Article contents
Strategies to tailor serrated flows in metallic glasses
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 January 2019
Abstract
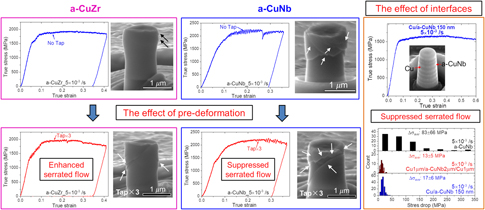
Serrated flow is one important characteristic of shear bands through which metallic glasses (MGs) accommodate plastic deformation. Serrated flow can be affected by intrinsic properties such as elastic modulus or extrinsic variables such as strain rate. However, the influences of pre-deformation and interfaces on serrated flow are less well understood. In this study, by using in situ micropillar compression inside a scanning electron microscope, we show that pre-deformation (consisting of cyclic loading/unloading below the nominal elastic limit) suppresses serrated flows in amorphous-CuNb but enhances serrated flows in amorphous-CuZr at both high and low strain rates. Moreover, layer interfaces in Cu/amorphous-CuNb multilayers mitigate serrated flows, and the average stress drop and strain duration associated with shear banding process can be tailored. Strain accommodation and energy dissipation via shear banding have clear impact on serrated flows. This study provides new perspectives on tailoring serrated flows and enhancing plastic deformation of MGs.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 8
- Cited by


