Article contents
Microstructure characteristics and constitutive modeling for elevated temperature flow behavior of Al–Cu–Li X2A66 alloy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 December 2017
Abstract
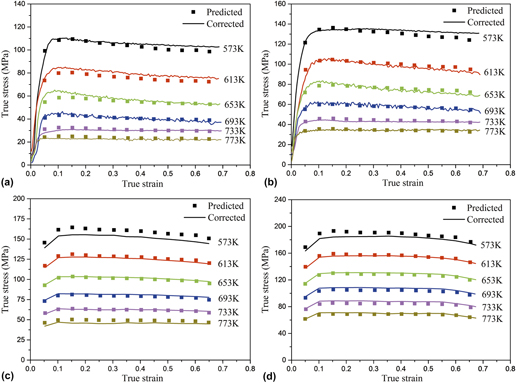
Uniaxial compression tests at the temperatures of 573–773 K and strain rates of 0.01–10 s−1 were conducted to investigate the hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Al–Cu–Li X2A66 alloy. The results indicate that the main dynamic softening mechanisms of the alloy are dynamic recovery and partial dynamic recrystallization. The flow stress increases obviously with the decrease of temperature or the increase of strain rate. The material constants considering the effect of strain were determined by sixth-order polynomial fitting based on the corrected data. The developed Arrhenius-type constitutive equation coupling temperature, strain rate, and strain was established and could well predict the flow stress in the whole range of temperatures and strain rates except at 1 s−1 and 573 K. Moreover, the values of correlation coefficient and average absolute relative error were calculated, which further proved that the proposed constitutive model has high accuracy and reliability.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Jürgen Eckert
References
REFERENCES
- 10
- Cited by


