Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Chu, X.
Wong, M. S.
Sproul, W. D.
and
Barnett, S. A.
1999.
Deposition, structure, and hardness of polycrystalline transition-metal nitride superlattice films.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 6,
p.
2500.
Misra, A.
Kung, H.
Mitchell, T. E.
and
Nastasi, M.
2000.
Residual stresses in polycrystalline Cu/Cr multilayered thin films.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 3,
p.
756.
Elmustafa, A.A
Eastman, J.A
Rittner, M.N
Weertman, J.R
and
Stone, D.S
2000.
Indentation size effect: large grained aluminum versus nanocrystalline aluminum-zirconium alloys.
Scripta Materialia,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 10,
p.
951.
Hirth, J.P
2000.
Some current topics in dislocation theory.
Acta Materialia,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 1,
p.
93.
Elmustafa, A. A.
Tambwe, M. F.
and
Stone, D. S.
2002.
Activation volume analysis of plastic deformation in fcc materials using nanoindentation.
MRS Proceedings,
Vol. 750,
Issue. ,
Misra, A.
Hirth, J. P.
and
Kung, H.
2002.
Single-dislocation-based strengthening mechanisms in nanoscale metallic multilayers.
Philosophical Magazine A,
Vol. 82,
Issue. 16,
p.
2935.
Elmustafa, A.A.
and
Stone, D.S.
2003.
Size-dependent hardness in annealed and work hardened α-brass and aluminum polycrystalline materials using activation volume analysis.
Materials Letters,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 5-6,
p.
1072.
Yoder, K B
Elmustafa, A A
Lin, J C
Hoffman, R A
and
Stone, D S
2003.
Activation analysis of deformation in evaporated molybdenum thin films.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 7,
p.
884.
Elmustafa, A.A.
and
Stone, D.S.
2003.
Nanoindentation and the indentation size effect: Kinetics of deformation and strain gradient plasticity.
Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 2,
p.
357.
Elmustafa, A.A
and
Stone, D.S
2003.
Stacking fault energy and dynamic recovery: do they impact the indentation size effect?.
Materials Science and Engineering: A,
Vol. 358,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
1.
Li, Qizhen
and
Anderson, Peter M.
2005.
Dislocation-based modeling of the mechanical behavior of epitaxial metallic multilayer thin films.
Acta Materialia,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 4,
p.
1121.
Haseeb, A.S.M.A.
2006.
Modeling of the effects of athermal flow strength and activation energy for dislocation glide on the nanoindentation creep of nickel thin film at room temperature.
Computational Materials Science,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 3,
p.
278.
Bhakhri, Vineet
and
Klassen, Robert J.
2007.
Haasen Plot Activation Analysis of Constant-Force Indentation Creep in FCC Systems.
MRS Proceedings,
Vol. 1049,
Issue. ,
Elmustafa, A.A.
and
Stone, D.S.
2007.
Strain rate sensitivity in nanoindentation creep of hard materials.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 10,
p.
2912.
Elmustafa, A.A.
Kose, S.
and
Stone, D.S.
2007.
The strain-rate sensitivity of the hardness in indentation creep.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 4,
p.
926.
Lewis, A.C.
Eberl, C.
Hemker, K.J.
and
Weihs, T.P.
2008.
Grain boundary strengthening in copper/niobium multilayered foils and fine-grained niobium.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 2,
p.
376.
Demkowicz, Michael J.
Wang, Jian
and
Hoagland, Richard G.
2008.
A Tribute to F.R.N. Nabarro.
Vol. 14,
Issue. ,
p.
141.
Lewis, A.C.
Heerden, D. van
Eberl, C.
Hemker, K.J.
and
Weihs, T.P.
2008.
Creep deformation mechanisms in fine-grained niobium.
Acta Materialia,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 13,
p.
3044.
Bhakhri, Vineet
and
Klassen, Robert J.
2009.
The strain-rate dependence of the nanoindentation stress of gold at 300 K: A deformation kinetics-based approach.
Journal of Materials Research,
Vol. 24,
Issue. 4,
p.
1456.
Dayal, P.
Savvides, N.
and
Hoffman, M.
2009.
Characterisation of nanolayered aluminium/palladium thin films using nanoindentation.
Thin Solid Films,
Vol. 517,
Issue. 13,
p.
3698.
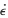 ) in 1 μm-thick Cu/Nb nanolayer composites. For t < 10 nm, we find that H correlates with t according to H = H0 = H1t-1/2, suggestive of a Hall–Petch mechanism with layer interfaces replacing grain boundaries as barriers against dislocation motion. The measured levels of ∂H/∂ ln
) in 1 μm-thick Cu/Nb nanolayer composites. For t < 10 nm, we find that H correlates with t according to H = H0 = H1t-1/2, suggestive of a Hall–Petch mechanism with layer interfaces replacing grain boundaries as barriers against dislocation motion. The measured levels of ∂H/∂ ln 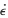 clearly indicate the operation of bulk-like dislocation mechanisms consistent with a Hall–Petch mechanism. However, based on a Haasen-plot activation analysis, it appears that the Hall–Petch coefficient, H1, is strongly rate-dependent, inconsistent with a conventional Hall–Petch mechanism. For specimens with t < 10 nm there is a saturation in hardness, but the rate sensitivity data indicate no clear evidence of a corresponding change in mechanism. Simple models are proposed.
clearly indicate the operation of bulk-like dislocation mechanisms consistent with a Hall–Petch mechanism. However, based on a Haasen-plot activation analysis, it appears that the Hall–Petch coefficient, H1, is strongly rate-dependent, inconsistent with a conventional Hall–Petch mechanism. For specimens with t < 10 nm there is a saturation in hardness, but the rate sensitivity data indicate no clear evidence of a corresponding change in mechanism. Simple models are proposed.

