Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 April 2013
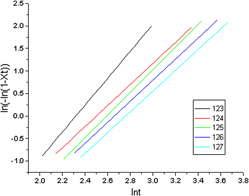
This study presents a polymerization of L-lactide and poly(ethylene glycol) of various molecular weights to produce biodegradable poly(L-lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol) (L-PEG) block copolymers. The chemical structures, crystallization behavior and thermal properties of L-PEG copolymers were investigated using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography, thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The analysis of isothermal crystallization behavior of L-PEG copolymers using the Avrami equation revealed that the grain growth of L-PEG200 and 600 were unstable, jumping between one dimension and two dimensions. By contrast, the grain growth of L-PEG2000 was more stable, with a growth trend toward three dimensions. The results of L-PEG isothermal crystallization by DSC indicate that within a range of 123–127 °C, the crystallization rate was higher at lower temperatures. The values of the crystallization constants in the Avrami equation were also lower.