Article contents
Temperature and DC bias dependence of the phase transition behavior of [011]- and [001]-oriented PIN–PMN–PT single crystals with MPB composition
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 October 2018
Abstract
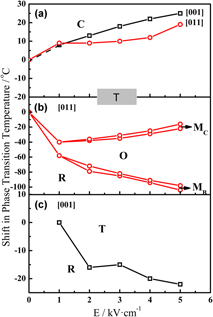
The phase transition behavior of [011]- and [001]-oriented 0.24PIN–0.43PMN–0.33PT single crystals was investigated through dielectric measurement in the process of heating and direct current (DC) bias. The phase transformation sequence in the [011]-oriented crystals is rhombohedral (R) → monoclinic (MB) → orthorhombic (O) → monoclinic (MC) → tetragonal (T) → cubic (C). The phase transition temperatures of R to MB $\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{\rm{R}} - {{\rm{M}}_{\rm{B}}}}}} \right)$ and MB to O
$\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{\rm{R}} - {{\rm{M}}_{\rm{B}}}}}} \right)$ and MB to O  $\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{{\rm{M}}_{\rm{B}}} - {\rm{O}}}}} \right)$ decrease; meanwhile, the transition temperatures of O to MC
$\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{{\rm{M}}_{\rm{B}}} - {\rm{O}}}}} \right)$ decrease; meanwhile, the transition temperatures of O to MC $\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{\rm{O}} - {{\rm{M}}_{\rm{C}}}}}} \right)$ phase, MC to T
$\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{\rm{O}} - {{\rm{M}}_{\rm{C}}}}}} \right)$ phase, MC to T  $\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{{\rm{M}}_{\rm{C}}} - {\rm{T}}}}} \right)$ phase, and T to C (TT–C) phase increase with the increase of DC bias. The phase transformation sequence in the [001]-oriented crystals is R → T → C. As DC bias increases, the transition temperature TR–T of R to T phase declines and the transition temperature TT–C rises. Intermediate phases MB, O, and MC are only found in the [011]-oriented crystal. The phase transition characteristics of the [011]-oriented crystals are rather more complex than those along [001] direction. The micro–macro domain transition at Tf is related to crystal orientation and DC bias voltage. The phase diagram in terms of temperature and bias voltage is established for [011]- and [001]-oriented 0.24PIN–0.43PMN–0.33PT crystals. The DC bias dependent dielectric properties and phase transition characteristics are also compared with the crystals along [111] direction.
$\left( {{{\rm{T}}_{{{\rm{M}}_{\rm{C}}} - {\rm{T}}}}} \right)$ phase, and T to C (TT–C) phase increase with the increase of DC bias. The phase transformation sequence in the [001]-oriented crystals is R → T → C. As DC bias increases, the transition temperature TR–T of R to T phase declines and the transition temperature TT–C rises. Intermediate phases MB, O, and MC are only found in the [011]-oriented crystal. The phase transition characteristics of the [011]-oriented crystals are rather more complex than those along [001] direction. The micro–macro domain transition at Tf is related to crystal orientation and DC bias voltage. The phase diagram in terms of temperature and bias voltage is established for [011]- and [001]-oriented 0.24PIN–0.43PMN–0.33PT crystals. The DC bias dependent dielectric properties and phase transition characteristics are also compared with the crystals along [111] direction.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


