Article contents
Phonons correction of the energy and photoionization cross section in polar semiconductors and hollow nanoparticles
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 June 2020
Abstract
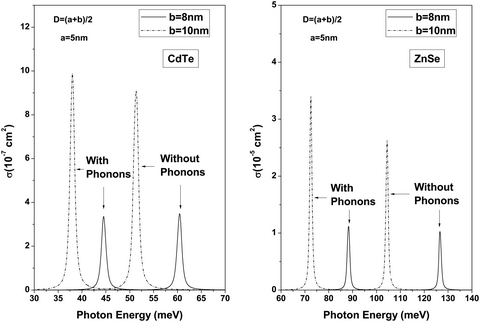
In this paper, we report a recent theoretical study of the calculation of the binding energy and photoionization cross section of a single dopant in a spherical hollow or core/shell quantum dot taking into account the interaction of the electron with longitudinal optical phonons. Using Frolich approach and Lee-low Pines transformation, we determine the impact of different parameters such as shell thickness and dopant position on the energy and optical response of a bound polaron for two types of ionic II–VI semiconductors CdTe and ZnSe with different phonon coupling constants. Regardless of the material used, the electron–phonon interaction visibly reduces binding energy. For photoionization cross section, a redshift of resonance peaks was found when the effect of phonons is taken into consideration or when the donor is moved away from the shell center. These calculations provide us insights when choosing between materials for optoelectronic applications.
Keywords
- Type
- Invited Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2020
References
- 3
- Cited by



