Article contents
Fabrication of carbon-nanotube-based sensor array and interference study
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 August 2011
Abstract
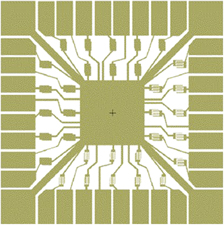
An array of 32 sensor elements with single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as the sensing medium has been fabricated. The microfabrication approach used allows reduction of the chip size and increases the number of sensor elements in a chip and is amenable for large wafer scale-up. The sensor array chip is designed as an electronic nose for use with the aid of a pattern recognition algorithm. The sensor chips were tested for NO2 sensing and interfering effects from humidity and a background of chlorine. The results indicate that NO2 can be detected at low concentration levels of 0.5 ppm in the presence of chlorine at 30 times higher concentrations. The sensor response is affected by humidity, which implies that the training data set for NO2 detection needs to be generated for multiple humidity levels for interpolation purposes during field use.
Keywords
- Type
- Invited Feature Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by


