Article contents
Pine-tree-like morphologies of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes: Electron field emission enhancement
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 September 2014
Abstract
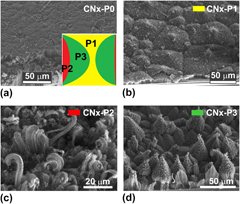
Nitrogen-doped multiwalled carbon nanotube (CNT) bundles exhibiting pine-tree-like morphologies were synthesized on silicon–silicon oxide (Si/SiO2) substrates using a pressure-controlled chemical vapor deposition process. Electron field emission (FE) measurements showed a notable emission improvement at low turn-on voltages for the CNT pine-like morphologies (e.g., 0.59 V/µm) in comparison with standard aligned N-doped CNTs (>1.5 V/µm). We envisage that these pine-tree-like structures could be potentially useful in the fabrication of efficient FE and photonic devices.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2014
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


