8c [middle part], fig. 8 g [lower part]). Cystophores are secondarily shifted, producing interverticillar arrangement (Fig. 15.6). Dragastanella massei n. comb. (Fig. 15.5, 15.6) shows primary laterals with a distinctly widened inner end, thus forming a type of inner cortex; similar widening also occurs in Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. The central fertile parts of the primary laterals are deprived of mineralization, thereby forming an annular channel at whorl level. The position of reproductive organs always appears to be of interverticillar type.
Dragastanella matesina (Barattolo, Reference Barattolo1980) new combination
- Reference Barattolo1980
Triploporella matesina Barattolo, p. 133, pl. VIII–XI.
Holotype
Oblique section from Barremian–lower Aptian limestone, southern slopes of Mt. Miletto (Matese Massif, Southern Italy), thin section S.200.a.11, Piero De Castro collection housed in the University of Naples Federico II. Illustrated in Barattolo (Reference Barattolo1980, pl. VIII, fig. 2).
Remarks
As described in Barattolo (Reference Barattolo1980, p. 137–138), primary laterals distally end with a single “pore,” interpreted as the uncalcified proximal part of a tuft of secondary laterals. Based on the evidence concerning Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp., the single rounded “pore” of Triploporella matesina more reasonably should be referred to the distal part of the primary lateral; thus, this species is assigned to the genus Dragastanella n. gen. Cystophores are located in the primary laterals, showing an internal type of arrangement (Fig. 15.8). Dragastanella matesina n. comb. (Fig. 15.7, 15.8) is smaller than Dragastanella transylvanica n. gen. n. sp. and its cystophores are larger, fewer in number per primary lateral, and with a primary location (internal type).
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Kołodziej (Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland) for determination of the corals, and G. Pleş and C. Balica (Babeş-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca, Romania) for redrawing Figures 1 and 2. We thank R. Riding (University of Tennessee, Knoxville, USA) for his very helpful review of the manuscript. A sincere thank you also goes to L. Carbone, Dipartimento di Matematica, Università di Napoli Federico II, for his background check on the mathematical part (Supplemental Data). We also thank reviewers S. LoDuca (Associate Editor of JP), B. Granier (Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Département des Sciences de la Terre et de l'Univers, FR), and M.A. Conrad (Genève, CH) for their useful suggestions that improved the manuscript.
Data availability statement
Data available from the Dryad Digital Repository: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.51c59zw84.





















