Article contents
Fabrication of ultralow-density quantum dots by droplet etching epitaxy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 October 2017
Abstract
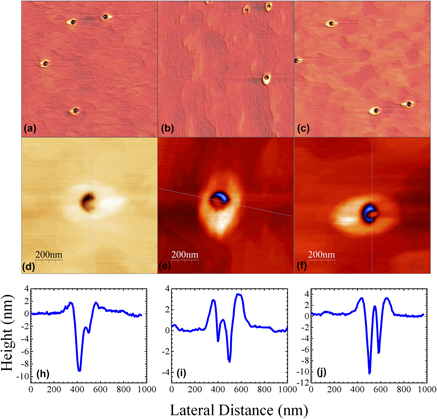
Isolated single quantum dots (QDs) enable the investigation of quantum-optics phenomena for the application of quantum information technologies. In this work, ultralow-density InAs QDs are grown by combining droplet etching epitaxy and the conventional epitaxy growth mode. An extreme low density of QDs (∼106 cm−2) is realized by creating low-density self-assembled nanoholes with the high temperature droplet etching epitaxy technique and then nanohole-filling. The preferred nucleation of QDs in nanoholes has been explained by a theoretical model. Atomic force microscopy and the photoluminescence technique are used to investigate the morphological and optical properties of the QD samples. By varying In coverages, the size of InAs QDs can be controlled. Moreover, with a thin GaAs cap layer, the position of QDs remains visible on the sample surface. Such a low density and surface signature of QDs make this growth method promising for single QD investigation and single dot device fabrication.
- Type
- Invited Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 32 , Issue 21: Focus Issue: Jan van der Merwe: Epitaxy and the Computer Age , 14 November 2017 , pp. 4095 - 4101
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Artur Braun
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by



