Article contents
Microstructure evolution and properties of in situ synthesized TiB2-reinforced aluminum alloy by laser surface alloying
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 November 2018
Abstract
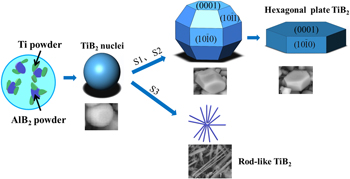
In the present work, the TiB2-reinforced AA6061 composites were successfully in situ synthesized by laser surface alloying using a mixture of Ti and AlB2 powders. The microstructure evolution and properties of the composites were systematically studied. The results showed that TiB2 particles displayed a homogeneous distribution in the aluminum matrix with controllable contents and morphologies. By adjusting the molar ratio of alloying powders, phase constitution of the composites was varied. Thermodynamic calculation was used to analyze the phase selection during the solidification. It was found that the morphology of TiB2 particles was converted from hexagonal plate into rod-like structure with an increase of Ti contents. Transmission electron microscopy results illustrated that the in situ synthesized TiB2 particles exhibited a well-bonded interface with the Al matrix. Properties characterization revealed a significant enhancement in microhardness and abrasion resistance compared with the aluminum substrate attributed to the presence of the TiB2 reinforcements. The strengthening and wear mechanism were also discussed.
Keywords
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


