Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 January 2013
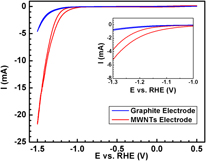
Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs), due to their unique electrical conductivity and mechanical properties, have led to our interest in their application of water splitting process. This carbon nanotube-based electrode, synthesized by plasma ehanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), provides a ∼6 times enhancement of hydrogen production via water electrolysis compared to a graphite electrode in acidic electrolyte. Our PECVD-grown vertically aligned carbon nanotubes show good adhesion to the graphite substrate and long-term sustainability in a strong acid solution without the need for any complicated and expensive pretreatment. Furthermore, the neutral potassium phosphate solution electrolyte (KPi electrolyte) using cobalt salt as the catalyst, as was reported recently, has been used to demonstrate the long-term compatibility of the MWNTs electrode under different electrolyte. MWNTs from thermal chemical vapor deposition growth technique were also fabricated and compared with the PECVD-grown samples.