No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Surface-interface micro-structures and mechanical properties of chemical vapor deposited diamond films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 September 2016
Abstract
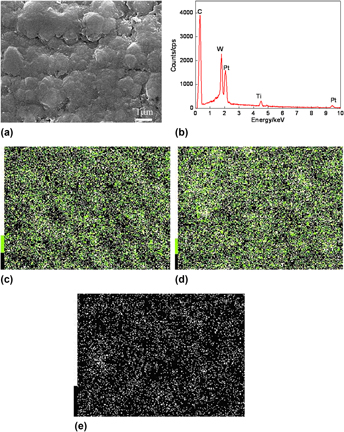
A diamond film was deposited on YT14 cemented carbide cutting tools with a chemical vapor deposition, the surface-interface morphologies, compositions of chemical elements, phases, atomic bonding energies, and structures of the films were analyzed with a scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer, x-ray diffraction, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Raman, respectively, and the mechanical properties of the film were characterized with a nanoindentation and scratch test, respectively. The results show that the surface of diamond film is continuous and dense, the surface roughness of the film is 79.2 nm, and the average grain size is 478.2 nm. The atomic binding energies of C1s are composed of sp 2 at the Raman shift of 1363.01 cm−1 and sp 3 at the Raman shift of 1556.26 cm−1. The hardness and equivalent elastic modulus of the film is 16.27397 GPa and 166.1791 GPa, respectively, and the binding strength of the film-substrate is 26.2 N, showing a high anti-scratch ability.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 31 , Issue 18: Focus Section: Reinventing Boron Chemistry for the 21st Century , 28 September 2016 , pp. 2906 - 2915
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016



