Article contents
Effect of defects on graphitization of SiC
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 December 2012
Abstract
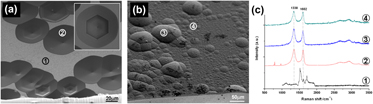
Epitaxial graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) grown on SiC have shown big potential in electronics. The motivation to produce faster and smaller electronic devices using less power opened the way to a study of how to produce controlled epitaxial graphene and CNTs on SiC. Since defects are among the important tools to control the properties of materials, the effects of defects on the carbon formation on SiC have been analyzed. In this study, the effects of defects on the carbon formation on SiC have been analyzed. We produced carbon films on the surface of four different SiC materials (polycrystalline sintered SiC disks, single crystalline SiC wafers, SiC whiskers, and nanowhiskers) by chlorination and vacuum annealing with the goal to understand the effects of surface defects on the carbon structure and the SiC decomposition rate. We have shown that grain boundaries, dislocations, scratches, surface steps, and external surfaces may greatly enhance the reaction rate and affect the final structure of carbon derived from SiC.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 28 , Issue 7: Focus Issue: De Novo Carbon Nanomaterials: Opportunities and Challenges in a Flat World , 14 April 2013 , pp. 952 - 957
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


