Article contents
High-temperature properties of titanium-substituted yttrium niobate
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 June 2019
Abstract
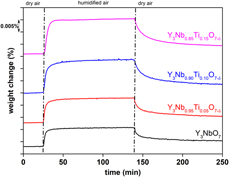
The defect fluorite titanium-doped yttrium niobate samples Y3Nb1−xTixO7−δ have been synthesized and investigated by the means of high-temperature X-ray diffraction, dilatometry, and thermogravimetry. Thermal expansion coefficients (TECs) as well as chemical expansion coefficients for material with 5, 10, and 15 mol% of titanium were determined. All investigated samples exhibit chemical contraction caused by Ti doping. The values of TECs obtained by two different methods show similar results, which suggests the isotropy of the polycrystalline ceramic. Thermogravimetric studies have shown that all of the compositions exhibit a mass increase upon being exposed to a humid air atmosphere. The total proton concentration calculated on the basis of these results was in the range of 0.1 mol%. Moreover, titanium content influences chemical expansion coefficient, water uptake, and protonic defects concentration, whereas it does not significantly affect the values of TECs.
- Type
- Invited Paper
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 34 , Issue 19: Focus Issue: Thermodynamics of Complex Solids , 14 October 2019 , pp. 3312 - 3318
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 2
- Cited by


