Article contents
Influence of iron doping on the structural, chemical, and optoelectronic properties of sputtered zinc oxide thin films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 September 2016
Abstract
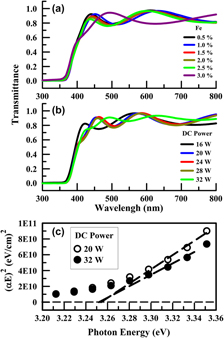
Iron (Fe)-doped zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films were deposited using two techniques: (i) radio-frequency (RF) sputtering of Fe-doped ZnO targets, and (ii) co-sputtering, where ZnO was RF-sputtered and iron was direct-current (DC)-sputtered. The as-deposited films were polycrystalline, with predominant growth along the (002) direction of hexagonal ZnO, and possessed a considerable concentration of oxygen vacancies. From an optoelectronic point of view, the films were highly transparent, with a band gap of 3.25 eV, and had electrical resistivity values in the range of 100–103 Ω cm. To improve the electrical conductivity of the films, they were annealed in a vacuum and in a hydrogen atmosphere. The annealing process did not affect the optical properties of the films. However, there were substantial structural and chemical changes in the films. Moreover, the electrical conductivity of the films was enhanced drastically upon annealing in hydrogen, where the electrical resistivity was reduced to 3.2 × 10−3 Ω cm.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by



