Article contents
Ferromagnetic signature in vanadium doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 October 2016
Abstract
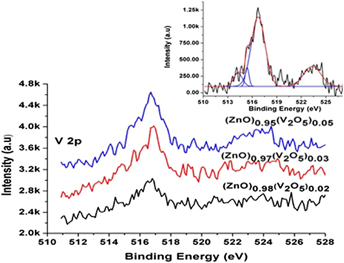
Dilute magnetic semiconductors are attractive due to their potential in spintronic devices. In this work, vanadium doped ZnO system has been studied to see its future as a dilute magnetic semiconductor. Vanadium doped ZnO thin films where vanadium percentage is 2, 3, and 5% are deposited by pulsed laser technique (PLD). The lattice parameter c derived from the (002) diffraction peak increases as vanadium content increases, suggesting vanadium substitution for Zn in ZnO lattice. Photoluminescence (PL) measurements at low temperature shows the emission peak at 3.30 eV which hint toward p-type doping in ZnO. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results show that vanadium exists in V2+ and V4+ valence state, which is in agreement with the XRD and PL results and support the vanadium doped ZnO phase. The ferromagnetic behavior also supports the formation of vanadium doped ZnO phase in thin film samples.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by



