Article contents
Facile preparation of hydrophilic sodium yttrium fluoride nanorods using hydrophobic nanospheres as precursor
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 June 2012
Abstract
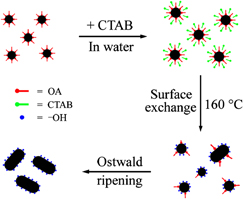
Synthesis of well-defined sodium yttrium fluoride (NaYF4) nanocrystals has been achieved in nonpolar solvents, but these nanocrystals possess a hydrophobic surface and need to be surface-modified for various biological applications. Development of facile aqueous solution method to synthesize one-dimensional NaYF4 with a hydrophilic surface still remains challenging. Herein, we demonstrate a simple route to prepare hydrophilic NaYF4 nanorods by using hydrophobic NaYF4 nanospheres as precursor. It is interesting to find that hydrothermal treatment of oleic acid-capped NaYF4 nanocrystals can not only induce anisotropic growth of these nanocrystals but also change their surface properties. The hydrophilic NaYF4 nanorods synthesized in this work has been well characterized and possible formation mechanism has also been discussed.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


