Article contents
Tuning the electronic and magnetic properties of PEDOT-PSS-coated graphene oxide nanocomposites for biomedical applications
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 September 2020
Abstract
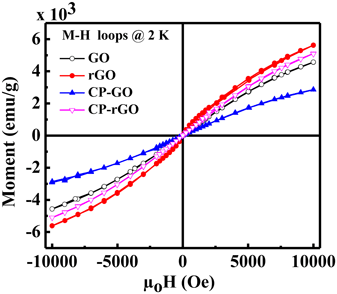
We have synthesized graphene oxide (GO) using Hummer's method which was subsequently reduced (rGO) by hydrazine hydrate. The synthesized GO was coated with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT-PSS) conducting polymer (CP) to obtain CP-GO which was also further reduced using hydrazine hydrate to form CP-rGO. Scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) techniques were used to study the electronic and structural properties of GO, rGO, CP-GO, and CP-rGO nanocomposites for biomedical applications. The superconducting quantum interference device method was used to investigate the magnetic properties of the nanocomposites. The electrical conductivity of the CP-GO nanocomposites was found to be ~104 times higher than that of GO due to an increase in sp2 content and subsequent decrease in oxygen functional groups. In rGO, we observed an improved paramagnetic saturation magnetization of approximately 5.6 × 0−3 emu/g at 2 K. The electronic and magnetic behavior of PEDOT-PSS-coated nanocomposites, as a result, were successfully tuned for potential biological and biomedical applications.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 12
- Cited by



