Article contents
Novel pot-shaped carbon nanomaterial synthesized in a submarine-style substrate heating CVD method
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 January 2016
Abstract
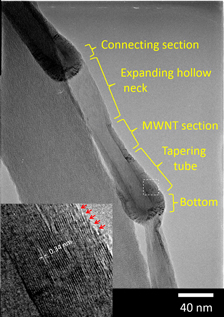
We have developed a new synthesis method that includes a chemical vapor deposition process in a chamber settled in organic liquid, and applied its nonequilibrium reaction field to the development of novel carbon nanomaterials. In the synthesis at 1110–1120 K, using graphene oxide as a catalyst support, iron acetate and cobalt acetate as catalyst precursors, and 2-propanol as a carbon source as well as the organic liquid, we succeeded to create carbon nanofiber composed of novel pot-shaped units, named carbon nanopot. A carbon nanopot has a complex and regular nanostructure consisting of several parts made of different layer numbers of graphene and a deep hollow space. Dense graphene edges, hydroxylated presumably, are localized around its closed end. The typical size of a carbon nanopot was 20–40 nm in outer diameter, 5–30 nm in inner diameter, and 100–200 nm in length. A growth model of carbon nanopot and its applications are proposed.
- Type
- Invited Feature Paper
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 31 , Issue 1: Annual Issue: Early Career Scholars in Materials Science , 14 January 2016 , pp. 117 - 126
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


