Article contents
Effect of experimental parameters and (Fe, Ni) doping on the structural, morphological, and optical properties of sol–gel dip-coated SnO2 films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 April 2017
Abstract
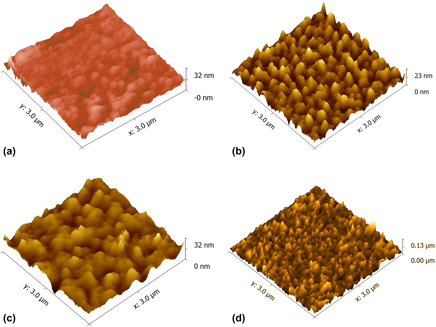
A pure and (Fe–Ni) doped tin oxide thin films were formed on glass substrates by sol–gel dip coating method. Some characterization techniques are used as X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–vis spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM) to study the effect of method conditions and dopants on the structural, morphological, and optical properties of thin films. According to XRD results, no phase attributed to Fe or Ni were detected, which suggests the incorporation of Fe and Ni in SnO2 network. All the diffraction peaks can be assigned as rutile phase of pure SnO2 except (111) is attributed to cubic phase. The optic analyses have shown an average transmittance between 70 and 90%, and showed a direct band gap reducing with increase in Fe doping (3.82–3.72 eV) and Ni content (3.82–3.69 eV). AFM images have revealed that surface roughness is affected strongly by deposition conditions and dopant contents.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Winston V. Schoenfeld
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by



